Unit 10 vocabulary
... dense flowing rock found below the crust and above the core. 3) Inner core: Solid innermost and hottest part of the earth, surrounded by the outer core (made of nickel and iron).. 4) Asthenosphere: Plastic-like layer of the Earth on which the lithospheric plates float and move around. Part of the up ...
... dense flowing rock found below the crust and above the core. 3) Inner core: Solid innermost and hottest part of the earth, surrounded by the outer core (made of nickel and iron).. 4) Asthenosphere: Plastic-like layer of the Earth on which the lithospheric plates float and move around. Part of the up ...
Earth Changes Jeopardy
... When great amounts of soil and rock slide down a slope due to water and gravity or an earthquake, it is called a ...
... When great amounts of soil and rock slide down a slope due to water and gravity or an earthquake, it is called a ...
Earth - GJAR
... between 8 km at the poles to 17 km at the equator, with some variation due to weather and seasonal factors. ...
... between 8 km at the poles to 17 km at the equator, with some variation due to weather and seasonal factors. ...
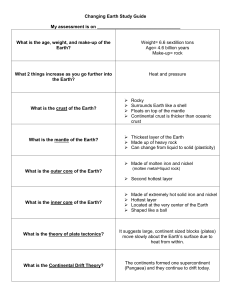
Changing Earth Study Guide My assessment is on What is the age
... What is the inner core of the Earth? ...
... What is the inner core of the Earth? ...
Chapter 1.1 – Earth Science
... In order to have good scientific data it must be accurate and precise! Percentage of error needs to be calculated based on repetitions of the measurements Models can be graphical, conceptual, physical, computer or mathematical to display the data ...
... In order to have good scientific data it must be accurate and precise! Percentage of error needs to be calculated based on repetitions of the measurements Models can be graphical, conceptual, physical, computer or mathematical to display the data ...
iscience earth science unit 1 chapter 2 study guide
... 1. How do Scientists know about the center of the earth? What is the deepest mine/well we have ever dug? Have we even been able to dig our way to the Mantle? Why not? ...
... 1. How do Scientists know about the center of the earth? What is the deepest mine/well we have ever dug? Have we even been able to dig our way to the Mantle? Why not? ...
Chapter 1, Changes to Earth`s Surface
... Mass movement – downhill movement of rock and soil because of gravity Lesson 2 Crust – other layer of Earth, made of rock Mantle – layer of rock beneath Earth’s crust Core – center layer of Earth Plates – rigid blocks of crust and upper mantle rock Magma – molten rock from Earth’s mantle Volcano – m ...
... Mass movement – downhill movement of rock and soil because of gravity Lesson 2 Crust – other layer of Earth, made of rock Mantle – layer of rock beneath Earth’s crust Core – center layer of Earth Plates – rigid blocks of crust and upper mantle rock Magma – molten rock from Earth’s mantle Volcano – m ...
Earth
... He used the length of a building shadow in Alexandria at noon on the summer solstice. He knew that, simultaneously, sunlight was hitting the bottom of a water well in Aswan. ...
... He used the length of a building shadow in Alexandria at noon on the summer solstice. He knew that, simultaneously, sunlight was hitting the bottom of a water well in Aswan. ...
Earth Science Review CST
... Now we know that today under extreme conditions we can create atoms with atomic number higher than 92. So we can also say that if such harsh conditions occur, it is possible that elements heavier than hydrogen could be formed. (this process is called nuclear fusion). conditions required for nuclear ...
... Now we know that today under extreme conditions we can create atoms with atomic number higher than 92. So we can also say that if such harsh conditions occur, it is possible that elements heavier than hydrogen could be formed. (this process is called nuclear fusion). conditions required for nuclear ...
The Moon - Earth Systems A
... The Moon passes behind the Earth and the Sun’s rays are blocked by the Earth’s shadow during full moon ...
... The Moon passes behind the Earth and the Sun’s rays are blocked by the Earth’s shadow during full moon ...
Dr. Cynthia Ebinger Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences University of Rochester
... 1986: S.M., Department of Earth, Atmospheric, & Planetary Sciences, M.I.T. 1982: B.S., Duke University (Durham, NC), Distinction EMPLOYMENT 2006- : Professor, Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of Rochester 2006-10: Adjunct Professor, Royal Holloway, University of London 1999 ...
... 1986: S.M., Department of Earth, Atmospheric, & Planetary Sciences, M.I.T. 1982: B.S., Duke University (Durham, NC), Distinction EMPLOYMENT 2006- : Professor, Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of Rochester 2006-10: Adjunct Professor, Royal Holloway, University of London 1999 ...
Earth*s Layers - Madison County Schools
... The continents of Earth look as if they could fit together like a giant jigsaw puzzle. A German scientist named Alfred Wegener came up with the Continental Drift Theory. This theory says that all the continents used to be together, but drifted apart over millions of years. ...
... The continents of Earth look as if they could fit together like a giant jigsaw puzzle. A German scientist named Alfred Wegener came up with the Continental Drift Theory. This theory says that all the continents used to be together, but drifted apart over millions of years. ...
- Astrogeographia
... By fixing the longitude alignment of Alnitak with the Great Pyramid, as well as the latitude alignment of the Celestial Equator with Jerusalem, it becomes possible to calculate the “star of birth” for every place on Earth. The Celestial Equator (yellow circle) ...
... By fixing the longitude alignment of Alnitak with the Great Pyramid, as well as the latitude alignment of the Celestial Equator with Jerusalem, it becomes possible to calculate the “star of birth” for every place on Earth. The Celestial Equator (yellow circle) ...
Document
... By fixing the longitude alignment of Alnitak with the Great Pyramid, as well as the latitude alignment of the Celestial Equator with Jerusalem, it becomes possible to calculate the “star of birth” for every place on Earth. The Celestial Equator (yellow circle) ...
... By fixing the longitude alignment of Alnitak with the Great Pyramid, as well as the latitude alignment of the Celestial Equator with Jerusalem, it becomes possible to calculate the “star of birth” for every place on Earth. The Celestial Equator (yellow circle) ...
Science study guide for Ch
... 12. At diverging boundaries, two plates move away from each other. 13. The thickest layer of the Earth is called the mantle. 14. At converging boundaries, two plate move toward each other. 15. The only layer of the Earth that is liquid is called outer core. 16. When one plate rides up over another a ...
... 12. At diverging boundaries, two plates move away from each other. 13. The thickest layer of the Earth is called the mantle. 14. At converging boundaries, two plate move toward each other. 15. The only layer of the Earth that is liquid is called outer core. 16. When one plate rides up over another a ...
Earth Science Vocab
... Tectonic plate- one of the large, moving pieces into which Earth’s lithosphere is broken and which commonly carries both oceanic and continental crust ...
... Tectonic plate- one of the large, moving pieces into which Earth’s lithosphere is broken and which commonly carries both oceanic and continental crust ...
Layers of the Earth Exit Slip Key
... 1. Imagine you could drill a hole all the way to the center of the Earth. Assuming that you drill the same speed the entire way, which layer would take the longest to drill through? a. Crust b. Mantle c. Outer core d. Inner core ...
... 1. Imagine you could drill a hole all the way to the center of the Earth. Assuming that you drill the same speed the entire way, which layer would take the longest to drill through? a. Crust b. Mantle c. Outer core d. Inner core ...
Geography Exercise ppt
... The Andes Mountains are part of the “Ring of Fire.” This region of the world has a high level of geographic instability due to the collision of the Earth’s tectonic plates. ...
... The Andes Mountains are part of the “Ring of Fire.” This region of the world has a high level of geographic instability due to the collision of the Earth’s tectonic plates. ...
Drawing the Earth
... Directions: You will be creating a representation of the Earth, its layers (structural and compositional) and spheres. You have three (3) options: 1. Work with a group (3-4) and make a large poster 2. Work individually or with a partner and create a smaller drawing (8.5 x 11) 3. Create a layered “bo ...
... Directions: You will be creating a representation of the Earth, its layers (structural and compositional) and spheres. You have three (3) options: 1. Work with a group (3-4) and make a large poster 2. Work individually or with a partner and create a smaller drawing (8.5 x 11) 3. Create a layered “bo ...
Chapter 1 notes - Freedom Area School District
... Middle latitudes (temperate regions)- between the tropic of cancer and the arctic circle and between the tropic of capricorn and the antarctic circle High latitudes (polar regions)- north of the arctic circle and south of ...
... Middle latitudes (temperate regions)- between the tropic of cancer and the arctic circle and between the tropic of capricorn and the antarctic circle High latitudes (polar regions)- north of the arctic circle and south of ...
History of geodesy
Geodesy (/dʒiːˈɒdɨsi/), also named geodetics, is the scientific discipline that deals with the measurement and representation of the Earth. The history of geodesy began in antiquity and blossomed during the Age of Enlightenment.Early ideas about the figure of the Earth held the Earth to be flat (see flat earth), and the heavens a physical dome spanning over it. Two early arguments for a spherical Earth were that lunar eclipses were seen as circular shadows which could only be caused by a spherical Earth, and that Polaris is seen lower in the sky as one travels South.