(C/1861 G1) which produces the Lyrids meteor showers
... generated by comets intersecting its orbit. While entering into the Earth’s atmosphere, the debris burn up and produce streaks of lights which can be viewed from Earth. During April 16-25, the Earth passes through the debris of Comet Thatcher (C/1861 G1) which produces the Lyrids meteor showers. Abo ...
... generated by comets intersecting its orbit. While entering into the Earth’s atmosphere, the debris burn up and produce streaks of lights which can be viewed from Earth. During April 16-25, the Earth passes through the debris of Comet Thatcher (C/1861 G1) which produces the Lyrids meteor showers. Abo ...
Name 2 movements of the Earth:
... Why does Earth have season’s? • Because the Earth is tilted, its surface gets different amounts of sunlight at different times in the year. ...
... Why does Earth have season’s? • Because the Earth is tilted, its surface gets different amounts of sunlight at different times in the year. ...
Chapter 2 Concept Review
... • What are the Earth’s pole-to-pole circumference and equatorial circumference measurements? – Pole-to-pole circumference = 40,007 km – Equatorial circumference = 40,074 km ...
... • What are the Earth’s pole-to-pole circumference and equatorial circumference measurements? – Pole-to-pole circumference = 40,007 km – Equatorial circumference = 40,074 km ...
Chapter 1 Study Guide
... What is the center of the solar system? Magma comes from what landform? About ____ percent of the earth’s surface is water. Australia- Is it in the N hemisphere or the S hemisphere? What are the layers of the earth from inside out? Define environment Cracks in the earth’s crust are called __________ ...
... What is the center of the solar system? Magma comes from what landform? About ____ percent of the earth’s surface is water. Australia- Is it in the N hemisphere or the S hemisphere? What are the layers of the earth from inside out? Define environment Cracks in the earth’s crust are called __________ ...
Changes Within the Earth
... • Crust Movements • Earth’s surface rock are fragile and can cause breakage in crust. ...
... • Crust Movements • Earth’s surface rock are fragile and can cause breakage in crust. ...
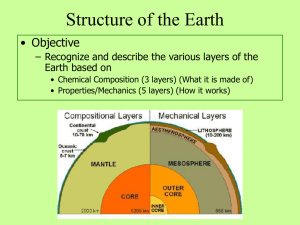
Structure of the Ear..
... How might the Earth’s surface be different if the Asthenosphere was solid? a. The Earth’s mountains would be much taller b. There would be more earthquakes c. The Earth’s mountain ranges would be more numerous d. There would be no mountains or earthquakes ...
... How might the Earth’s surface be different if the Asthenosphere was solid? a. The Earth’s mountains would be much taller b. There would be more earthquakes c. The Earth’s mountain ranges would be more numerous d. There would be no mountains or earthquakes ...
Earth`s Layers Quiz Study Guide
... Draw a diagram and label the layers of the Earth (crust, mantle, outer core, inner core). ...
... Draw a diagram and label the layers of the Earth (crust, mantle, outer core, inner core). ...
Grade Nine Science
... • The Earth rotates (spins) on an axis. • It takes 24 hours to do one rotation around its axis. • This motion causes most stars, sun and moon to appear to rise in the east and set in the west. • The Earth’s axis is an imaginary line that connects the North Pole to the South Pole. ...
... • The Earth rotates (spins) on an axis. • It takes 24 hours to do one rotation around its axis. • This motion causes most stars, sun and moon to appear to rise in the east and set in the west. • The Earth’s axis is an imaginary line that connects the North Pole to the South Pole. ...
8 Grade Science Curriculum Motion and Forces
... 1. Diversity of species occurs through gradual processes over many generations. Fossil records provide evidence that changes have occurred in number and types of species. ...
... 1. Diversity of species occurs through gradual processes over many generations. Fossil records provide evidence that changes have occurred in number and types of species. ...
Study Guide 2-1 1. List the Compositional Layers and identify what
... b. Oblate Spheroid c. Differentiation d. Seismic Waves e. Plasticity ...
... b. Oblate Spheroid c. Differentiation d. Seismic Waves e. Plasticity ...
Name: 7th Grade Science Earth History Test Review Be able to
... -The difference between an object that is more dense than another. -How convection currents work and how they cause plates to move? -The three different plate boundaries and the processes they create that change the Earth’s surface. (Convergent, Divergent, and Transform). -Examples of weathering, er ...
... -The difference between an object that is more dense than another. -How convection currents work and how they cause plates to move? -The three different plate boundaries and the processes they create that change the Earth’s surface. (Convergent, Divergent, and Transform). -Examples of weathering, er ...
Plate Tectonics Crossword
... 10. a mechanism for plate motion in plate tectonics 13. the earth's interior between the crust and the core ...
... 10. a mechanism for plate motion in plate tectonics 13. the earth's interior between the crust and the core ...
History of geodesy
Geodesy (/dʒiːˈɒdɨsi/), also named geodetics, is the scientific discipline that deals with the measurement and representation of the Earth. The history of geodesy began in antiquity and blossomed during the Age of Enlightenment.Early ideas about the figure of the Earth held the Earth to be flat (see flat earth), and the heavens a physical dome spanning over it. Two early arguments for a spherical Earth were that lunar eclipses were seen as circular shadows which could only be caused by a spherical Earth, and that Polaris is seen lower in the sky as one travels South.