Mass on a plane with friction
... 2 attached masses on an inclined plane But how do you determine if acceleration will be up or down the plane? Compare the values of m1gsinθ and m2g to determine which is bigger. If m1gsinθ is bigger it will pull the mass down the plane. If m2g is bigger it will pull the mass up the plane. In genera ...
... 2 attached masses on an inclined plane But how do you determine if acceleration will be up or down the plane? Compare the values of m1gsinθ and m2g to determine which is bigger. If m1gsinθ is bigger it will pull the mass down the plane. If m2g is bigger it will pull the mass up the plane. In genera ...
Chapter 5 Forces
... Newton’s laws review • Newton’s Second Law – If there is a non-zero net force on a body, then it will accelerate. • Newton’s Second Law describes a Nonequilibrium Situation. • A Non-equilibrium Situation is one in which the acceleration of a body is not equal to zero. ...
... Newton’s laws review • Newton’s Second Law – If there is a non-zero net force on a body, then it will accelerate. • Newton’s Second Law describes a Nonequilibrium Situation. • A Non-equilibrium Situation is one in which the acceleration of a body is not equal to zero. ...
Chapter 4 Oscillatory Motion
... to rotate in a plane about some (frictionless!) pivot. Such a system is known as a physical pendulum and is diagrammed in Fig. 4.5 (b). Suppose we look at the line which joins the pivot to the center of mass of the object. If θ is the angle which this line makes with the vertical, and if we again us ...
... to rotate in a plane about some (frictionless!) pivot. Such a system is known as a physical pendulum and is diagrammed in Fig. 4.5 (b). Suppose we look at the line which joins the pivot to the center of mass of the object. If θ is the angle which this line makes with the vertical, and if we again us ...
motion in two dimension
... put one on another and each moved in slightly different directions . The platform on top will experience simultaneous motion in four directions. For a well leveled platform though, the motion will only be in two dimensions. Do not confuse direction with dimension . There is indefinite number of dire ...
... put one on another and each moved in slightly different directions . The platform on top will experience simultaneous motion in four directions. For a well leveled platform though, the motion will only be in two dimensions. Do not confuse direction with dimension . There is indefinite number of dire ...
week 1
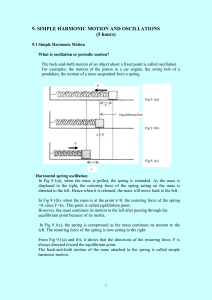
... It is important to understand the difference between the mass and weight of a body! Mass is an absolute property of a body. It is independent of the gravitational field in which it is measured. The mass provides a measure of the resistance of a body to a change in velocity, as defined by Newton’s se ...
... It is important to understand the difference between the mass and weight of a body! Mass is an absolute property of a body. It is independent of the gravitational field in which it is measured. The mass provides a measure of the resistance of a body to a change in velocity, as defined by Newton’s se ...
Torque - rcasao
... As we have seen over and over again, a force is a push or a pull, and an unbalanced force causes an object to move (to accelerate). All the motion we have dealt with so far has moved objects from one point in space to another. This type of motion involving a displacement is called translational moti ...
... As we have seen over and over again, a force is a push or a pull, and an unbalanced force causes an object to move (to accelerate). All the motion we have dealt with so far has moved objects from one point in space to another. This type of motion involving a displacement is called translational moti ...
Tuesday, June 26, 2007 - UTA High Energy Physics page.
... If the direction of linear velocity points to the origin of rotation, the particle does not have any angular momentum. If the linear velocity is perpendicular to position vector, the particle moves exactly the same way as a point on a 8rim. ...
... If the direction of linear velocity points to the origin of rotation, the particle does not have any angular momentum. If the linear velocity is perpendicular to position vector, the particle moves exactly the same way as a point on a 8rim. ...
Experiment: Uniform Circular Motion
... The OzoMaps for this Experiment Pages 3 through 5 contain the OzoMaps that are needed for doing this experiment. The OzoMap of page 3 has Ozobot moving on a large circle, while the OzoMaps of pages 4 and 5 have Ozobot moving on medium and small circles, respectively. The ramps to the left of each o ...
... The OzoMaps for this Experiment Pages 3 through 5 contain the OzoMaps that are needed for doing this experiment. The OzoMap of page 3 has Ozobot moving on a large circle, while the OzoMaps of pages 4 and 5 have Ozobot moving on medium and small circles, respectively. The ramps to the left of each o ...
Why do things move? - USU Department of Physics
... accelerate and change its rotational velocity. Rotational acceleration is the rate of change in rotational velocity. Δω α= t units: rev / sec2 or rad / sec2 Δv • Note: ‘α’ is analogous to linear acceleration (a = t ). Example: Spinning up a wheel will cause its velocity to increase as it accelerate ...
... accelerate and change its rotational velocity. Rotational acceleration is the rate of change in rotational velocity. Δω α= t units: rev / sec2 or rad / sec2 Δv • Note: ‘α’ is analogous to linear acceleration (a = t ). Example: Spinning up a wheel will cause its velocity to increase as it accelerate ...
Topic 4: Dynamics – Force, Newton’s Three Laws, and Friction
... 6. A ball is thrown parallel to the ground by a student. The first Newton law says the ball will continue in a straight line, but it doesn’t. Why not? Newton 2nd Law: 1. If a net force gets larger on an accelerating mass, how will the mass respond? 2. If a truck loaded with bricks is accelerating, ...
... 6. A ball is thrown parallel to the ground by a student. The first Newton law says the ball will continue in a straight line, but it doesn’t. Why not? Newton 2nd Law: 1. If a net force gets larger on an accelerating mass, how will the mass respond? 2. If a truck loaded with bricks is accelerating, ...
Chapter 2
... • A body that is rotating tends to remain rotating. • A body that is not rotating tends to remain not rotating. ...
... • A body that is rotating tends to remain rotating. • A body that is not rotating tends to remain not rotating. ...
Newton`s Second Law
... same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object: ...
... same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object: ...
File - Physics Made Easy
... Moon revolves around the earth in a circular orbit and the earth moon system goes round the sun in elliptical orbit (as shown), Both Earth & moon move along the circular paths about their cm such that they are always on opp. Sides of it. It is the cm of earth moon system that exactly follow the ...
... Moon revolves around the earth in a circular orbit and the earth moon system goes round the sun in elliptical orbit (as shown), Both Earth & moon move along the circular paths about their cm such that they are always on opp. Sides of it. It is the cm of earth moon system that exactly follow the ...