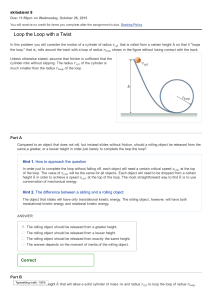
Higher Mechanics Notes
... Power is the rate of transformation of energy from one form to another. P = ...
... Power is the rate of transformation of energy from one form to another. P = ...
File
... Newton’s first law is also known as the law of inertia. •Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in the speed or direction of its motion. •The inertia of an object is related to its mass. •The more massive an object is, the more inertia it has, and the more it will resist having its m ...
... Newton’s first law is also known as the law of inertia. •Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in the speed or direction of its motion. •The inertia of an object is related to its mass. •The more massive an object is, the more inertia it has, and the more it will resist having its m ...
lectures-6-9
... Question 2. A 6 kg object is to be given an acceleration of 0.7 m.s-2 along the +x direction calculate the value of the force acting on it. Question 3. Find the weight of the following masses (a) 10 kg (b) 60 kg Question 4. Calculate the mass of a body which has a weight of 100 N. Question 5. Calcul ...
... Question 2. A 6 kg object is to be given an acceleration of 0.7 m.s-2 along the +x direction calculate the value of the force acting on it. Question 3. Find the weight of the following masses (a) 10 kg (b) 60 kg Question 4. Calculate the mass of a body which has a weight of 100 N. Question 5. Calcul ...
AP Physics 1- Dynamics Practice Problems ANSWERS FACT
... Q27. Four blocks of masses 20kg, 30kg, 40kg, and 50kg are stacked on top of one another in an elevator in order of decreasing mass with the lightest mass on the top of the stack. The elevator moves downward with an acceleration of 3.2 m/s 2. Find the contact force between the 30kg and 40kg masses. ( ...
... Q27. Four blocks of masses 20kg, 30kg, 40kg, and 50kg are stacked on top of one another in an elevator in order of decreasing mass with the lightest mass on the top of the stack. The elevator moves downward with an acceleration of 3.2 m/s 2. Find the contact force between the 30kg and 40kg masses. ( ...
Lecture-08-09
... a) moves to the left, because the force of static friction is larger than the applied force b) moves to the right, because the applied force is larger than the static friction force c) the box does not move, because the static friction force is larger than the applied force d) the box does not move, ...
... a) moves to the left, because the force of static friction is larger than the applied force b) moves to the right, because the applied force is larger than the static friction force c) the box does not move, because the static friction force is larger than the applied force d) the box does not move, ...
Monday, April 14, 2008
... The above condition is sufficient for a point-like object to be at its translational equilibrium. However for an object with size this is not sufficient. One more condition is needed. What is it? Let’s consider two forces equal in magnitude but in opposite direction acting on a rigid object as shown ...
... The above condition is sufficient for a point-like object to be at its translational equilibrium. However for an object with size this is not sufficient. One more condition is needed. What is it? Let’s consider two forces equal in magnitude but in opposite direction acting on a rigid object as shown ...
Ch 8 – Oscillation
... • Period and frequency are closely connected; they contain the same information. T = 1/f f = 1/T ...
... • Period and frequency are closely connected; they contain the same information. T = 1/f f = 1/T ...
2-d motion - U of M Physics
... Choose a function to represent the graph of horizontal position versus time and another for the graph of vertical position versus time. Can you determine any of the constants from your graph? You can waste a lot of time if you just try to guess the constants in your equations. How can you tell when ...
... Choose a function to represent the graph of horizontal position versus time and another for the graph of vertical position versus time. Can you determine any of the constants from your graph? You can waste a lot of time if you just try to guess the constants in your equations. How can you tell when ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... Force on ball is to the LEFT Magnitude of 600 N (~120 lbs) ...
... Force on ball is to the LEFT Magnitude of 600 N (~120 lbs) ...