Newton’s Laws of Motion
... “If I have ever made any valuable discoveries, it has been owing more to patient attention, than to any other talent.” -Sir Isaac Newton ...
... “If I have ever made any valuable discoveries, it has been owing more to patient attention, than to any other talent.” -Sir Isaac Newton ...
Physics Review #1
... A boy pushes his wagon at constant speed along a level sidewalk. The graph represents the relationship between the horizontal force exerted by the boy and the distance the wagon moves. As the boy pushes the wagon, what happens to the wagon’s energy? (A) Gravitational potential energy increases. (B) ...
... A boy pushes his wagon at constant speed along a level sidewalk. The graph represents the relationship between the horizontal force exerted by the boy and the distance the wagon moves. As the boy pushes the wagon, what happens to the wagon’s energy? (A) Gravitational potential energy increases. (B) ...
Slide 1
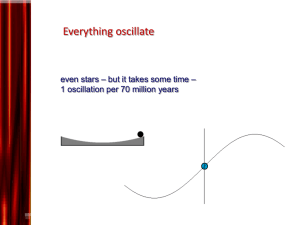
... In our everyday life we observe that objects change their state of motion. In fact everything that happens in the Universe results from a change in motion. That is a static inert object does not contribute to any of the things we consider to be useful. The functioning of our body depends on continua ...
... In our everyday life we observe that objects change their state of motion. In fact everything that happens in the Universe results from a change in motion. That is a static inert object does not contribute to any of the things we consider to be useful. The functioning of our body depends on continua ...
5.3 Friction on level surface
... A person is trying to judge if a picture (mass = 1.10 kg) is properly positioned by temporarily pressing it against a wall. The pressing force is perpendicular to the wall. The coefficient of static friction between the picture and the wall is 0.660. What is the minimum amount of pressing force that ...
... A person is trying to judge if a picture (mass = 1.10 kg) is properly positioned by temporarily pressing it against a wall. The pressing force is perpendicular to the wall. The coefficient of static friction between the picture and the wall is 0.660. What is the minimum amount of pressing force that ...
Wednesday, Mar. 27, 2002
... angular momentum. We’ve used linear momentum to solve physical problems with linear motions, angular momentum will do the same for rotational motions. z Let’s consider a point-like object ( particle) with mass m located at the vector location r and moving with linear velocity v L=rxp The instantaneo ...
... angular momentum. We’ve used linear momentum to solve physical problems with linear motions, angular momentum will do the same for rotational motions. z Let’s consider a point-like object ( particle) with mass m located at the vector location r and moving with linear velocity v L=rxp The instantaneo ...
PowerPoint Presentation - ABOUT TEAL
... velocity is the slope of position vs t, acceleration is the slope of velocity vs t and the curvature of position vs t ...
... velocity is the slope of position vs t, acceleration is the slope of velocity vs t and the curvature of position vs t ...
PH2213 : Examples from Chapter 7 : Work and Kinetic Energy Key
... derive the acceleration of the blocks, from which we could find the speed at which the 12 kg block hits the floor (4.43 m/s). Here, we will use work-energy to find a solution. Let’s label things with ‘A‘ representing the 4 kg block, and ‘B’ will represent quantities associated with the 12 kg block. ...
... derive the acceleration of the blocks, from which we could find the speed at which the 12 kg block hits the floor (4.43 m/s). Here, we will use work-energy to find a solution. Let’s label things with ‘A‘ representing the 4 kg block, and ‘B’ will represent quantities associated with the 12 kg block. ...
Force and Motion Force Classifying Forces
... Newton’s Laws of Motion 1) An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity (that is, in a straight line with constant speed) unless it experiences a net external force 2) The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force act ...
... Newton’s Laws of Motion 1) An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity (that is, in a straight line with constant speed) unless it experiences a net external force 2) The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force act ...
Chapter 3
... straight line , unless it is compelled to change that state by forces acting upon it. An equivalent statement of the first law is that : An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion at constant velocity, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This, at first, do ...
... straight line , unless it is compelled to change that state by forces acting upon it. An equivalent statement of the first law is that : An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion at constant velocity, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This, at first, do ...
Chapter 5 Applying Newton`s Laws
... surface and another one is parallel to the contact surface: ⃗n − normal force always perpendicular to the contact surface ⃗f − friction force is always parallel to the contact surface . Both forces arise due to microscopic (electromagnetic) interaction between molecules, but we shall only study thei ...
... surface and another one is parallel to the contact surface: ⃗n − normal force always perpendicular to the contact surface ⃗f − friction force is always parallel to the contact surface . Both forces arise due to microscopic (electromagnetic) interaction between molecules, but we shall only study thei ...
Chapter 5 PPT
... The forces are applied perpendicularly to each other The resultant (or net) force is the hypotenuse Forces are vectors, so you must use the rules for vector addition to find the net force acting on an object ...
... The forces are applied perpendicularly to each other The resultant (or net) force is the hypotenuse Forces are vectors, so you must use the rules for vector addition to find the net force acting on an object ...
Mass on a plane with friction
... 2 attached masses on an inclined plane But how do you determine if acceleration will be up or down the plane? Compare the values of m1gsinθ and m2g to determine which is bigger. If m1gsinθ is bigger it will pull the mass down the plane. If m2g is bigger it will pull the mass up the plane. In genera ...
... 2 attached masses on an inclined plane But how do you determine if acceleration will be up or down the plane? Compare the values of m1gsinθ and m2g to determine which is bigger. If m1gsinθ is bigger it will pull the mass down the plane. If m2g is bigger it will pull the mass up the plane. In genera ...