Forces - Weebly
... How could the forces on the tennis ball, apple, and bullet, be the same as on the racquet, Earth, and rifle? The 3rd Law says they must be, the effects are different because of the 2nd Law! ...
... How could the forces on the tennis ball, apple, and bullet, be the same as on the racquet, Earth, and rifle? The 3rd Law says they must be, the effects are different because of the 2nd Law! ...
and 2-Dimensions
... acceleration a = gsinθ = 9.8 µsm2 sin 15 = 2.54 sm2 . b. If the block travels 2m then the final speed is given by v f = 2a∆x = 2 × 2.54 sm2 × 2m = 10.15 ms . c. When we included friction, as in class, the acceleration is lower and is given by a = gsinθ − µ k g cosθ = 9.8 µsm2 sin 15 − 0.25 × 9.8 µsm ...
... acceleration a = gsinθ = 9.8 µsm2 sin 15 = 2.54 sm2 . b. If the block travels 2m then the final speed is given by v f = 2a∆x = 2 × 2.54 sm2 × 2m = 10.15 ms . c. When we included friction, as in class, the acceleration is lower and is given by a = gsinθ − µ k g cosθ = 9.8 µsm2 sin 15 − 0.25 × 9.8 µsm ...
for A Tutorial Computer
... refer to rotation about the world space axes, or about the present local frame axes. Here the order of rotations will be fixed as x-rotation, then yrotation, then z-rotation. These are called Euler rotations. Euler rotations can come in various orders; using the order x, then y, then z, the x-rotat ...
... refer to rotation about the world space axes, or about the present local frame axes. Here the order of rotations will be fixed as x-rotation, then yrotation, then z-rotation. These are called Euler rotations. Euler rotations can come in various orders; using the order x, then y, then z, the x-rotat ...
Mechanics Notes II Forces, Inertia and Motion The mathematics of
... As a physicist we are interested in discovering the Laws of Nature in their most simple form. Since particle interactions result in changes in the velocity of a particle, we are motivated to try and express the laws of motion in terms of the change in velocity of a particle: d~v /dt. Therefore, we b ...
... As a physicist we are interested in discovering the Laws of Nature in their most simple form. Since particle interactions result in changes in the velocity of a particle, we are motivated to try and express the laws of motion in terms of the change in velocity of a particle: d~v /dt. Therefore, we b ...
reading – motion and forces review – innovation lab
... Direct and Inverse Relationships Newton’s second law shows that there is a direct relationship between force and acceleration. The greater the force that is applied to an object of a given mass, the more the object will accelerate. For example, doubling the force on the object doubles its accelerati ...
... Direct and Inverse Relationships Newton’s second law shows that there is a direct relationship between force and acceleration. The greater the force that is applied to an object of a given mass, the more the object will accelerate. For example, doubling the force on the object doubles its accelerati ...
1 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 30. Determine the acceleration of the moon about the Earth. (GIVEN: MEarth = 5.98 x 1024 kg and Earthmoon distance = 3.84 x 108 m) (2.70*10-3m/s2) 31. Determine the orbital speed of the International Space Station - orbiting at 350 km above the surface of the Earth. (7698 m/s) 32. Hercules is hoping ...
... 30. Determine the acceleration of the moon about the Earth. (GIVEN: MEarth = 5.98 x 1024 kg and Earthmoon distance = 3.84 x 108 m) (2.70*10-3m/s2) 31. Determine the orbital speed of the International Space Station - orbiting at 350 km above the surface of the Earth. (7698 m/s) 32. Hercules is hoping ...
Chapter11
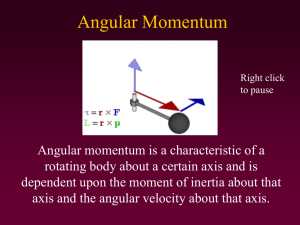
... 11.7.4. Three objects, a solid sphere, a hollow ring, and a solid disk, have the same radius R. A string is wrapped around each object and the same tangential force is applied to each object at R and time t = 0 s. Which one of the following statements concerning the angular momentum of these object ...
... 11.7.4. Three objects, a solid sphere, a hollow ring, and a solid disk, have the same radius R. A string is wrapped around each object and the same tangential force is applied to each object at R and time t = 0 s. Which one of the following statements concerning the angular momentum of these object ...
Physical Science
... starting point, at a velocity slower than the motion from 0 to 3 seconds. From 13 to 15 seconds the object is not moving relative to the starting point. From 15 to 21 seconds the object is accelerating (speeding up) as it moves away from the starting point. You do NOT need to construct or analyze v ...
... starting point, at a velocity slower than the motion from 0 to 3 seconds. From 13 to 15 seconds the object is not moving relative to the starting point. From 15 to 21 seconds the object is accelerating (speeding up) as it moves away from the starting point. You do NOT need to construct or analyze v ...
Chap.4 Conceptual Modules Fishbane
... A very large truck sits on a frozen lake. Assume there is no friction between the tires and the ice. A fly suddenly smashes against the front window. What will happen to the truck? ...
... A very large truck sits on a frozen lake. Assume there is no friction between the tires and the ice. A fly suddenly smashes against the front window. What will happen to the truck? ...