Circular Motion - KRob`s AP Physics 1 & 2
... Consider an object moving in a circle around a specific origin. The DISTANCE the object covers in ONE REVOLUTION is called the CIRCUMFERENCE. The TIME that it takes to cover this distance is called the PERIOD. Another term is FREQUENCY This the number rotations or cycles/sec. The unit is 1/sec or he ...
... Consider an object moving in a circle around a specific origin. The DISTANCE the object covers in ONE REVOLUTION is called the CIRCUMFERENCE. The TIME that it takes to cover this distance is called the PERIOD. Another term is FREQUENCY This the number rotations or cycles/sec. The unit is 1/sec or he ...
Homework Week 6
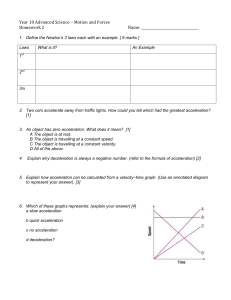
... Directions: Answer the following questions using your notes. 1. _____________ causes an object to move. 2. An example of friction is __________. 3. Newton's third law of motion states that __________. 4. What is the friction between a rolling object and the surface it rolls on called? 5. What is the ...
... Directions: Answer the following questions using your notes. 1. _____________ causes an object to move. 2. An example of friction is __________. 3. Newton's third law of motion states that __________. 4. What is the friction between a rolling object and the surface it rolls on called? 5. What is the ...
Lecture 3
... coordinate system, at constant speed. At time t1=5.0 s, it is at point (5.0 m, 6.0 m) with velocity (3.0 m/s) ĵ and acceleration in the positive x direction. At time t2=10.0 s, it has velocity (-3.0 m/s) and acceleration in the positive y direction. What are î the (a) x and (b) y coordinates of th ...
... coordinate system, at constant speed. At time t1=5.0 s, it is at point (5.0 m, 6.0 m) with velocity (3.0 m/s) ĵ and acceleration in the positive x direction. At time t2=10.0 s, it has velocity (-3.0 m/s) and acceleration in the positive y direction. What are î the (a) x and (b) y coordinates of th ...
Exam 1
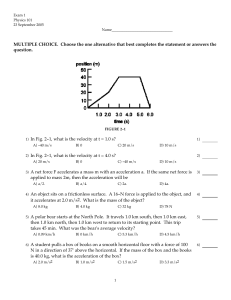
... An object has a mass of 60 kg on the Earth. What is the mass of the object on the surface of the Moon where the acceleration due to gravity is only 1/6 of that on the Earth? A) 60 kg ...
... An object has a mass of 60 kg on the Earth. What is the mass of the object on the surface of the Moon where the acceleration due to gravity is only 1/6 of that on the Earth? A) 60 kg ...
Acceleration
... Because the car has travelled a greater distance each second, it must have a greater velocity each second. By definition it is accelerating because the car is changing velocity. ...
... Because the car has travelled a greater distance each second, it must have a greater velocity each second. By definition it is accelerating because the car is changing velocity. ...
Content Area: Newtonian Mechanics Unit: 5 Topic (s): Circular
... 2. Adapt the concept of a net (or unbalanced) linear force (as defined by Newton’s Second Law of Motion) for use with net circular (centripetal) force 3. Identify the contributing factors for Universal Gravitation 4. Combine concepts of weight and universal gravitation to determine the local gravita ...
... 2. Adapt the concept of a net (or unbalanced) linear force (as defined by Newton’s Second Law of Motion) for use with net circular (centripetal) force 3. Identify the contributing factors for Universal Gravitation 4. Combine concepts of weight and universal gravitation to determine the local gravita ...
1) A car starts to accelerate from rest with a=0
... 3) A mass of 7.0 kg lying on a slope (370 with respect to the ground) is connected via a string over a massless pulley to a second mass m2 (see drawing). Assuming that the slope is frictionless, what is the mass of m2 if the system remains stationary (i.e. the masses do not start to move when releas ...
... 3) A mass of 7.0 kg lying on a slope (370 with respect to the ground) is connected via a string over a massless pulley to a second mass m2 (see drawing). Assuming that the slope is frictionless, what is the mass of m2 if the system remains stationary (i.e. the masses do not start to move when releas ...
laws of motion - WordPress.com
... then the body is thrown forward & backward or the bus continue to move for some time. When a car moves along a circular path, the body moves along with the curve as well. ...
... then the body is thrown forward & backward or the bus continue to move for some time. When a car moves along a circular path, the body moves along with the curve as well. ...
1. The frog leaps from its resting position at the lake`s bank onto a lily
... B An object in motion tends to remain in motion in the absence of an external force. C A moving object having constant velocity contains kinetic energy. D An object’s weight is proportional to its mass. 3. When a car suddenly stops, a book lying on the car seat slides forward. Why does the book cont ...
... B An object in motion tends to remain in motion in the absence of an external force. C A moving object having constant velocity contains kinetic energy. D An object’s weight is proportional to its mass. 3. When a car suddenly stops, a book lying on the car seat slides forward. Why does the book cont ...
questions on Newton`s laws File
... the plane accelerates forward at 2.0 m/s2, what is the magnitude of the resistive force exerted by the air on the airplane? 5. A 5.0-g bullet leaves the muzzle of a rifle with a speed of 320 m/s. What total force (assumed constant) is exerted on the bullet while it is traveling down the 0.82-m-long ...
... the plane accelerates forward at 2.0 m/s2, what is the magnitude of the resistive force exerted by the air on the airplane? 5. A 5.0-g bullet leaves the muzzle of a rifle with a speed of 320 m/s. What total force (assumed constant) is exerted on the bullet while it is traveling down the 0.82-m-long ...
File
... but the displacements are not. As a result, the velocity isn’t constant so the two objects are accelerating. ...
... but the displacements are not. As a result, the velocity isn’t constant so the two objects are accelerating. ...