Ch. 7 Forces and Motion in Two Dimensions
... – Relate the height, time in the air, and the initial velocity of a projectile using its vertical motion, then determine the range. – Explain how the shape of the trajectory of a moving object depends upon the frame of reference from which it is observed. ...
... – Relate the height, time in the air, and the initial velocity of a projectile using its vertical motion, then determine the range. – Explain how the shape of the trajectory of a moving object depends upon the frame of reference from which it is observed. ...
3, 4, 6, 9, 14 / 5, 8, 13, 18, 23, 27, 32, 52
... the object could be accelerating if the direction of the velocity is changing. ...
... the object could be accelerating if the direction of the velocity is changing. ...
المحاضرة الثالثة Circular Motion
... If the acceleration ac is not perpendicular to the path, there would be a component parallel to the path and also the velocity and lead to a change in the speed of the particle and this is inconsist with uniform circular motion. To derive the equation of acceleration of circular path consider th ...
... If the acceleration ac is not perpendicular to the path, there would be a component parallel to the path and also the velocity and lead to a change in the speed of the particle and this is inconsist with uniform circular motion. To derive the equation of acceleration of circular path consider th ...
Introduction to Forces Guided Notes
... In 17th c. ____________________________ also theorized that force is NOT needed to keep an object in the motion (straight-line, constant speed). Instead, he believed forces change motion. Every object resists change to its state of motion/velocity. To change it, the force must act on it. We call thi ...
... In 17th c. ____________________________ also theorized that force is NOT needed to keep an object in the motion (straight-line, constant speed). Instead, he believed forces change motion. Every object resists change to its state of motion/velocity. To change it, the force must act on it. We call thi ...
Document
... A car drives past point x=0 at time t=0 at a constant speed of 50 km/hr. Shortly after it accelerates rapidly to 100 km/hr at t1. It holds this speed until a rabbit runs onto the road at t2 when the car comes to a screeching stop. Which of the curves shown above best represents the car’s i) velocity ...
... A car drives past point x=0 at time t=0 at a constant speed of 50 km/hr. Shortly after it accelerates rapidly to 100 km/hr at t1. It holds this speed until a rabbit runs onto the road at t2 when the car comes to a screeching stop. Which of the curves shown above best represents the car’s i) velocity ...
Unit 6 Powerpoint
... depends on the mass of the object and the tension in the cord The centripetal force is supplied by the tension ...
... depends on the mass of the object and the tension in the cord The centripetal force is supplied by the tension ...
Motion – many examples surround us an ice skater coasting
... a. How high does it climb ? We know vo = 10m/s and v = 0 v = vo –g t or 0 = 10 m/s – (10m/s2) t or t = 1 sec But x = vot – (1/2)gt2 = x = (10m/s)(1s) – (1/2)(-10m/s2)(1s)2 or x = 5 meters How fast does it come back at you? (discussed in class) ...
... a. How high does it climb ? We know vo = 10m/s and v = 0 v = vo –g t or 0 = 10 m/s – (10m/s2) t or t = 1 sec But x = vot – (1/2)gt2 = x = (10m/s)(1s) – (1/2)(-10m/s2)(1s)2 or x = 5 meters How fast does it come back at you? (discussed in class) ...
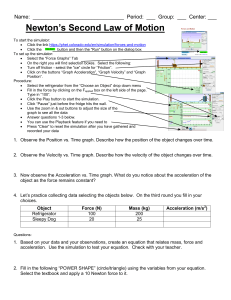
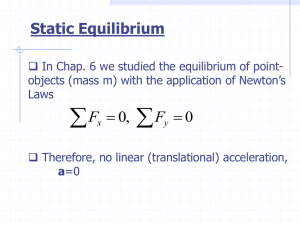
2. Laws of Motion
... What is Newton’s second law? If the resultant force acting on an object is not zero, all the forces are said to be unbalanced. This forms the basis of Newton’s second law of motion, which states: If the forces on an object are unbalanced, two things about the object can change: the speed of the o ...
... What is Newton’s second law? If the resultant force acting on an object is not zero, all the forces are said to be unbalanced. This forms the basis of Newton’s second law of motion, which states: If the forces on an object are unbalanced, two things about the object can change: the speed of the o ...
Newton`s 2nd Law
... Feather falls slowly due to air resistance force. If we remove the air (create a vacuum) then feather and coin fall with same acceleration. ...
... Feather falls slowly due to air resistance force. If we remove the air (create a vacuum) then feather and coin fall with same acceleration. ...