Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
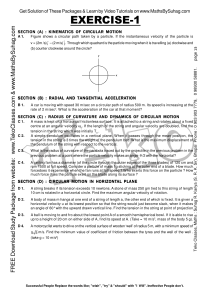
... Non-uniform Circular Motion For an object moving along a curved trajectory, with non-uniform speed a = ar + at (radial and tangential) ...
... Non-uniform Circular Motion For an object moving along a curved trajectory, with non-uniform speed a = ar + at (radial and tangential) ...
Lecture 20.TorqueRot..
... Conceptual Quiz: A mechanic is finding it very difficult to muster enough torque to twist a stubborn bolt with a wrench, and she wishes she had a length of pipe to place over the wrench handle to increase her leverage. Will torque be increased if the mechanic pulls just as hard on a length of rope ...
... Conceptual Quiz: A mechanic is finding it very difficult to muster enough torque to twist a stubborn bolt with a wrench, and she wishes she had a length of pipe to place over the wrench handle to increase her leverage. Will torque be increased if the mechanic pulls just as hard on a length of rope ...
q - MACscience
... it’s Lewis’ turn to push. Cameron and Chris decide to climb into the centre of the roundabout instead of sitting on the seats at the outside. This reduces the inertia of the roundabout + friends to 7000kgm2. ► If Lewis pushes with the same force of 120N for 25s, what will the final angular speed of ...
... it’s Lewis’ turn to push. Cameron and Chris decide to climb into the centre of the roundabout instead of sitting on the seats at the outside. This reduces the inertia of the roundabout + friends to 7000kgm2. ► If Lewis pushes with the same force of 120N for 25s, what will the final angular speed of ...
PhysicalScienceLawsofMotion(Ch.2)
... • For every action force, there is a reaction force that is equal in strength but opposite in direction. • In any collision, momentum is transferred from one object to another. ...
... • For every action force, there is a reaction force that is equal in strength but opposite in direction. • In any collision, momentum is transferred from one object to another. ...
Lesson 1 - Fair Lawn Schools
... object applies a force on another, the second object applies an equal force in the opposite direction on the first object. • The forces of a force pair do not cancel because they act on different objects. • According to the law of conservation of momentum, momentum is conserved during a collision un ...
... object applies a force on another, the second object applies an equal force in the opposite direction on the first object. • The forces of a force pair do not cancel because they act on different objects. • According to the law of conservation of momentum, momentum is conserved during a collision un ...
File
... field forces. Two charged particles would feel the effects of both fields. Imagine two electrons attracting each other due to the gravitational force and repelling each other due to the electrostatic force. • Which force is greater? • Is one slightly greater or much greater than the other, or are th ...
... field forces. Two charged particles would feel the effects of both fields. Imagine two electrons attracting each other due to the gravitational force and repelling each other due to the electrostatic force. • Which force is greater? • Is one slightly greater or much greater than the other, or are th ...
Force and Motion
... , tells you that if you double the force, you will double the object’s acceleration. If you apply the same force to several different objects, the one with the most mass will have the smallest acceleration and the one with the least mass will have the greatest acceleration. If you apply the same for ...
... , tells you that if you double the force, you will double the object’s acceleration. If you apply the same force to several different objects, the one with the most mass will have the smallest acceleration and the one with the least mass will have the greatest acceleration. If you apply the same for ...
Measuring the Motion of a Toy Car
... passes over the starting line, and clock the time that it takes to travel the distance x. Call this time (t). d. Repeat this procedure several times, until you are satisfied about two ideas: (the car should be moving when it passes the two points.) 1) The vehicle is indeed traveling with a velocity ...
... passes over the starting line, and clock the time that it takes to travel the distance x. Call this time (t). d. Repeat this procedure several times, until you are satisfied about two ideas: (the car should be moving when it passes the two points.) 1) The vehicle is indeed traveling with a velocity ...
Lesson 2 - Choteau Schools
... • An object’s momentum is in the same direction as its velocity. – According to Newton’s first law, if the net force on an object is zero, neither its velocity nor its momentum change. – Because momentum is the product of mass and velocity, the force on an object equals its change in momentum. ...
... • An object’s momentum is in the same direction as its velocity. – According to Newton’s first law, if the net force on an object is zero, neither its velocity nor its momentum change. – Because momentum is the product of mass and velocity, the force on an object equals its change in momentum. ...
Physics 231 Topic 3: Forces & Laws of Motion
... “In the beginning of 1665 I found the…rule for reducing any dignity of binomial to a series. The same year in May I found the method of tangents and in November the method of fluxions and in the next year in January had the Theory of Colours and in May following I had the entrance into the inverse m ...
... “In the beginning of 1665 I found the…rule for reducing any dignity of binomial to a series. The same year in May I found the method of tangents and in November the method of fluxions and in the next year in January had the Theory of Colours and in May following I had the entrance into the inverse m ...
2.3 Unbalanced Forces and Acceleration
... • The pairs are equal in magnitude. • The forces do not cancel out because they act on different objects. ...
... • The pairs are equal in magnitude. • The forces do not cancel out because they act on different objects. ...