ISNS4371_011107_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... fall from tree and suddenly understood gravity - published most famous book in science in 1687 - Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica - Principia for short ...
... fall from tree and suddenly understood gravity - published most famous book in science in 1687 - Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica - Principia for short ...
Motion and Forces Powerpoint
... Describing Motion with Graphs • A graph that shows how distance and time are related is a distance-time graph. • The y-axis shows the distance an object travels from a reference point, and time is on the x-axis. • If the angle of the line on a distance-time graph changes, you know that the speed ch ...
... Describing Motion with Graphs • A graph that shows how distance and time are related is a distance-time graph. • The y-axis shows the distance an object travels from a reference point, and time is on the x-axis. • If the angle of the line on a distance-time graph changes, you know that the speed ch ...
K E N D
... Physics is a quantitative science, based on measurement of physical quantities.Certain physical quantities have been chosen as fundamental or base quantities. The fundamental quantities that are chosen are Length, Mass, Time, electric current, thermodynamic temperature, amount of substance, and lu ...
... Physics is a quantitative science, based on measurement of physical quantities.Certain physical quantities have been chosen as fundamental or base quantities. The fundamental quantities that are chosen are Length, Mass, Time, electric current, thermodynamic temperature, amount of substance, and lu ...
Lesson 1 - Physical Quantities and units - science
... To find the velocity from a displacement-time graph we have seen that we take the gradient of the line. But if the acceleration is non-uniform it is, by definition, changing. So we can only work out the acceleration at specific points, or instants. We call this taking the instantaneous acceleration. ...
... To find the velocity from a displacement-time graph we have seen that we take the gradient of the line. But if the acceleration is non-uniform it is, by definition, changing. So we can only work out the acceleration at specific points, or instants. We call this taking the instantaneous acceleration. ...
SPH4UI Lecture 1 Notes
... • With the angles between F and the axes, Fx F cos x Fy F cos y Fz F cos z ...
... • With the angles between F and the axes, Fx F cos x Fy F cos y Fz F cos z ...
Chapter 8 Accelerated Circular Motion
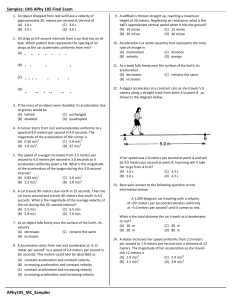
... The model airplane has a mass of 0.90 kg and moves at constant speed on a circle that is parallel to the ground. The path of the airplane and the guideline lie in the same horizontal plane because the weight of the plane is balanced by the lift generated by its wings. Find the tension in the 17 m gu ...
... The model airplane has a mass of 0.90 kg and moves at constant speed on a circle that is parallel to the ground. The path of the airplane and the guideline lie in the same horizontal plane because the weight of the plane is balanced by the lift generated by its wings. Find the tension in the 17 m gu ...
2.1 Forces and Motions
... Consider a body on which no net force acts. If the body is at rest, it will remain at rest. If the body is moving with a constant velocity, it will continue to do so. Inertial frame of reference: A non-accelerating frame of reference in which Newton’s first law is valid. ...
... Consider a body on which no net force acts. If the body is at rest, it will remain at rest. If the body is moving with a constant velocity, it will continue to do so. Inertial frame of reference: A non-accelerating frame of reference in which Newton’s first law is valid. ...
Target Ideas for Cycle I
... 6. Motion Without an Unbalanced Force Idea: No unbalanced force means the forces are balanced. If the object is at rest and there are no unbalanced forces acting on the object, the object will stay at rest. If the object is moving and there are no unbalanced forces acting on the object, the object w ...
... 6. Motion Without an Unbalanced Force Idea: No unbalanced force means the forces are balanced. If the object is at rest and there are no unbalanced forces acting on the object, the object will stay at rest. If the object is moving and there are no unbalanced forces acting on the object, the object w ...
rotation and angular momentum
... around the pole to bring the large block back to its original location. The small blocks are detached from the rod and then suspended from each end of the rod, using strings of length l. The system is again released from rest so that as the large block descends and the apparatus rotates, the small b ...
... around the pole to bring the large block back to its original location. The small blocks are detached from the rod and then suspended from each end of the rod, using strings of length l. The system is again released from rest so that as the large block descends and the apparatus rotates, the small b ...
Inertial Forces and the Laws of Dynamics
... its acceleration is equal to the sum of all forces acting on the point. But this is completely wrong, because only the accelerating forces are presented on the right-hand side of Eq(3). Equation (3) itself expresses an equilibrium between the accelerating forces and the inertial force reflected on i ...
... its acceleration is equal to the sum of all forces acting on the point. But this is completely wrong, because only the accelerating forces are presented on the right-hand side of Eq(3). Equation (3) itself expresses an equilibrium between the accelerating forces and the inertial force reflected on i ...