topic 1 - Dr. Mohd Afendi Bin Rojan, CEng MIMechE
... 2) We can now determine the amount of time required for the motorcycle to stop (v = 0). Use vo = 27 m/s. 0 = -3t2 + 27 => t = 3 s 3) Now calculate the distance traveled in 3s by integrating the velocity using so = 0: s t v = ds / dt => ds = v dt => ds = (-3t 2 + vo)dt ...
... 2) We can now determine the amount of time required for the motorcycle to stop (v = 0). Use vo = 27 m/s. 0 = -3t2 + 27 => t = 3 s 3) Now calculate the distance traveled in 3s by integrating the velocity using so = 0: s t v = ds / dt => ds = v dt => ds = (-3t 2 + vo)dt ...
Ch6 - Force and Motion-II
... What if the string breaks? • If the string breaks, no net force acts on the ball, so it obeys Newton’s first law and moves in a straight line. ...
... What if the string breaks? • If the string breaks, no net force acts on the ball, so it obeys Newton’s first law and moves in a straight line. ...
Taking Notes for Class - Teacher Resource Center
... The three laws of motion were first compiled in his work Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy) commonly known as the Principia, although this was not published until 1687. Newton's Laws of Motion Three physical laws that form the basis for class ...
... The three laws of motion were first compiled in his work Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy) commonly known as the Principia, although this was not published until 1687. Newton's Laws of Motion Three physical laws that form the basis for class ...
ODU-Mechanics-Questions
... (a) What is the reading on the balance when the lift is stationary? (b) The lift now accelerates upwards at 1·50 m s 2 . What is the new reading on the balance? (c) The lift then travels upwards at a constant speed of 5·00 m s 1 . What is the new reading on the balance? (d) For the last stage of t ...
... (a) What is the reading on the balance when the lift is stationary? (b) The lift now accelerates upwards at 1·50 m s 2 . What is the new reading on the balance? (c) The lift then travels upwards at a constant speed of 5·00 m s 1 . What is the new reading on the balance? (d) For the last stage of t ...
VCE Physics
... note what you need to find, then choose the most appropriate equation. In some cases you also need to define a _____________direction, up or down for vertical motion, left or right for horizontal motion questions ...
... note what you need to find, then choose the most appropriate equation. In some cases you also need to define a _____________direction, up or down for vertical motion, left or right for horizontal motion questions ...
Chapter 1 - UniMAP Portal
... 2) We can now determine the amount of time required for the motorcycle to stop (v = 0). Use vo = 27 m/s. 0 = -3t2 + 27 => t = 3 s 3) Now calculate the distance traveled in 3s by integrating the velocity using so = 0: s t v = ds / dt => ds = v dt => ds = (-3t 2 + vo)dt ...
... 2) We can now determine the amount of time required for the motorcycle to stop (v = 0). Use vo = 27 m/s. 0 = -3t2 + 27 => t = 3 s 3) Now calculate the distance traveled in 3s by integrating the velocity using so = 0: s t v = ds / dt => ds = v dt => ds = (-3t 2 + vo)dt ...
additional assignments
... beneath it. (b) Would this value change as the plane moves away from the same point? Explain. 38. A ball of mass 175 g is attached to a string and it is twirled around in a horizontal circle of radius 75.0 cm at a frequency of 2.00 Hz. It revolves clockwise as seen from above. (a) Find the magnitude ...
... beneath it. (b) Would this value change as the plane moves away from the same point? Explain. 38. A ball of mass 175 g is attached to a string and it is twirled around in a horizontal circle of radius 75.0 cm at a frequency of 2.00 Hz. It revolves clockwise as seen from above. (a) Find the magnitude ...
8-23-10 Newtons laws template
... • Newton’s First Law (Law of Inertial) – A body in motion stays in motion at constant velocity and a body at rest stays at rest unless acted upon by a net external force. – It is often said that the Law of Inertia violates “common sense”. Why do you think some people say that? ...
... • Newton’s First Law (Law of Inertial) – A body in motion stays in motion at constant velocity and a body at rest stays at rest unless acted upon by a net external force. – It is often said that the Law of Inertia violates “common sense”. Why do you think some people say that? ...
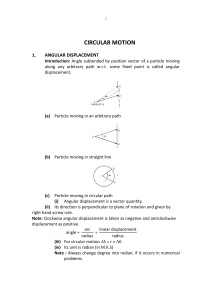
Rotational speed
... center of gravity is A) displaced from its center. B) in the same place as its center of mass. C) stabilized by its structure. D) relatively low for such a tall building. E) above a place of support. ...
... center of gravity is A) displaced from its center. B) in the same place as its center of mass. C) stabilized by its structure. D) relatively low for such a tall building. E) above a place of support. ...
July 2016 Exam Review
... Recall that the centripetal acceleration of the stone is v2/r, and if the speed is constant, then so is the centripetal acceleration. How can it be that the centripetal acceleration, which points towards the centre of the circle, is constant even though the direction of the weight force, which is do ...
... Recall that the centripetal acceleration of the stone is v2/r, and if the speed is constant, then so is the centripetal acceleration. How can it be that the centripetal acceleration, which points towards the centre of the circle, is constant even though the direction of the weight force, which is do ...
Rotational Dynamics and Static Equilibrium
... 11-4 Center of Mass and Balance This fact can be used to find the center of mass of an object – suspend it from different axes and trace a vertical line. The center of mass is where the lines meet. ...
... 11-4 Center of Mass and Balance This fact can be used to find the center of mass of an object – suspend it from different axes and trace a vertical line. The center of mass is where the lines meet. ...
Newton's Second Law of Motion
... a constant speed along a straight line (constant velocity). Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to any change in its state of motion, including changes to its speed and direction. ...
... a constant speed along a straight line (constant velocity). Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to any change in its state of motion, including changes to its speed and direction. ...
Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem for Rotational Motion
... moment of inertia, force with torque, kinetic energy with rotational kinetic energy, and momentum with angular momentum. The relationships between the rotational terms are identical to the relationships between the linear motion terms. Furthermore, we can often convert linear motion expressions to r ...
... moment of inertia, force with torque, kinetic energy with rotational kinetic energy, and momentum with angular momentum. The relationships between the rotational terms are identical to the relationships between the linear motion terms. Furthermore, we can often convert linear motion expressions to r ...