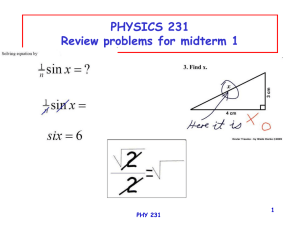
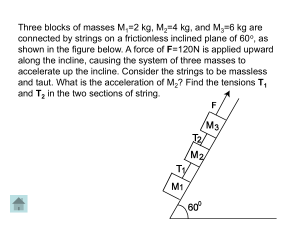
PHYSICS 231 Review problems for midterm 1 1 PHY 231
... force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the speed (not a vector, just a positive number) increases. So answer c is correct. PHY 231 ...
... force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the speed (not a vector, just a positive number) increases. So answer c is correct. PHY 231 ...
Newton`s Laws PPT
... a constant speed along a straight line (constant velocity). Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to any change in its state of motion, including changes to its speed and direction. ...
... a constant speed along a straight line (constant velocity). Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to any change in its state of motion, including changes to its speed and direction. ...
F - AdvancedPlacementPhysicsC
... perpendicular to the surface), but W is not along either coordinate axis. Remember that W=Mg, where g is gravitational acceleration, which always points downward (towards Earth). ...
... perpendicular to the surface), but W is not along either coordinate axis. Remember that W=Mg, where g is gravitational acceleration, which always points downward (towards Earth). ...
MCQs - Moalims.com
... 25. The vector product of and is ___________. (-,, r) 26. A vector which can be displaced parallel to it self and applied at any point is known as __________. (Null vector, Free Vector, Position Vector) 27. A vector, which can represent the position of a point with respect to some fixed point in coo ...
... 25. The vector product of and is ___________. (-,, r) 26. A vector which can be displaced parallel to it self and applied at any point is known as __________. (Null vector, Free Vector, Position Vector) 27. A vector, which can represent the position of a point with respect to some fixed point in coo ...
Forces and Motion
... • When an object is in free fall it will accelerate due to gravity at 10ms-2. • When objects fall from a large height they do not continue to accelerate but eventually reach a constant speed. This speed is called terminal velocity. • This occurs because eventually air resistance will be evenly balan ...
... • When an object is in free fall it will accelerate due to gravity at 10ms-2. • When objects fall from a large height they do not continue to accelerate but eventually reach a constant speed. This speed is called terminal velocity. • This occurs because eventually air resistance will be evenly balan ...
File - Mr. Downing Science 20
... Since uniform motion is rare in the natural world, there is often a necessity to use these new formulas. When you are not given a distance value in a question but you know: → ________________________________ ( ______________________________) and a time → an _______________________ (or the object s ...
... Since uniform motion is rare in the natural world, there is often a necessity to use these new formulas. When you are not given a distance value in a question but you know: → ________________________________ ( ______________________________) and a time → an _______________________ (or the object s ...
Kinematics
... and acceleration vs. time. What the above device shows is that, when looking at a graph of x vs. t, the velocity at some time is found by looking at the slope of the graph at that point. For instance, if I want to know the velocity of an object at t = 5 s, I would determine the slope of the displace ...
... and acceleration vs. time. What the above device shows is that, when looking at a graph of x vs. t, the velocity at some time is found by looking at the slope of the graph at that point. For instance, if I want to know the velocity of an object at t = 5 s, I would determine the slope of the displace ...
04 Newtons Second Law
... a. Choose Set Up Sensors ► Show All Interfaces from the Experiment menu. b. Click the image of the Photogate, select Set Distance or Length, then select Cart Picket Fence from the list of devices. c. Choose Data Collection from the Experiment menu. In the Mode list, click Digital ...
... a. Choose Set Up Sensors ► Show All Interfaces from the Experiment menu. b. Click the image of the Photogate, select Set Distance or Length, then select Cart Picket Fence from the list of devices. c. Choose Data Collection from the Experiment menu. In the Mode list, click Digital ...
Equilibrium Workbook
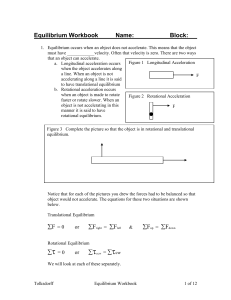
... 4. Rotational equilibrium occurs when the forces on an object are balanced so that the object cannot rotate. For an object to rotate it must rotate about a point – like a wheel rotates around the axel. The point of rotation is the center of the axel. The point of rotation is called a fulcrum. A forc ...
... 4. Rotational equilibrium occurs when the forces on an object are balanced so that the object cannot rotate. For an object to rotate it must rotate about a point – like a wheel rotates around the axel. The point of rotation is the center of the axel. The point of rotation is called a fulcrum. A forc ...
Net Force
... on the sled. The combined mass of the sled and the coach is 300 kg. The sled accelerates at a rate of 0.580 m/s2. – What if another coach hopped on the sled, doubling the mass of the coach-sled system? What would be the new net force (*assuming the acceleration stayed the same)? (HINT – do you need ...
... on the sled. The combined mass of the sled and the coach is 300 kg. The sled accelerates at a rate of 0.580 m/s2. – What if another coach hopped on the sled, doubling the mass of the coach-sled system? What would be the new net force (*assuming the acceleration stayed the same)? (HINT – do you need ...
Newton`s First and Second Law of Motion Video Script
... Since horizontal motion was not thought to be natural, there had to be some cause, a push or a pull. A ball moves horizontally through the air because of the force exerted on it by the thrower’s arm. A ship moves because the wind pushes it, just like the carriage moves because the horse pulls it. F ...
... Since horizontal motion was not thought to be natural, there had to be some cause, a push or a pull. A ball moves horizontally through the air because of the force exerted on it by the thrower’s arm. A ship moves because the wind pushes it, just like the carriage moves because the horse pulls it. F ...
Rotational Dynamics - Piri Reis Üniversitesi
... When using conservation of energy, both rotational and translational kinetic energy must be taken into account. All these objects have the same potential energy at the top, but the time it takes them to get down the incline depends on how much rotational inertia they have. ...
... When using conservation of energy, both rotational and translational kinetic energy must be taken into account. All these objects have the same potential energy at the top, but the time it takes them to get down the incline depends on how much rotational inertia they have. ...