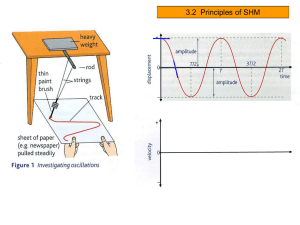
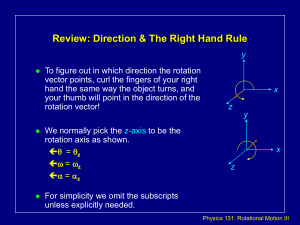
Chapter 4 - Nicholls State University
... The block is moving at constant speed, so it must have no net force on it. The forces ...
... The block is moving at constant speed, so it must have no net force on it. The forces ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... It opposes motion ! Parallel to a surface Perpendicular to a surface Normal force How do we characterize this in terms we have learned? A resulting force in a direction opposite to the direction of motion (actual or implied)! ...
... It opposes motion ! Parallel to a surface Perpendicular to a surface Normal force How do we characterize this in terms we have learned? A resulting force in a direction opposite to the direction of motion (actual or implied)! ...
PHYSICS
... 7. A cannon shoots a projectile at 200 m/sec at an angle of 30 degrees above horizontal. The horizontal range of the cannon is a. 1764 m b. 3530 m c. 7058 m d. 2040 m e. 4080 m 8. A marble moving at 2 m/sec rolls off a tabletop that is 1 m high. It hits the ground how many m from the edge of the tab ...
... 7. A cannon shoots a projectile at 200 m/sec at an angle of 30 degrees above horizontal. The horizontal range of the cannon is a. 1764 m b. 3530 m c. 7058 m d. 2040 m e. 4080 m 8. A marble moving at 2 m/sec rolls off a tabletop that is 1 m high. It hits the ground how many m from the edge of the tab ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion
... An inertial reference frame is one in which Newton’s law of inertia is valid. All accelerating reference frames are non-inertial. Examples of non-inertial reference frames: In an accelerating car, accelerating elevator, accelerating rocket, in a centrifuge (ac inward) and in a car making a turn (dir ...
... An inertial reference frame is one in which Newton’s law of inertia is valid. All accelerating reference frames are non-inertial. Examples of non-inertial reference frames: In an accelerating car, accelerating elevator, accelerating rocket, in a centrifuge (ac inward) and in a car making a turn (dir ...
Lectures in physics Part 1: Mechanics Przemysław Borys 7.11.2013
... is insufficient! This becomes even more evident in the component notation, where on the left hand side the vector is represented by three numbers in an Euclidean space, while on the right hand side we have only one number! . The vector addition in terms of components can be easily understood. It sim ...
... is insufficient! This becomes even more evident in the component notation, where on the left hand side the vector is represented by three numbers in an Euclidean space, while on the right hand side we have only one number! . The vector addition in terms of components can be easily understood. It sim ...
9 - tucek
... rotation of the motor and bit -because of the conservation of the angular momentum, the direction of rotation of a spinning object can be changed only by applying a torque -when a top is vertical, there is no torque on it and the direction of its rotation does not change -if the top is tipped, torqu ...
... rotation of the motor and bit -because of the conservation of the angular momentum, the direction of rotation of a spinning object can be changed only by applying a torque -when a top is vertical, there is no torque on it and the direction of its rotation does not change -if the top is tipped, torqu ...
PH212Chapter11_15
... Rotating about a Fixed Axis • Angular momentum as analogue of linear momentum (What could we conclude?) • Scalar expressions for angular momentum, the relation of torque and angular momentum, and conservation of angular momentum ...
... Rotating about a Fixed Axis • Angular momentum as analogue of linear momentum (What could we conclude?) • Scalar expressions for angular momentum, the relation of torque and angular momentum, and conservation of angular momentum ...
Helpful text on "system" problems w/ Newton`s Laws
... The vertical forces balance each other - consistent with the fact that there is no vertical acceleration. The horizontal forces do not balance each other. The net force can be determined as the vector sum of Fapp and Ffrict. That is, Fnet = 45.0 N, right + 29.4 N, left; these add to 15.6 N, right. T ...
... The vertical forces balance each other - consistent with the fact that there is no vertical acceleration. The horizontal forces do not balance each other. The net force can be determined as the vector sum of Fapp and Ffrict. That is, Fnet = 45.0 N, right + 29.4 N, left; these add to 15.6 N, right. T ...
VU2 Movement 2008
... – kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy close to the Earth’s surface; – potential energy and kinetic energy in springs; ...
... – kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy close to the Earth’s surface; – potential energy and kinetic energy in springs; ...
CHAPTER 9 ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS
... distance. Work and torque are distinctly different physical quantities, as is evident by considering the distances in the definitions. Work is defined by W = ( F cos θ )s , according to Equation 6.1, where F is the magnitude of the force, θ is the angle between the force and the displacement, and s ...
... distance. Work and torque are distinctly different physical quantities, as is evident by considering the distances in the definitions. Work is defined by W = ( F cos θ )s , according to Equation 6.1, where F is the magnitude of the force, θ is the angle between the force and the displacement, and s ...
SPH3U1: DYNAMICS TEST Answer Section
... 15. The property of matter that resists a change in an object's motion is called ____________________. 16. According to Newton's second law, the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the ____________________ and inversely proportional to the ____________________. 17. Imagine you're s ...
... 15. The property of matter that resists a change in an object's motion is called ____________________. 16. According to Newton's second law, the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the ____________________ and inversely proportional to the ____________________. 17. Imagine you're s ...