Torque Rotational Dynamics
... Summary of Chapter 8, cont. • The equations for rotational motion with constant angular acceleration have the same form as those for linear motion with constant acceleration. • Torque is the product of force and lever arm. • The rotational inertia depends not only on the mass of an object but also ...
... Summary of Chapter 8, cont. • The equations for rotational motion with constant angular acceleration have the same form as those for linear motion with constant acceleration. • Torque is the product of force and lever arm. • The rotational inertia depends not only on the mass of an object but also ...
Newton’s Second Law of Motion – Force & Acceleration
... Usually called the law of inertia Every object continues in a state of rest, or of motion in a straight line at constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by an unbalanced force exerted upon it ...
... Usually called the law of inertia Every object continues in a state of rest, or of motion in a straight line at constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by an unbalanced force exerted upon it ...
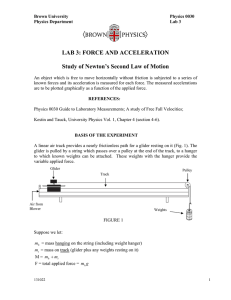
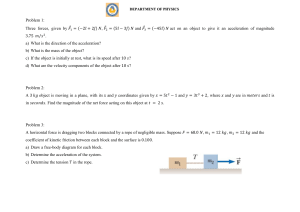
1. Activity #1: Calibrating Force sensors
... objects either did not move or they moved with constant velocity. Velocity is the slope of a displacement-time graph. During the Discovering Motion lab session, the slope of the displacement-time graph was either zero or some other constant number. There was no acceleration: whether you stood still ...
... objects either did not move or they moved with constant velocity. Velocity is the slope of a displacement-time graph. During the Discovering Motion lab session, the slope of the displacement-time graph was either zero or some other constant number. There was no acceleration: whether you stood still ...
RP 3P1 Force and Motion - NC Science Wiki
... an unbalanced force does act on an object, the object's motion changes. Depending on the direction of the force relative to the direction of motion, the object may change its speed (a falling apple) or its direction of motion (the moon in its curved orbit), or both (a fly ball). The greater the amou ...
... an unbalanced force does act on an object, the object's motion changes. Depending on the direction of the force relative to the direction of motion, the object may change its speed (a falling apple) or its direction of motion (the moon in its curved orbit), or both (a fly ball). The greater the amou ...
Universal force-motion equations and solar system implementation
... f. All celestial bodies revolve around the superior one, commonly in the same direction with its (superior’s) rotation, g. All celestial bodies, by some means or other, generally rotate around their own axis. The observations listed above has been ignored, not recognized as a problem and considered ...
... f. All celestial bodies revolve around the superior one, commonly in the same direction with its (superior’s) rotation, g. All celestial bodies, by some means or other, generally rotate around their own axis. The observations listed above has been ignored, not recognized as a problem and considered ...
horizontal velocity - Marble Falls High School
... A projectile is any object upon which the only force is gravity. Projectiles travel with a parabolic trajectory due to the influence of gravity. There are no horizontal forces acting upon projectiles and thus no horizontal acceleration. The horizontal velocity of a projectile is constant. there is a ...
... A projectile is any object upon which the only force is gravity. Projectiles travel with a parabolic trajectory due to the influence of gravity. There are no horizontal forces acting upon projectiles and thus no horizontal acceleration. The horizontal velocity of a projectile is constant. there is a ...
p14jmacProjectile Motion
... A projectile is any object upon which the only force is gravity. Projectiles travel with a parabolic trajectory due to the influence of gravity. There are no horizontal forces acting upon projectiles and thus no horizontal acceleration. The horizontal velocity of a projectile is constant. there is a ...
... A projectile is any object upon which the only force is gravity. Projectiles travel with a parabolic trajectory due to the influence of gravity. There are no horizontal forces acting upon projectiles and thus no horizontal acceleration. The horizontal velocity of a projectile is constant. there is a ...