* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Samples
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Time dilation wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Speeds and feeds wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Variable speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Minkowski diagram wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
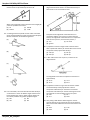
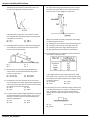
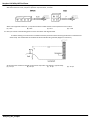
Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam 1. An object dropped from rest will have a velocity of approximately 30. meters per second at the end of (A) 1.0 s (C) 3.0 s (B) 2.0 s (D) 4.0 s 2. Oil drips at 0.4-second intervals from a car that has an oil leak. Which pattern best represents the spacing of oil drops as the car accelerates uniformly from rest? (A) (B) (C) (D) 9. A softball is thrown straight up, reaching a maximum height of 20 meters. Neglecting air resistance, what is the ball's approximate vertical speed when it hits the ground? (A) 10 m/sec (C) 15 m/sec (B) 20 m/sec (D) 40 m/sec 10. Acceleration is a vector quantity that represents the timerate of change in (A) momentum (C) distance (B) velocity (D) energy 11. As a body falls freely near the surface of the Earth, its acceleration (A) decreases (C) remains the same (B) increases 12. A jogger accelerates at a constant rate as she travels 5.0 meters along a straight track from point A to point B ,as shown in the diagram below. 3. If the mass of an object were doubled, its acceleration due to gravity would be (A) halved (C) unchanged (B) doubled (D) quadrupled 4. A runner starts from rest and accelerates uniformly to a speed of 8.0 meters per second in 4.0 seconds. The magnitude of the acceleration of the runner is (C) 9.8 m/s2 (A) 0.50 m/s2 2 (B) 2.0 m/s (D) 32 m/s2 5. The speed of a wagon increases from 2.5 meters per second to 9.0 meters per second in 3.0 seconds as it accelerates uniformly down a hill. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the wagon during this 3.0-second interval? (A) 0.83 m/s2 (C) 3.0 m/s2 2 (B) 2.2 m/s (D) 3.8 m/s2 6. A car travels 90. meters due north in 15 seconds. Then the car turns around and travels 40. meters due south in 5.0 seconds. What is the magnitude of the average velocity of the car during this 20.-second interval? (A) 2.5 m/s (C) 6.5 m/s (B) 5.0 m/s (D) 7.0 m/s 7. As an object falls freely near the surface of the Earth, its velocity (A) decreases (C) remains the same (B) increases 8. A locomotive starts from rest and accelerates at 0.12 meter per second2 to a speed of 2.4 meters per second in 20. seconds. This motion could best be described as (A) constant acceleration and constant velocity (B) increasing acceleration and constant velocity (C) constant acceleration and increasing velocity (D) increasing acceleration and increasing velocity APhy105_MC_Samples If her speed was 2.0 meters per second at point A and will be 3.0 meters per second at point B, how long will it take her to go from A to B? (A) 1.0 s (C) 3.3 s (B) 2.0 s (D) 4.2 s 13. Base your answer to the following question on the information below. A 1,000-kilogram car traveling with a velocity of +20. meters per second decelerates uniformly at –5.0 meters per second2 until it comes to rest. What is the total distance the car travels as it decelerates to rest? (A) 10. m (C) 40. m (B) 20. m (D) 80. m 14. A skater increases her speed uniformly from 2.0 meters per second to 7.0 meters per second over a distance of 12 meters. The magnitude of her acceleration as she travels this 12 meters is (A) 1.9 m/s2 (C) 2.4 m/s2 2 (B) 2.2 m/s (D) 3.8 m/s2 Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam 15. An observer recorded the data above for the motion of a car undergoing constant acceleration. What was the magnitude of the acceleration of the car? (C) 1.5 m/s2 (A) 1.3 m/s2 2 (B) 2.0 m/s (D) 4.5 m/s2 16. A clam dropped by a sea gull takes 3.0 seconds to hit the ground. What is the sea gull's approximate height above the ground at the time the clam was dropped? (A) 15 m (C) 45 m (B) 30. m (D) 90. m 17. A car having an initial speed of 16 meters per second is uniformly brought to rest in 4.0 seconds. How far does the car travel during this 4.0-second interval? (A) 32 m (C) 96 m (B) 82 m (D) 4.0 m 18. Base your answer to the following question on the information below. A stream is 30. meters wide and its current flows southward at 1.5 meters per second. A toy boat is launched with a velocity of 2.0 meters per second eastward from the west bank of the stream. How much time is required for the boat to reach the opposite bank of the stream? (A) 8.6 s (C) 15 s (B) 12 s (D) 60. s 22. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which represents a 10-kilogram object at rest at point A. The object accelerates uniformly from point A to point B in 4 seconds, attaining a maximum speed of 10 meters per second at point B. The object then moves up the incline. [Neglect friction.] What distance did the object travel in moving from point A to point B? (A) 2.5 m (C) 20. m (B) 10. m (D) 100 m 23. A rocket initially at rest on the ground lifts off vertically with a constant acceleration of 2.0 × 101 meters per second 2 . How long will it take the rocket to reach an altitude of 9.0 × 103 meters? (A) 3.0 × 101 s (C) 4.5 × 102 s 1 (D) 9.0 × 102 s (B) 4.3 × 10 s 24. Base your answer to the following question on the information below: A 10.-kilogram object, starting from rest, slides down a frictionless incline with a constant acceleration of 2.0 m/sec2 for four seconds. Which graph below best represents the relationship between acceleration (a) and time (t) for the object? (A) (C) (B) (D) 19. A ball is thrown horizontally at a speed of 24 meters per second from the top of a cliff. If the ball hits the ground 4.0 seconds later, approximately how high is the cliff? (A) 6.0 m (C) 78 m (B) 39 m (D) 96 m 20. A car travels 20. meters east in 1.0 second. The displacement of the car at the end of this 1.0-second interval is (A) 20. m (C) 20. m east (B) 20. m/s (D) 20. m/s east 21. The average speed of a plane was 600 kilometers per hour. How long did it take the plane to travel 120 kilometers? (A) 0.2 hour (C) 0.7 hour (B) 0.5 hour (D) 5 hours APhy105_MC_Samples 25. An object accelerates uniformly from rest to a speed of 50. meters per second in 5.0 seconds. The average speed of the object during the 5.0-second interval is (A) 5.0 m/s (C) 25 m/s (B) 10. m/s (D) 50. m/s Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam 26. An object, initially at rest, falls freely near the Earth's surface. How long does it take the object to attain a speed of 98 meters per second? (A) 0.1 sec (C) 98 sec (B) 10 sec (D) 960 sec 33. The displacement-time graph below represents the motion of a cart along a straight line. 27. One car travels 40. meters due east in 5.0 seconds, and a second car travels 64 meters due west in 8.0 seconds. During their periods of travel, the cars definitely had the same (A) average velocity (C) change in momentum (B) total displacement (D) average speed 28. What is the average velocity of a car that travels 30. kilometers due west in 0.50 hour? (A) 15 km/hr (C) 15 km/hr west (B) 60. km/hr (D) 60. km/hr west Base your answers to questions 29 and 30 on the graph below which represents the relationship between speed and time for an object in motion along a straight line. 29. During which interval is the object's acceleration the greatest? (A) AB (C) DE (B) CD (D) EF 30. During the interval t = 8 seconds to t = 10 seconds, the speed of the object is (A) zero (C) decreasing (B) increasing (D) constant, but not zero 31. A 1-kilogram object rests on a horizontal table top. The force that the table top exerts on the object is (A) 1 N (C) 0 N (B) 2 N (D) 9.8 N 32. What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between two 5.0-kilogram masses separated by a distance of 5.0 meters? (C) 6.7 × 10 –11 N (A) 5.0 × 100 N –10 N (D) 1.3 × 10 –11 N (B) 3.3 × 10 APhy105_MC_Samples During which interval was the cart accelerating? (A) AB (C) CD (B) BC (D) DE 34. Base your answer to the following question on the graph below, which represents the relationship between the displacement of an object and its time of travel along a straight line. What is the average speed of the object during the first 4.0 seconds? (A) 0 m/s (C) 8 m/s (B) 2 m/s (D) 4 m/s 35. Which graph best represents the motion of an object that was initially at rest and is accelerating uniformly? (A) (C) (B) (D) Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam 36. Which graph best represents the relationship between the acceleration of an object falling freely near the surface of Earth and the time that it falls? (A) (B) 37. Base your answer to the following question on the accompanying graph which represents the motions of four cars on a straight road. (C) (D) Base your answers to questions 40 through 42 on the graph below, which represents the motion of cars A and B on a straight track. Car B passes car A at the same instant that car A starts from rest at t = 0 seconds. The speed of car C at t = 20 seconds is closest to (A) 60 m/sec (C) 3.0 m/sec (B) 45 m/sec (D) 600 m/sec 38. The uniform motion of a cart is shown in the distance versus time graph below. What is the average speed of the cart? 40. What is the acceleration of car A during the interval between t = 0 and t = 60? (A) 1 m./sec./sec. (C) 20 m./sec./sec. (B) 10 m./sec./sec. (D) 30 m./sec./sec. 41. During the time intervals given below, which car traveled the greatest distance? (A) car A from t = 0 to t = 30 (B) car A from t = 30 to t = 60 (C) car B from t = 0 to t = 30 (D) car B from t = 30 to t = 60 (A) 0.5 m/s (B) 2 m/s (C) 5 m/s (D) 50 m/s 39. If the sum of all the forces acting on a car is zero, then the speed of the car always (A) decreases (C) remains the same (B) increases APhy105_MC_Samples 42. How far did car A travel in the interval between t = 0 and t = 60? (A) 30 m. (C) 1,800 m. (B) 360 m. (D) 3,600 m. 43. What is the magnitude of the net force acting on a 2.0 × 103- kilogram car as it accelerates from rest to a speed of 15 meters per second in 5.0 seconds? (C) 3.0 × 104 N (A) 6.0 × 103 N 4 (B) 2.0 × 10 N (D) 6.0 × 104 N Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam 44. Which graph best represents the relationship between Base your answers to questions 46 and 47 on the graph below velocity and time for an object which accelerates uniformly which represents the displacement of an object as a function of for 2 seconds, then moves at a constant velocity for 1 time. second, and finally decelerates for 3 seconds? (A) (B) 46. How far is the object from the starting point at the end of 3 seconds? (A) 0 m (C) 3.0 m (B) 2.0 m (D) 9.0 m (C) (D) 47. During which time interval is the object accelerating? (A) 0-2 s (C) 3-4 s (B) 2-3 s (D) 4-6 s 48. The graph below represents the motion of an object traveling in a straight line as a function of time. What is the average speed of the object during the first four seconds? 45. Base your answer to the following question on Cars A and B both start from rest at the same location at the same time. (A) 1 m/s (B) 2 m/s (C) 0.5 m/s (D) 0 m/s 49. At a given location on the earth's surface, which graph best represents the relationship between an object's mass (M) and weight (W) ? Compared to the speed of car B at 6 seconds, the speed of car A at 6 seconds is (A) less (C) the same (B) greater APhy105_MC_Samples (A) (C) (B) (D) Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam 50. A force of F Newtons gives an object with a mass of M an acceleration of A. The same force F will give a second object with a mass of 2M an acceleration of (A) A/2 (C) A (B) 2A (D) A/4 51. A container of rocks with a mass of 65.0 kilograms is brought back from the Moon’s surface where the acceleration due to gravity is 1.62 meters per second 2 . What is the weight of the container of rocks on Earth’s surface? (A) 638 N (C) 105 N (B) 394 N (D) 65.0 N 59. A box decelerates as it moves to the right along a horizontal surface, as shown in the diagram at the right. Which vector best represents the force of friction on the box? (C) (A) 52. A 50-kilogram student, standing on the Earth, attracts the Earth with a force closest to (A) 0 N (C) 50 N (B) 5 N (D) 500 N 53. On the surface of planet X, the acceleration due to gravity is 16 meters per seconds. What is the weight of a 6.0kilogram mass located on the surface of planet X? (A) 2.7 N (C) 96 N (B) 59 N (D) 940 N (D) (B) 60. The diagram below shows a granite block being slid at constant speed across a horizontal concrete floor by a force parallel to the floor. 54. If the mass of a moving object could be doubled, the inertia of the object would be (A) halved (C) unchanged (B) doubled (D) quadrupled 55. When an unbalanced force of 10. Newtons is applied to an object whose mass is 4.0 kilograms, the acceleration of the object will be (C) 9.8 m/s2 (A) 40. m/s2 2 (B) 2.5 m/s (D) 0.40 m/s2 56. An object with a mass of 0.5 kilogram starts from rest and achieves a maximum speed of 20 meters per second in 0.01 second. What average unbalanced force accelerates this object? (A) 1,000 N (C) 0.1 N (B) 10 N (D) 0.001 N Which pair of quantities could be used to determine the coefficient of friction for the granite on the concrete? (A) mass and speed of the block (B) mass and normal force on the block (C) frictional force and speed of the block (D) frictional force and normal force on the block 61. The diagram below represents a car resting on a hill. 57. When a force of 50 Newtons acts on a mass of 10 kilograms, the resulting acceleration will be (C) 40 m/s2 (A) 500 m/s2 2 (B) 60 m/s (D) 5 m/s2 58. According to your reference table, Approximate Coefficents of Friction, what is the minimum horizontal force needed to start a 300. kilogram steel block on a steel table in motion? (A) 5.70 N (C) 1710 N (B) 7.40 N (D) 2220 N APhy105_MC_Samples Which vector best represents the weight of the car? (A) A (C) C (B) B (D) D Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam 62. In the diagram below, the weight of a box on a plane inclined at 30.º is represented by the vector W. 65. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which shows a cart held motionless by an external force F on a frictionless incline. What is the magnitude of the component of the weight (W ) that acts parallel to the incline? (A) W (C) 0.87 W (B) 0.50 W (D) 1.5 W 63. A 1.0-kilogram block is placed on each of four frictionless planes inclined at different angles. On which inclined plane will the acceleration of the block be greatest? (A) (B) Compared to the magnitude of the external force F required to hold the cart at point C on the frictionless surface, the magnitude of the external force F required to hold the cart at point C, if friction were present, is (A) less (C) the same (B) greater 66. A projectile is fired at an angle of 53º to the horizontal with a speed of 80. meters per second. What is the vertical component of the project initial velocity? (A) 130 m/s (C) 64 m/s (B) 100 m/s (D) 48 m/s 67. A 100.-newton force acts on point P, as shown in the diagram below. (C) (D) 64. Four cannonballs, each with mass M and initial velocity V, are fired from a cannon at different angles relative to the Earth. Neglecting air friction, which angular direction of the cannon produces the greatest projectile height? (A) 90º (C) 45º (B) 70º (D) 20º APhy105_MC_Samples The magnitude of the vertical component of this force is approximately (A) 30. N (C) 71 N (B) 50. N (D) 87 N 68. A projectile is fired from a gun near the surface of Earth. The initial velocity of the projectile has a vertical component of 98 meters per second and a horizontal component of 49 meters per second. How long will it take the projectile to reach the highest point in its path? (A) 5.0 s (C) 20. s (B) 10. s (D) 100. s 69. Jill is pulling a 200. Newton sled through the snow at constant velocity using a horizontal force of 10. Newtons. What is the kinetic coefficient of friction of the sled on the snow? (A) 0.02 (C) 0.20 (B) 0.05 (D) 20 Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam 70. The diagram below shows a golf ball being struck by a club. The ball leaves the club with a speed of 40. meters per second at an angle of 60.° with the horizontal. If the ball strikes the ground 7.1 seconds later, how far from the golfer does the ball land? [Assume level ground and neglect air resistance.] (A) 35 m (C) 140 m (B) 71 m (D) 280 m 71. The diagram below represents a box shown sliding down an inclined plane. Toward which point will the force of friction on the box be directed? 75. The diagram below shows the muzzle of a cannon located 50. meters above the ground. When the cannon is fired, a ball leaves the muzzle with an initial horizontal speed of 250. meters per second. [Neglect air resistance.] Which action would most likely increase the time of flight of a ball fired by the cannon? (A) pointing the muzzle of the cannon toward the ground (B) moving the cannon closer to the edge of the cliff (C) positioning the cannon higher above the ground (D) giving the ball a greater initial horizontal velocity 76. The table below lists the coefficients of kinetic friction for four materials sliding over steel. (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 72. According to your table, Approximate Coefficents of Friction, which road surface would offer the greatest traction for rubber tires? (A) dry concrete (C) dry asphalt (B) wet concrete (D) wet asphalt 73. Jim wishes to push a 100. N wood crate across a wood floor. According to your table, Approximate Coefficents of Friction, what is the minimum horizontal force that would be required to start the crate moving? (A) 30. N (C) 72 N (B) 42 N (D) 100 N 74. In order to keep an object weighing 20 Newtons moving at constant speed along a horizontal surface, a force of 10 Newtons is required. The force of friction between the surface and the object is (A) 0 N (C) 20 N (B) 10 N (D) 30 N A 10.-kilogram block of each of these materials is pulled horizontally across a steel floor at constant velocity. Which block requires the smallest applied force to keep it moving at constant velocity? (A) aluminum (C) copper (B) brass (D) steel 77. A box initially at rest on a level floor is being acted upon by a variable horizontal force, as shown in the diagram at the right. Compared to the force required to start the box moving, the force required to keep it moving at constant speed is (A) less (B) greater APhy105_MC_Samples (C) the same Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam 78. The diagram below shows a student applying a 10.-newton force to slide a piece of wood at constant speed across a horizontal surface. After the wood is cut in half, one piece is placed on top of the other, as shown. What is the magnitude of the force, F, required to slide the stacked wood at constant speed across the surface? (A) 40 N (B) 20 N (C) 10 N (D) 5.0 N 79. Base your answer to the following question on the information and diagram below. A student standing on a knoll throws a snowball horizontally 4.5 meters above the level ground toward a smokestack 15 meters away. The snowball hits the smokestack 0.65 second after being released. [Neglect air resistance.] At the instant the snowball is released, the horizontal component of its velocity is approximately (A) 6.9 m/s (B) 9.8 m/s (C) 17 m/s APhy105_MC_Samples (D) 23 m/s Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam Base your answers to questions 80 through 82 on on the diagram and information below. A machine launches a tennis ball at an angle of 45° with the horizontal, as shown. The ball has an initial vertical velocity of 9.0 meters per second and an initial horizontal velocity of 9.0 meters per second. The ball reaches its maximum height 0.92 second after its launch. [Neglect air resistance and assume the ball lands at the same height above the ground from which it was launched.] 80. The total horizontal distance traveled by the tennis ball during the entire time it is in the air is approximately (A) 23 m (B) 17 m (C) 8.3 m (D) 4.1 m 81. The speed at which the launcher fires tennis balls is constant, but the angle between the launcher and the horizontal can be varied. As the angle is decreased from 45° to 30.°, the range of the tennis balls (A) decreases (B) increases (C) remains the same 82. The speed of the tennis ball as it leaves the launcher is approximately (A) 4.5 m/s (B) 8.3 m/s (C) 13 m/s 83. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which represents a 3.0-kilogram mass being moved at a constant speed by a force of 6.0 Newtons. The magnitude of the force of friction acting on the mass is (A) 0 N (C) 3 N (B) 1.8 N (D) 6 N 84. An artillery shell is fired at an angle to the horizontal. Its initial velocity has a vertical component of 150 meters per second and a horizontal component of 260 meters per second. What is the magnitude of the initial velocity of the shell? (C) 3.0 × 102 m/s (A) 9.0 × l04 m/s 2 (D) 1.1 × 102 m/s (B) 4.1 × 10 m/s APhy105_MC_Samples (D) 18 m/s Base your answers to questions 85 and 86 on the information below. A ball is projected vertically upward from the surface of the Earth with an initial speed of +49 meters per second. The ball reaches its maximum height in 5.0 seconds. (Disregard air resistance.) 85. What is the total displacement of the ball from the time it is thrown until it returns to the point from which it was thrown? (A) 248 m (C) 49 m (B) 9.8 m (D) 0 m 86. What is the maximum height reached by the ball? (A) 24.5 m (C) 122.5 m (B) 49.0 m (D) 245 m 87. A golf ball is hit with an initial velocity of 15 meters per second at an angle of 35 degrees above the horizontal. What is the vertical component of the golf ball’s initial velocity? (A) 8.6 m/s (C) 12 m/s (B) 9.8 m/s (D) 15 m/s Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam Base your answers to questions 88 and 89 on the information and diagram below. A child kicks a ball with an initial velocity of 8.5 meters per second at an angle of 35º with the horizontal, as shown. The ball has an initial vertical velocity of 4.9 meters per second and a total time of flight of 1.0 second. [Neglect air resistance.] 91. A 0.2-kilogram red ball is thrown horizontally at a speed of 4 meters per second from a height of 3 meters. A 0.4kilogram green ball is thrown horizontally from the same height at a speed of 8 meters per second. Compared to the time it takes the red ball to reach the ground, the time it takes the green ball to reach the ground is (A) one-half as great (C) the same (B) twice as great (D) four times as great Base your answers to questions 92 and 93 on the information below. Projectile A is launched horizontally at a speed of 20. meters per second from the top of a cliff and strikes a level surface below, 3.0 seconds later. Projectile B is launched horizontally from the same location at a speed of 30. meters per second. 88. The horizontal component of the ball’s initial velocity is approximately (A) 3.6 m/s (C) 4.9 m/s (B) 7.0 m/s (D) 13 m/s 89. The maximum height reached by the ball is approximately (A) 1.2 m (C) 4.9 m (B) 2.5 m (D) 8.5 m 90. The diagram below shows a student throwing a baseball horizontally at 25 meters per second from a cliff 45 meters above the level ground. 92. The time it takes projectile B to reach the level surface is (A) 4.5 s (C) 3.0 s (B) 2.0 s (D) 10. s 93. Approximately how high is the cliff? (A) 29 m (C) 60. m (B) 44 m (D) 104 m Base your answers to questions 94 and 95 on the diagram below which shows a ball projected horizontally with an initial velocity of 20. meters per second east, off a cliff 100. meters high. [Neglect air resistance.] 94. How many seconds does the ball take to reach the ground? (A) 4.5 s (C) 9.8 s (B) 20. s (D) 2.0 s 95. During the flight of the ball, what is the direction of its acceleration? (A) downward (C) westward (B) upward (D) eastward Approximately how far from the base of the cliff does the ball hit the ground? [Neglect air resistance.] (A) 45 m (C) 140 m (B) 75 m (D) 230 m APhy105_MC_Samples 96. What is the period of orbit of a communications satellite in geosynchronous orbit about Earth? (A) 1 year (C) 12 hours (B) 24 hours (D) 60 minutes Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam 97. A ball is projected horizontally to the right from a height of 50. meters, as shown in the diagram below. 99. Base your answer to the following question on the information below. An outfielder throws a baseball to the first baseman at a speed of 19.6 meters per second and an angle of 30.° above the horizontal. Which pair represents the initial horizontal velocity (vx) and initial vertical velocity (vy) of the baseball? (A) vx = 17.0 m/s, vy = 9.80 m/s (B) vx = 9.80 m/s, vy = 17.0 m/s (C) vx = 19.4 m/s, vy = 5.90 m/s (D) vx = 19.6 m/s, vy = 19.6 m/s 100. Base your answer to the following question on the information and diagram below. Which diagram best represents the position of the ball at 1.0-second intervals? [Neglect air resistance.] A cannon elevated at an angle of 35º to the horizontal fires a cannonball, which travels the path shown in the diagram below. [Neglect air resistance and assume the ball lands at the same height above the ground from which it was launched.] If the ball lands 7.0 × 102 meters from the cannon 10. seconds after it was fired, what is the horizontal component of its initial velocity? (A) 70. m/s (C) 35 m/s (B) 49 m/s (D) 7.0 m/s (A) (C) 101. A ball is thrown at an angle of 38° to the horizontal. What happens to the magnitude of the ball’s vertical acceleration during the total time interval that the ball is in the air? (A) It decreases, then increases. (B) It decreases, then remains the same. (C) It increases, then decreases. (D) It remains the same. 102. A vector makes an angle, ‡, with the horizontal. The horizontal and vertical components of the vector will be equal in magnitude if angle ‡ is (A) 30° (C) 60° (B) 45° (D) 90° (B) (D) 98. A ball thrown vertically upward reaches a maximum height of 30. meters above the surface of Earth. At its maximum height, the speed of the ball is (A) 0.0 m/s (C) 3.1 m/s (B) 9.8 m/s (D) 24 m/s APhy105_MC_Samples 103. A basketball player jumped straight up to grab a rebound. If she was in the air for 0.80 second, how high did she jump? (A) 0.50 m (C) 1.2 m (B) 0.78 m (D) 3.1 m Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam 104. Projectiles are fired from different angles with the same initial speed of 14 meters per second. The graph below shows the range of the projectiles as a function of the original angle of inclination to the ground, neglecting air resistance. Base your answers to questions 108 through 110 on the information and diagram below. A ball is thrown horizontally with an initial velocity of 20.0 meters per second from the top of a tower 60.0 meters high. The graph shows that the range of the projectiles is (A) the same for all angles (B) the same for angles of 20.º and 80.º (C) greatest for an angle of 45º (D) greatest for an angle of 90.º 105. Base your answer to the following question on the information below. A toy projectile is fired from the ground vertically upward with an initial velocity of +29 meters per second. The projectile arrives at its maximum altitude in 3.0 seconds. [Neglect air resistance.] The greatest height the projectile reaches is approximately (A) 23 m (C) 87 m (B) 44 m (D) 260 m 106. A ball is thrown horizontally from the top of a building with an initial velocity of 15 meters per second. At the same instant, a second ball is dropped from the top of the building. The two balls have the same (A) path as they fall (B) final velocity as they reach the ground (C) initial horizontal velocity (D) initial vertical velocity 107. Compared to the mass of an object at the surface of the Earth, the mass of the object a distance of two Earth radii from the center of the Earth is (A) the same (C) one-half as great (B) twice as great (D) one-fourth as great 108. What is the approximate total time required for the ball to reach the ground? [Neglect air resistance.] (A) 12.2 s (C) 3.00 s (B) 2.04 s (D) 3.50 s 109. What is the initial vertical velocity of the ball? (A) 0 m/s (C) 20.0 m/s (B) 9.81 m/s (D) 60.0 m/s 110. What is the horizontal velocity of the ball just before it reaches the ground? [Neglect air resistance.] (A) 9.81 m/s (C) 34.3 m/s (B) 20.0 m/s (D) 68.6 m/s 111. A 2-kilogram block is dropped from the roof of a tall building at the same time a 6-kilogram ball is thrown horizontally from the same height. Which statement best describes the motion of the block and the motion of the ball? [Neglect air resistance.] (A) The 2-kg block hits the ground first because it has no horizontal velocity. (B) The 6-kg ball hits the ground first because it has more mass. (C) The 6-kg ball hits the ground first because it is round. (D) The block and the ball hit the ground at the same time because they have the same vertical acceleration. 112. A mass of 10 kilograms is revolving at a linear speed of 5 meters per second in a circle with a radius of 10 meters. The centripetal force acting on the mass is (A) 5 N (C) 20 N (B) 10 N. (D) 25 N APhy105_MC_Samples Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam 113. Four different balls are thrown horizontally off the top of four cliffs. In which diagram does the ball have the shortest time of flight? (A) Base your answers to questions 117 through 119 on the following information. In the diagram below, a 10.-kilogram sphere, A, is projected horizontally with a velocity of 30. meters per second due east from a height of 20. meters above level ground. At the same instant, a 20.-kilogram sphere, B, is projected horizontally with a velocity of 10. meters per second due west from a height of 80. meters above level ground. [Neglect air friction.] (C) (B) (D) 114. Gravitational force F exists between point objects A and B separated by distance R. If the mass of A is doubled and distance R is tripled, what is the new gravitational force between A and B? (A) 2F 9 (B) 2F 3 (C) 3F 2 (D) 9F 2 115. An object weighs 200. Newtons at a distance of 100. kilometers above the center of a small uniform planet. How much will the object weigh 200. kilometers above the planet's center? (A) 400. N (C) 50.0 N (B) 100. N (D) 25.0 N 116. Base your answer to the following question on the information below. A car traveling at a speed of 13 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 25 meters per second in 5.0 seconds. A truck traveling at a constant speed covers the same total distance as the car in the same 5.0-second time interval. Determine the speed of the truck. APhy105_MC_Samples 117. Compared to the vertical acceleration of sphere A, the vertical acceleration of sphere B is (A) the same (C) one-half as great (B) twice as great (D) four times as great 118. Initially, the spheres are separated by a horizontal distance of 100. meters. What is the horizontal separation of the spheres at the end of 1.5 seconds? (A) 15 m (C) 40. m (B) 30 m (D) 45 m 119. The magnitude of the horizontal acceleration of sphere A is (C) 9.8 m/s2 (A) 0.0 m/s2 2 (B) 2.0 m/s (D) 15 m/s2 Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam 120. Base your answer to the following question on the information and diagram below. The diagram shows a student seated on a rotating circular platform, holding a 2.0-kilogram block with a spring scale. The block is 1.2 meters from the center of the platform. The block has a constant speed of 8.0 meters per second. [Frictional forces on the block are negligible.] Base your answers to questions 122 and 123 on the information and diagram below. A roller coaster cart starts from rest and accelerates, due to gravity, down a track. The cart starts at a height that enables it to complete a loop in the track. [Neglect friction.] 122. Which diagram best represents the path followed by an object that falls off the cart when the cart is at point D? Which statement best describes the block’s movement as the platform rotates? (A) Its velocity is directed tangent to the circular path, with an inward acceleration. (B) Its velocity is directed tangent to the circular path, with an outward acceleration. (C) Its velocity is directed perpendicular to the circular path, with an inward acceleration. (D) Its velocity is directed perpendicular to the circular path, with an outward acceleration. 121. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which represents a mass of 10.0 kilograms traveling at constant speed of 4. meters per second in a horizontal circular path about point D. Which quantity would increase if the radius increased? (A) period (C) mass (B) tangential velocity (D) centripetal acceleration APhy105_MC_Samples (A) (B) (C) (D) 123. The magnitude of the centripetal force keeping the cart in circular motion would be greatest at point (A) A (C) C (B) B (D) D 124. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which represents a ball of mass M attached to a string. The ball moves at a constant speed around a flat horizontal circle of radius R. If the string is shortened while the speed of the ball remains the same, the centripetal acceleration will (A) decrease (C) remain the same (B) increase Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam 125. Base your answer to the following question on the information and diagram below. A 1200-kilogram car traveling at a constant speed of 9.0 meters per second turns at an intersection. The car follows a horizontal circular path with a radius of 25 meters to point P. The magnitude of the centripetal force acting on the car as it travels around the circular path is approximately (C) 3.9 × 103 N (A) 1.1 × 104 N 4 (B) 1.2 × 10 N (D) 4.3 × 102 N 126. Base your answer to the following question on the information and diagram below. A 1.00 × 103 -kilogram car is driven clockwise around a flat circular track of radius 25.0 meters. The speed of the car is a constant 5.00 meters per second. Base your answers to questions 127 through 130 on the diagram below which represents a 2.0-kilogram mass moving in a circular path on the end of a string 0.50 meter long. The mass moves in a horizontal plane at a constant speed of 4.0 meters per second. 127. The speed of the mass is changed to 2.0 meters per second. Compared to the centripetal acceleration of the mass when moving at 4.0 meters per second, its centripetal acceleration when moving at 2.0 meters per second would be (A) half as great (C) one-fourth as great (B) twice as great (D) four times great 128. The force exerted on the mass by the string is (A) 8 N (C) 32 N (B) 16 N (D) 64 N 129. The centripetal force acting on the mass is directed toward point (A) A (C) C (B) B (D) D 130. In the position shown in the diagram, the momentum of the mass is directed toward point (A) A (C) C (B) B (D) D Which factor, when doubled, would produce the greatest change in the centripetal force acting on the car? (A) mass of the car (C) velocity of the car (B) radius of the track (D) weight of the car APhy105_MC_Samples Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam Base your answers to questions 131 through 135 on the diagram below which represents a 5.0-kilogram object revolving around a circular track in a horizontal plane at a constant speed. The radius of the track is 20. meters and the centripetal force on the object is 4.0 × 102 Newtons. 136. An object on the end of a string rotates clockwise in a circle as shown in the diagram below. If the string breaks when the object is at point X, which arrow below best represents the path of the object after the string has broken? 131. The object's centripetal acceleration is (A) 0.012 m/s² (C) 80. m/s² (B) 20. m/s² (D) 1.0 × 102 m/s2 132. In the position shown, the object's centripetal acceleration is directed toward point (A) A (C) C (B) B (D) D 133. In the position shown, the object's velocity is directed toward point (A) A (C) C (B) B (D) D 134. The object's speed is (A) 20. m/s (B) 40. m/s (C) 60. m/s (D) 80. m/s 135. If the radius of the track is increased, the centripetal force necessary to keep the object revolving at the same speed would (A) decrease (C) remain the same (B) increase APhy105_MC_Samples (A) (C) (B) (D) Samples: UHS APhy 105 Final Exam Base your answers to questions 137 through 139 on the diagram below which shows a 2.0-kilogram model airplane attached to a wire. The airplane is flying clockwise in a horizontal circle of radius 20. meters at 30. meters per second. 138. The centripetal force acting on the airplane at the position shown is directed toward point (A) A (C) C (B) B (D) D 139. What is the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of the airplane? (C) 45 m/s2 (A) 0 m/s2 2 (B) 1.5 m/s (D) 90. m/s2 137. If the wire breaks when the airplane is at the position shown, the airplane will move toward point (A) A (C) C (B) B (D) D APhy105_MC_Samples