the design of vortex induced vibration fluid kinetic energy harvesters
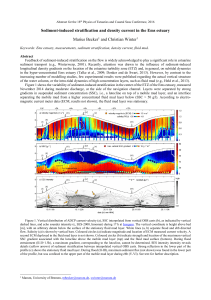
... In this paper, a fluid kinetic energy harvester based on vortices induced vibration has been proposed. The related theoretical background has been introduced as well. Several simulations are presented for the optimization of the final harvester’s performance. The first experimental result shows, tha ...
... In this paper, a fluid kinetic energy harvester based on vortices induced vibration has been proposed. The related theoretical background has been introduced as well. Several simulations are presented for the optimization of the final harvester’s performance. The first experimental result shows, tha ...
Analysis-of-Optical-Flow-Techniques-in-Video
... Video is considered as an ordered collection of frames or images which allows the computation of optical flow vectors as either instantaneous frame velocities or discrete displacement of pixels from one image or frame to another. Based on Taylor series assumptions flow vectors between subsequent fra ...
... Video is considered as an ordered collection of frames or images which allows the computation of optical flow vectors as either instantaneous frame velocities or discrete displacement of pixels from one image or frame to another. Based on Taylor series assumptions flow vectors between subsequent fra ...
Fluid Mechanics - 上海交通大学工程力学教学基地
... • The solid object will no change inside the a closed container • The liquid will change its shape to conform to that of the container and will take on the same boundaries as the container up to the maximum depth of the liquid ...
... • The solid object will no change inside the a closed container • The liquid will change its shape to conform to that of the container and will take on the same boundaries as the container up to the maximum depth of the liquid ...
Introduction of compressible flow
... as the average of the pressures acting on the two end surfaces. dFµ is the frictional force. ...
... as the average of the pressures acting on the two end surfaces. dFµ is the frictional force. ...
Basics
... • Water is flowing at a velocity of 30 meters per second from a spillway outlet. What is this speed in feet per second? • Steps: (1) write down the value you have, then (2) select a conversion factor and write it as a fraction so the unit you want to get rid of is on the opposite side, and cancel. T ...
... • Water is flowing at a velocity of 30 meters per second from a spillway outlet. What is this speed in feet per second? • Steps: (1) write down the value you have, then (2) select a conversion factor and write it as a fraction so the unit you want to get rid of is on the opposite side, and cancel. T ...
Springs in Series
... Object T has a higher average density than object B. Object B has a higher average density than object T. Both objects have the same average density. Archimedes' principle is helpful in solving quantitative (usually statics) problems as well. If an object is moving in a liquid, however, the resultin ...
... Object T has a higher average density than object B. Object B has a higher average density than object T. Both objects have the same average density. Archimedes' principle is helpful in solving quantitative (usually statics) problems as well. If an object is moving in a liquid, however, the resultin ...
The Normal Pleura
... The lung is covered with visceral pleura The adjacent surfaces of the mediastinum, chest wall, and diaphragm are lined by parietal pleura. These layers are in continuity both at the hilum and below, where they form the pulmonary ligament. The visceral and parietal pleura are separated by a p ...
... The lung is covered with visceral pleura The adjacent surfaces of the mediastinum, chest wall, and diaphragm are lined by parietal pleura. These layers are in continuity both at the hilum and below, where they form the pulmonary ligament. The visceral and parietal pleura are separated by a p ...
Specification For Insertion Type Magnetic Flowmeter
... USB to Digital (S3L) Configuration/Diagnostic Tool shall be used to span (in 4-20 mA models), and/or customize performance features including Noise Rejection Filter, Low Flow Cutoff, Averaging Time, and Sensitivity. ...
... USB to Digital (S3L) Configuration/Diagnostic Tool shall be used to span (in 4-20 mA models), and/or customize performance features including Noise Rejection Filter, Low Flow Cutoff, Averaging Time, and Sensitivity. ...
Pressure
... where is the density of the fluid. The same is true for Q. Since Y and Z are at the same depth, their pressures are the same. Therefore, if the containers hold the same type of fluid, the pressure at Z is the same as the pressure at Q, even though the containers have different shapes. We can repea ...
... where is the density of the fluid. The same is true for Q. Since Y and Z are at the same depth, their pressures are the same. Therefore, if the containers hold the same type of fluid, the pressure at Z is the same as the pressure at Q, even though the containers have different shapes. We can repea ...
Unit Operation-II
... •Period of constant-velocity fall - Free settling velocity or terminal velocity, vt ...
... •Period of constant-velocity fall - Free settling velocity or terminal velocity, vt ...
lecture 5 - darroesengineering
... King Heiro ordered a new crown to be made from pure gold. When he received the crown, he suspected that other metals had been used in its construction. Archimedes discovered that the crown required a force of 4.7 lbf to suspend it when immerse water, and that it displaced 18.9 in3. of water. He conc ...
... King Heiro ordered a new crown to be made from pure gold. When he received the crown, he suspected that other metals had been used in its construction. Archimedes discovered that the crown required a force of 4.7 lbf to suspend it when immerse water, and that it displaced 18.9 in3. of water. He conc ...
8th- Chapter 11 Review Game
... • An object that is more dense than the fluid in which it is immersed will ...
... • An object that is more dense than the fluid in which it is immersed will ...
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids (liquids and gases) in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Some of its principles are even used in traffic engineering, where traffic is treated as a continuous fluid, and crowd dynamics. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves calculating various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and time.Before the twentieth century, hydrodynamics was synonymous with fluid dynamics. This is still reflected in names of some fluid dynamics topics, like magnetohydrodynamics and hydrodynamic stability, both of which can also be applied to gases.