Introduction to the immersed boundary method
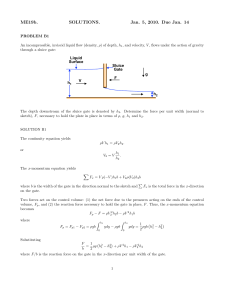
... Quasi-rigid means that the object is slightly deformable but sufficiently rigid for its purpose. It is not possible to review all of these methods in this lecture. The quasi-rigid method by Feng and Michaelides [8] and the implicit method introduced by Wu and Shu [12] are briefly described in the fo ...
... Quasi-rigid means that the object is slightly deformable but sufficiently rigid for its purpose. It is not possible to review all of these methods in this lecture. The quasi-rigid method by Feng and Michaelides [8] and the implicit method introduced by Wu and Shu [12] are briefly described in the fo ...
Physics 6B Hydrodynamics
... If the Reynolds number is low, then viscosity plays a significant role, and the fluid will exhibit laminar flow, but Bernoulli’s equation will not be satisfied. In this case we can use a different formula to relate the flow rate to the pressure difference. This is Poiseuille’s equation. ...
... If the Reynolds number is low, then viscosity plays a significant role, and the fluid will exhibit laminar flow, but Bernoulli’s equation will not be satisfied. In this case we can use a different formula to relate the flow rate to the pressure difference. This is Poiseuille’s equation. ...
11.2 Physics 6B Fluids - Hydrodynamics
... If the Reynolds number is low, then viscosity plays a significant role, and the fluid will exhibit laminar flow, but Bernoulli’s equation will not be satisfied. In this case we can use a different formula to relate the flow rate to the pressure difference. This is Poiseuille’s equation. ...
... If the Reynolds number is low, then viscosity plays a significant role, and the fluid will exhibit laminar flow, but Bernoulli’s equation will not be satisfied. In this case we can use a different formula to relate the flow rate to the pressure difference. This is Poiseuille’s equation. ...
Chapter 2 - Portal UniMAP
... 79 % N2, 21 % O2 and (b) from its approximate mass composition of 76.7 % N2, 23.3 % O2 ...
... 79 % N2, 21 % O2 and (b) from its approximate mass composition of 76.7 % N2, 23.3 % O2 ...
1204pdf - FSU High Energy Physics
... The general behavior of fluid in motion is very comples, because of the phenomen of turbulence. But there are some easy concepts governing the non-turbulent, steady-state flow of an incompressible fluid. Continuity equation (Figure 13-13 of Tipler-Mosca): Let v the velocity of the flow and A be the ...
... The general behavior of fluid in motion is very comples, because of the phenomen of turbulence. But there are some easy concepts governing the non-turbulent, steady-state flow of an incompressible fluid. Continuity equation (Figure 13-13 of Tipler-Mosca): Let v the velocity of the flow and A be the ...
Raskevicius - NSERC
... rock samples both proximal and distal to the mine site. Care is being taken to only analyze rock samples from drill core which are free from quartz-carbonate veins, since these veins will produce isotopic compositions different than the altered rocks. Also, attempts are being made to develop a metho ...
... rock samples both proximal and distal to the mine site. Care is being taken to only analyze rock samples from drill core which are free from quartz-carbonate veins, since these veins will produce isotopic compositions different than the altered rocks. Also, attempts are being made to develop a metho ...
CURRENT FLOW/ ELECTRON FLOW IN FILM CAPACITORS
... supply), all the electrons already present in the metallized portion of layer 1 is attracted to the positive terminal of the supply. So the electron flow is from right to left. Since all the electrons removed, the layer becomes positively charged. In layer 2, more number of electrons will get inject ...
... supply), all the electrons already present in the metallized portion of layer 1 is attracted to the positive terminal of the supply. So the electron flow is from right to left. Since all the electrons removed, the layer becomes positively charged. In layer 2, more number of electrons will get inject ...
Fisher Color Letterhead
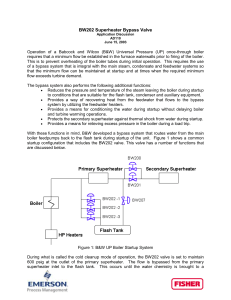
... This is to prevent overheating of the boiler tubes during initial operation. This requires the use of a bypass system that is integral with the main steam, condensate and feedwater systems so that the minimum flow can be maintained at startup and at times when the required minimum flow exceeds turbi ...
... This is to prevent overheating of the boiler tubes during initial operation. This requires the use of a bypass system that is integral with the main steam, condensate and feedwater systems so that the minimum flow can be maintained at startup and at times when the required minimum flow exceeds turbi ...
Magnetic Flowmeter Fundamentals
... the magnet coils periodically with a low frequency square wave. With this design the flow signal is a dc pulse with an amplitude proportional to the velocity of the fluid conductor. There is no need to compensate for voltage and frequency variations on the ac power line. Although stray noise may be ...
... the magnet coils periodically with a low frequency square wave. With this design the flow signal is a dc pulse with an amplitude proportional to the velocity of the fluid conductor. There is no need to compensate for voltage and frequency variations on the ac power line. Although stray noise may be ...
Physical Principles - Thayer School of Engineering
... Because fluid motions occur under the action of pressure and other forces, a necessary budget is that for momentum. The momentum of a piece of matter in movement is equal to the product of its mass by its velocity. In general, the velocity is a three-dimensional vector, ~u, and on a per-volume basis ...
... Because fluid motions occur under the action of pressure and other forces, a necessary budget is that for momentum. The momentum of a piece of matter in movement is equal to the product of its mass by its velocity. In general, the velocity is a three-dimensional vector, ~u, and on a per-volume basis ...
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids (liquids and gases) in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Some of its principles are even used in traffic engineering, where traffic is treated as a continuous fluid, and crowd dynamics. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves calculating various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and time.Before the twentieth century, hydrodynamics was synonymous with fluid dynamics. This is still reflected in names of some fluid dynamics topics, like magnetohydrodynamics and hydrodynamic stability, both of which can also be applied to gases.