Forces 2-1b0y3mn
... AP Physics – Newton’s Laws Nmea _____________________________________________________________________ ...
... AP Physics – Newton’s Laws Nmea _____________________________________________________________________ ...
Centripetal Acceleration and Force
... Circular Motion and Gravitation Notes 1 – Centripetal Acceleration and Force This unit we will investigate the special case of kinematics and dynamics of objects in uniform circular motion. First let’s consider a mass on a string being twirled in a horizontal circle at a constant speed. Let’s determ ...
... Circular Motion and Gravitation Notes 1 – Centripetal Acceleration and Force This unit we will investigate the special case of kinematics and dynamics of objects in uniform circular motion. First let’s consider a mass on a string being twirled in a horizontal circle at a constant speed. Let’s determ ...
CP Physics Semester 1 Final Exam Review Packet 2016
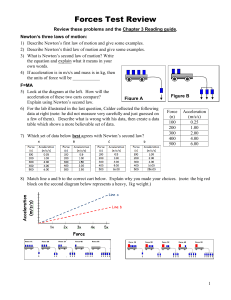
... 42. What unit of distance should you use if you are measuring the length of a chalk? 43. What unit of distance should you use if you are measure the length of a flight? 44. If a car travels 200 meters in 23 seconds, what is the average speed? ...
... 42. What unit of distance should you use if you are measuring the length of a chalk? 43. What unit of distance should you use if you are measure the length of a flight? 44. If a car travels 200 meters in 23 seconds, what is the average speed? ...
Galileo
... happens to its acceleration? 2) If you push the same, but the cart is loaded so that it has 5 x the mass, what happens to the acceleration? 3) If you push 5 x harder when its mass is 5 x greater, what happens to the acceleration? ...
... happens to its acceleration? 2) If you push the same, but the cart is loaded so that it has 5 x the mass, what happens to the acceleration? 3) If you push 5 x harder when its mass is 5 x greater, what happens to the acceleration? ...
HW#6: Fallin` Up
... Please answer in complete sentences. 1) Galileo figured out that all objects fall toward the earth at the same rate regardless of their mass. In fact, all objects accelerate toward the Earth at a rate of 9.8 meters per second every second. What is one factor that could affect the acceleration of an ...
... Please answer in complete sentences. 1) Galileo figured out that all objects fall toward the earth at the same rate regardless of their mass. In fact, all objects accelerate toward the Earth at a rate of 9.8 meters per second every second. What is one factor that could affect the acceleration of an ...
Notes on Terminal Velocity and Simple Harmonic Motion – Physics C
... At t=0, the acceleration is g, since the velocity is zero. This can be confirmed using Newton’s Second Law, mg-kv=ma, and mg-0=ma so therefore a=g at t=0. After a long time, the acceleration of the object is zero. It is important to help the students learn to plug in these limiting values to determi ...
... At t=0, the acceleration is g, since the velocity is zero. This can be confirmed using Newton’s Second Law, mg-kv=ma, and mg-0=ma so therefore a=g at t=0. After a long time, the acceleration of the object is zero. It is important to help the students learn to plug in these limiting values to determi ...
Chapter 3 - Cloudfront.net
... Gravity is a distance force (or as your book says “action-at-a-distance force”). No one really knows how distance forces work or why… It is still hotly debated and ...
... Gravity is a distance force (or as your book says “action-at-a-distance force”). No one really knows how distance forces work or why… It is still hotly debated and ...
Proficiency Review
... A. When a magnetic field changes an electric current will be induced. B. Magnets are needed for an electrical current to flow through wires. C. High voltage is needed to transfer electric current long distances. D. A higher voltage is needed to run large appliances than small ones. ...
... A. When a magnetic field changes an electric current will be induced. B. Magnets are needed for an electrical current to flow through wires. C. High voltage is needed to transfer electric current long distances. D. A higher voltage is needed to run large appliances than small ones. ...
Mass versus weight

In everyday usage, the mass of an object is often referred to as its weight though these are in fact different concepts and quantities. In scientific contexts, mass refers loosely to the amount of ""matter"" in an object (though ""matter"" may be difficult to define), whereas weight refers to the force experienced by an object due to gravity. In other words, an object with a mass of 1.0 kilogram will weigh approximately 9.81 newtons (newton is the unit of force, while kilogram is the unit of mass) on the surface of the Earth (its mass multiplied by the gravitational field strength). Its weight will be less on Mars (where gravity is weaker), more on Saturn, and negligible in space when far from any significant source of gravity, but it will always have the same mass.Objects on the surface of the Earth have weight, although sometimes this weight is difficult to measure. An example is a small object floating in a pool of water (or even on a dish of water), which does not appear to have weight since it is buoyed by the water; but it is found to have its usual weight when it is added to water in a container which is entirely supported by and weighed on a scale. Thus, the ""weightless object"" floating in water actually transfers its weight to the bottom of the container (where the pressure increases). Similarly, a balloon has mass but may appear to have no weight or even negative weight, due to buoyancy in air. However the weight of the balloon and the gas inside it has merely been transferred to a large area of the Earth's surface, making the weight difficult to measure. The weight of a flying airplane is similarly distributed to the ground, but does not disappear. If the airplane is in level flight, the same weight-force is distributed to the surface of the Earth as when the plane was on the runway, but spread over a larger area.A better scientific definition of mass is its description as being composed of inertia, which basically is the resistance of an object being accelerated when acted on by an external force. Gravitational ""weight"" is the force created when a mass is acted upon by a gravitational field and the object is not allowed to free-fall, but is supported or retarded by a mechanical force, such as the surface of a planet. Such a force constitutes weight. This force can be added to by any other kind of force.For example, in the photograph, the girl's weight, subtracted from the tension in the chain (respectively the support force of the seat), yields the necessary centripetal force to keep her swinging in an arc. If one stands behind her at the bottom of her arc and abruptly stops her, the impetus (""bump"" or stopping-force) one experiences is due to acting against her inertia, and would be the same even if gravity were suddenly switched off.While the weight of an object varies in proportion to the strength of the gravitational field, its mass is constant (ignoring relativistic effects) as long as no energy or matter is added to the object. Accordingly, for an astronaut on a spacewalk in orbit (a free-fall), no effort is required to hold a communications satellite in front of him; it is ""weightless"". However, since objects in orbit retain their mass and inertia, an astronaut must exert ten times as much force to accelerate a 10‑ton satellite at the same rate as one with a mass of only 1 ton.On Earth, a swing set can demonstrate this relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. If one were to stand behind a large adult sitting stationary on a swing and give him a strong push, the adult would temporarily accelerate to a quite low speed, and then swing only a short distance before beginning to swing in the opposite direction. Applying the same impetus to a small child would produce a much greater speed.