53 - Angelfire
... 2.55. The speed of a bullet as it travels down the barrel of a rifle toward the opening is given by the expression v = (-5.0 x 107)t2 + (3.0 x 105)t, where v is in meters per second and t is in seconds. The acceleration of the bullet just as it leaves the barrel is zero. (a) Determine the accelerati ...
... 2.55. The speed of a bullet as it travels down the barrel of a rifle toward the opening is given by the expression v = (-5.0 x 107)t2 + (3.0 x 105)t, where v is in meters per second and t is in seconds. The acceleration of the bullet just as it leaves the barrel is zero. (a) Determine the accelerati ...
Newton`s second law of motion
... If the ending force acting on an object is not zero, all the forces are said to be unbalanced. This forms the basis of Newton’s second law of motion, which states: If the forces on an object are unbalanced, two things about the object can change: the speed of the object may change – it may either ...
... If the ending force acting on an object is not zero, all the forces are said to be unbalanced. This forms the basis of Newton’s second law of motion, which states: If the forces on an object are unbalanced, two things about the object can change: the speed of the object may change – it may either ...
Torque - wellsphysics
... You can sum the forces acting on an object and apply Newton’s Second Law for linear motion. ...
... You can sum the forces acting on an object and apply Newton’s Second Law for linear motion. ...
Dynamics-PE2013
... F is the summation of external forces required to bring about the acceleration aG to the center of mass of the particle system of total mass mt. The problems that this Force-Acceleration addresses are similar to those of single particles. Work/Energy Formulation of particle Kinetics The energy form ...
... F is the summation of external forces required to bring about the acceleration aG to the center of mass of the particle system of total mass mt. The problems that this Force-Acceleration addresses are similar to those of single particles. Work/Energy Formulation of particle Kinetics The energy form ...
Document
... which Data regarding the angular motion of the radial line r are given, or in Cases where the path can be conveniently expressed in terms of these coordinates. ...
... which Data regarding the angular motion of the radial line r are given, or in Cases where the path can be conveniently expressed in terms of these coordinates. ...
Force and motion 1
... * know some different types of forces * know and be able to apply Newton’s second law to simple examples of objects moving in a straight line * understands the idea of equilibrium. ...
... * know some different types of forces * know and be able to apply Newton’s second law to simple examples of objects moving in a straight line * understands the idea of equilibrium. ...
Newton`s Three Laws of Motion
... unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. • Unbalanced forces cause acceleration. – When you roll a ball, why doesn’t it roll on ...
... unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. • Unbalanced forces cause acceleration. – When you roll a ball, why doesn’t it roll on ...
Lecture-15-10
... and mass 0.742 kg. If the bucket is allowed to fall, (a) what is its linear acceleration? (b) What is the angular acceleration of the pulley? (c) How far does the bucket drop in 1.50 s? ...
... and mass 0.742 kg. If the bucket is allowed to fall, (a) what is its linear acceleration? (b) What is the angular acceleration of the pulley? (c) How far does the bucket drop in 1.50 s? ...
Physics ~ Fall Final Review
... DISCLAIMER: These problems include some possibilities for the test. Therefore, the answer to the question, “If I know everything on this sheet, am I guaranteed an A on the final?” is NO. For comprehensive review, you must study old test and quizzes, homework sets, corresponding sections of the text ...
... DISCLAIMER: These problems include some possibilities for the test. Therefore, the answer to the question, “If I know everything on this sheet, am I guaranteed an A on the final?” is NO. For comprehensive review, you must study old test and quizzes, homework sets, corresponding sections of the text ...
Torque - curtehrenstrom.com
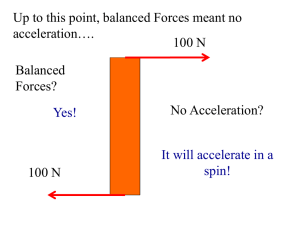
... A net force will cause and object to accelerate in one dimension, but what about rotational acceleration? Would a Force exerted at .5r from the center produce the same rotational acceleration around the center as……. ….. the same force exerted at r from the center? ...
... A net force will cause and object to accelerate in one dimension, but what about rotational acceleration? Would a Force exerted at .5r from the center produce the same rotational acceleration around the center as……. ….. the same force exerted at r from the center? ...
SCRIBBLE PAD
... • Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first. • Force pairs do not act on the same object • The effect of a reaction can be difficult to see • More examples: – Rabbit hopping – Bat hitting ball – Shuttle taking off ...
... • Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first. • Force pairs do not act on the same object • The effect of a reaction can be difficult to see • More examples: – Rabbit hopping – Bat hitting ball – Shuttle taking off ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion (power point file)
... rest or constant motion (velocity) in a straight line unless acted on by an external force that changes that state • A body cannot be made to change its speed or direction unless acted upon by a force(s) • Difficult to prove on earth due to the presence of friction and air resistance BioLab - Biomec ...
... rest or constant motion (velocity) in a straight line unless acted on by an external force that changes that state • A body cannot be made to change its speed or direction unless acted upon by a force(s) • Difficult to prove on earth due to the presence of friction and air resistance BioLab - Biomec ...
R - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... where F > 0 corresponds to an attractive force and u = 1/r. In the case of a particle moving under a force of gravitational attraction, we substitute F = GMm/r2 into this equation. Measuring q from the axis OA joining the focus O to the point A of the trajectory closest to O, we find ...
... where F > 0 corresponds to an attractive force and u = 1/r. In the case of a particle moving under a force of gravitational attraction, we substitute F = GMm/r2 into this equation. Measuring q from the axis OA joining the focus O to the point A of the trajectory closest to O, we find ...
File
... v: velocity (m/s) ω: angular velocity (rad/s) : angular accel (rad/s2) a: acceleration (m/s2) Constant eq’ns: Constant a eq’ns: ωf = ωi + Δt ...
... v: velocity (m/s) ω: angular velocity (rad/s) : angular accel (rad/s2) a: acceleration (m/s2) Constant eq’ns: Constant a eq’ns: ωf = ωi + Δt ...
PHYS2101: General Physics I
... Analyse problems into components and treat each component using the relevant physical laws. Assess the use of different principles and approaches in solutions of the problems in linear and rotational motions. Experience applications of dynamics and kinematics in common real-life situations. ...
... Analyse problems into components and treat each component using the relevant physical laws. Assess the use of different principles and approaches in solutions of the problems in linear and rotational motions. Experience applications of dynamics and kinematics in common real-life situations. ...