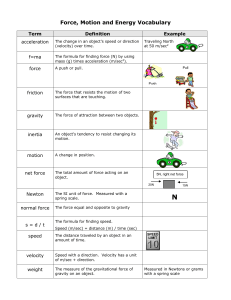
FORCE and MOTION UNIT VOCABULARY
... The force equal and opposite to gravity The formula for finding speed. Speed (m/sec) = distance (m) / time (sec) The distance traveled by an object in an amount of time. ...
... The force equal and opposite to gravity The formula for finding speed. Speed (m/sec) = distance (m) / time (sec) The distance traveled by an object in an amount of time. ...
Chapter_10
... d) At the final speed, with what force does the fly (m = 0.01 kg, r = 0.50 m) need to hold on, so that it won’t fall off? (Note difference between angular and centripetal acceleration). ...
... d) At the final speed, with what force does the fly (m = 0.01 kg, r = 0.50 m) need to hold on, so that it won’t fall off? (Note difference between angular and centripetal acceleration). ...
Newton`s Laws - AdvancedPlacementPhysicsC
... An object in motion remains in motion in a straight line and at a constant speed OR an object at rest remains at rest, UNLESS acted upon by an EXTERNAL (unbalanced) force. acc 0 F 0 The bottom line: There is NO ACCELERATION (no change in velocity) unless a force acts, but you can have MOTIO ...
... An object in motion remains in motion in a straight line and at a constant speed OR an object at rest remains at rest, UNLESS acted upon by an EXTERNAL (unbalanced) force. acc 0 F 0 The bottom line: There is NO ACCELERATION (no change in velocity) unless a force acts, but you can have MOTIO ...
forces and the laws of motion - PAMS-Doyle
... that they would both hit the ground at the same time. He was right. • When the only force acting on a falling object is gravity, they are in free fall. • Acceleration of a falling object is due to the force of gravity is 9.8 m/sec/sec. • 1 meter = 9.8 m/sec/sec • 2 meters = 19.6 m/sec/sec • 3 meters ...
... that they would both hit the ground at the same time. He was right. • When the only force acting on a falling object is gravity, they are in free fall. • Acceleration of a falling object is due to the force of gravity is 9.8 m/sec/sec. • 1 meter = 9.8 m/sec/sec • 2 meters = 19.6 m/sec/sec • 3 meters ...
Rotational Motion - Damien Honors Physics
... then balance pencil on your finger. • Each penny exerts a torque that is equal to its weight (force of gravity) times the distance r from the balance point on your finger. • Torques are equal but opposite in direction so net torque=0 • If you placed 2 pennies on one side, where could you place the s ...
... then balance pencil on your finger. • Each penny exerts a torque that is equal to its weight (force of gravity) times the distance r from the balance point on your finger. • Torques are equal but opposite in direction so net torque=0 • If you placed 2 pennies on one side, where could you place the s ...
Unit 7
... Defining Torque as a Force at a distance from a pivot point Examples: Pushing on a door why is the hinge placed where it is? Meterstick determining the balancing point on a meterstick Torque is defined as the ability of a force to rotate an object around some axis. Second law of Equilibrium su ...
... Defining Torque as a Force at a distance from a pivot point Examples: Pushing on a door why is the hinge placed where it is? Meterstick determining the balancing point on a meterstick Torque is defined as the ability of a force to rotate an object around some axis. Second law of Equilibrium su ...
Energy Forms of Energy Types of Mechanical Energy Laws of
... • If the resultant force acting on a body is a conservative force then the body’s total mechanical energy will be conserved. • Resultant force will be conservative if all external forces are conservative. • A force is conservative if it does no work around a closed path (motion cycle). ...
... • If the resultant force acting on a body is a conservative force then the body’s total mechanical energy will be conserved. • Resultant force will be conservative if all external forces are conservative. • A force is conservative if it does no work around a closed path (motion cycle). ...
Sections 13.1-13.4 - University of Mary Hardin–Baylor
... kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth’s surface, g can be taken as g = 9.81 m/s2. W (N) = m (kg) g (m/s2) => N = kg·m/s2 FPS System: In the FPS system of uni ...
... kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth’s surface, g can be taken as g = 9.81 m/s2. W (N) = m (kg) g (m/s2) => N = kg·m/s2 FPS System: In the FPS system of uni ...
Newton`s Second Law - Philadelphia University
... kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth’s surface, g can be taken as g = 9.81 m/s2. W (N) = m (kg) g (m/s2) => N = kg·m/s2 FPS System: In the FPS system of uni ...
... kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth’s surface, g can be taken as g = 9.81 m/s2. W (N) = m (kg) g (m/s2) => N = kg·m/s2 FPS System: In the FPS system of uni ...
Work and Energy - MIT OpenCourseWare
... It turns out that in many situations, these integrations can be carried beforehand to produce equations that relate the velocities at the initial and final integration points. In this way, the velocity can be obtained directly, thus making it unnecessary to solve for the acceleration. We shall see th ...
... It turns out that in many situations, these integrations can be carried beforehand to produce equations that relate the velocities at the initial and final integration points. In this way, the velocity can be obtained directly, thus making it unnecessary to solve for the acceleration. We shall see th ...
Vectors Problem Set 1
... a. What is the magnitude and direction of the resultant force? b. What is the magnitude and direction of the equilibrant force? 2. A hiker leaves camp and walks 10 km due North and 10 km due West. a. What is the distance walked by the hiker/ b. What is the displacement of the hiker from the starting ...
... a. What is the magnitude and direction of the resultant force? b. What is the magnitude and direction of the equilibrant force? 2. A hiker leaves camp and walks 10 km due North and 10 km due West. a. What is the distance walked by the hiker/ b. What is the displacement of the hiker from the starting ...
Powerpoint for today
... An object that is at rest will remain at rest and an object that is moving will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed, if and only if the sum of the forces acting on that object is zero. Newton's 2nd Law acceleration of an object = sum of forces acting on that object / the mass of ...
... An object that is at rest will remain at rest and an object that is moving will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed, if and only if the sum of the forces acting on that object is zero. Newton's 2nd Law acceleration of an object = sum of forces acting on that object / the mass of ...
Simple machines Jacquelyn
... effort by traveling a greater distance. Plank or other plane surface placed at an angle to a horizontal surface and used to heavy weights to a higher level with little force. It is a simple machine. ...
... effort by traveling a greater distance. Plank or other plane surface placed at an angle to a horizontal surface and used to heavy weights to a higher level with little force. It is a simple machine. ...
PH212Chapter11_15
... the external torque along the rotation axis, the angular momentum along the rotation axis, the moment of inertia about the rotation axis, the angular velocity about the rotation axis, and the angular acceleration about the rotation axis • Examples of rotation only (Precession) • Examples with transl ...
... the external torque along the rotation axis, the angular momentum along the rotation axis, the moment of inertia about the rotation axis, the angular velocity about the rotation axis, and the angular acceleration about the rotation axis • Examples of rotation only (Precession) • Examples with transl ...
Physics XI 1 A particle of mass 200 kg is displaced horizontal
... inclined at an angle of 60 degrees with the horizontal with a force of 100 N. Calculate the work done. What is the work done if the friction of 0.5 is introduced. Can this work be reclaimed? What is the work done by frictional force in this case. ...
... inclined at an angle of 60 degrees with the horizontal with a force of 100 N. Calculate the work done. What is the work done if the friction of 0.5 is introduced. Can this work be reclaimed? What is the work done by frictional force in this case. ...