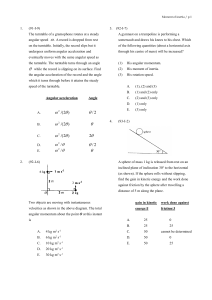
Force
... Field forces are exerted without contact. – Also known as non contact forces or action at distances forces ...
... Field forces are exerted without contact. – Also known as non contact forces or action at distances forces ...
Rotational
... E. The solid cylinder has greater rotational kinetic energy at the bottom of the incline. ...
... E. The solid cylinder has greater rotational kinetic energy at the bottom of the incline. ...
VOLCANOES AND PLATE TECTONICS
... Calculating Force: What is the net force acting on a .15 kg hockey puck accelerating at a rate of 12 m/s2. (*Show all work: Set-up, Substitute, Solve) F= m*a= .15kg* 12m/s2 = 1.8 N Explain how force, mass and acceleration are related by Newton’s second law of motion. Acceleration = F/m F= m*a m= F/a ...
... Calculating Force: What is the net force acting on a .15 kg hockey puck accelerating at a rate of 12 m/s2. (*Show all work: Set-up, Substitute, Solve) F= m*a= .15kg* 12m/s2 = 1.8 N Explain how force, mass and acceleration are related by Newton’s second law of motion. Acceleration = F/m F= m*a m= F/a ...
Rigid Body Dynamics chapter 10 continues
... Many machines employ cams for various purposes, such as opening and closing valves. In Figure P10.29, the cam is a circular disk rotating on a shaft that does not pass through the center of the disk. In the manufacture of the cam, a uniform solid cylinder of radius R is first machined. Then an off- ...
... Many machines employ cams for various purposes, such as opening and closing valves. In Figure P10.29, the cam is a circular disk rotating on a shaft that does not pass through the center of the disk. In the manufacture of the cam, a uniform solid cylinder of radius R is first machined. Then an off- ...
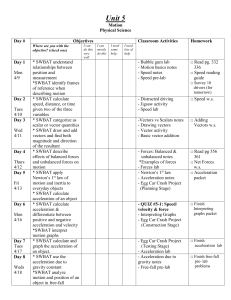
Physical Science Chapter 1 & 2 Motion & Force
... 1. International System of Units: The metric system 2. Length – measured in meters 3. Mass – grams 4. Volume – liters a) 1ml = 1cm3 5. Weight – Newtons 6. Density – mass / volume D. Speed – the distance an object travels in one unit of time 1. a magnitude only: it only tells us “how much” 2. 75 mile ...
... 1. International System of Units: The metric system 2. Length – measured in meters 3. Mass – grams 4. Volume – liters a) 1ml = 1cm3 5. Weight – Newtons 6. Density – mass / volume D. Speed – the distance an object travels in one unit of time 1. a magnitude only: it only tells us “how much” 2. 75 mile ...
CHAPTER 11 HW SOLUTIONS
... 12. All the forces are being evaluated at the origin (since particle A is there), and all ...
... 12. All the forces are being evaluated at the origin (since particle A is there), and all ...
08 lecture ppt
... Both the normal force and the weight act through the center of mass so Στ = 0. 0 This means that the object cannot rotate when only these two forces are applied. ...
... Both the normal force and the weight act through the center of mass so Στ = 0. 0 This means that the object cannot rotate when only these two forces are applied. ...
Jeopardy - QuestGarden.com
... equal pull, the reason the Earth goes around the Sun and not the other way round is due to the Sun’s _____ ______ ...
... equal pull, the reason the Earth goes around the Sun and not the other way round is due to the Sun’s _____ ______ ...
Gravitation PowerPoint
... A 50-kilogram passenger on an amusement park ride stands with his back against the wall of a cylindrical room with radius of 3 m. What is the centripetal force of the wall pressing into his back when the room spins and he is ...
... A 50-kilogram passenger on an amusement park ride stands with his back against the wall of a cylindrical room with radius of 3 m. What is the centripetal force of the wall pressing into his back when the room spins and he is ...
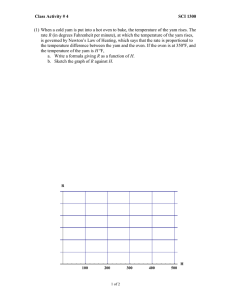
The following table converts degrees Fahrenheit to degrees
... Motion, F=m a, says that the net downward force, F, on the body is proportional to its downward acceleration, a. The net force, F, consists of the force due to gravity, Fg, which acts downward, minus the air resistance, Fr, which acts upward. The force due to gravity is m g, where g is a constant. A ...
... Motion, F=m a, says that the net downward force, F, on the body is proportional to its downward acceleration, a. The net force, F, consists of the force due to gravity, Fg, which acts downward, minus the air resistance, Fr, which acts upward. The force due to gravity is m g, where g is a constant. A ...
Forces (Dynamics) – Notes Day 1
... The forces are represented by ___________________ Size of the arrow reflects :_______________________________ Direction of the arrow shows _____________________________ Each arrow is labeled to ___________________________________ Arrows are always drawn ___________________________________ ...
... The forces are represented by ___________________ Size of the arrow reflects :_______________________________ Direction of the arrow shows _____________________________ Each arrow is labeled to ___________________________________ Arrows are always drawn ___________________________________ ...
Dynamics
... Light, inextensible strings AC and DF are attached to each side of a block of mass 11 kg which is on a rough horizontal table. The string sections BC and DE are parallel to the table and the strings pass over smooth pulleys at B and E. Objects of mass 5 kg and 12 kg are attached to the free ends A a ...
... Light, inextensible strings AC and DF are attached to each side of a block of mass 11 kg which is on a rough horizontal table. The string sections BC and DE are parallel to the table and the strings pass over smooth pulleys at B and E. Objects of mass 5 kg and 12 kg are attached to the free ends A a ...
Document
... The tangential acceleration, at = dv/dt, represents the time rate of change in the magnitude of the velocity. Depending on the direction of Ft, the particle’s speed will either be increasing or decreasing The normal acceleration, an = v2/r, represents the time rate of change in the direction of the ...
... The tangential acceleration, at = dv/dt, represents the time rate of change in the magnitude of the velocity. Depending on the direction of Ft, the particle’s speed will either be increasing or decreasing The normal acceleration, an = v2/r, represents the time rate of change in the direction of the ...
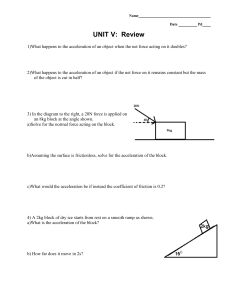
Unit 5 Review
... 2)What happens to the acceleration of an object if the net force on it remains constant but the mass of the object is cut in half? ...
... 2)What happens to the acceleration of an object if the net force on it remains constant but the mass of the object is cut in half? ...
Packet 5 - Cir Motion Torque
... 2008M2. The horizontal uniform rod shown above has length 0.60 m and mass 2.0 kg. The left end of the rod is attached to a vertical support by a frictionless hinge that allows the rod to swing up or down. The right end of the rod is supported by a cord that makes an angle of 30° with the rod. A spri ...
... 2008M2. The horizontal uniform rod shown above has length 0.60 m and mass 2.0 kg. The left end of the rod is attached to a vertical support by a frictionless hinge that allows the rod to swing up or down. The right end of the rod is supported by a cord that makes an angle of 30° with the rod. A spri ...