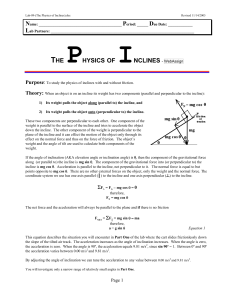
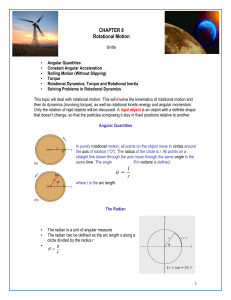
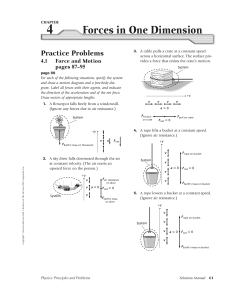
Honors Physics I - Neshaminy School District
... whatever frame of reference is chosen, for there is no motionless frame from which to judge all motion. Whenever one thing exerts a force on another, an equal amount of force is exerted back on it. Any object maintains a constant speed and direction of motion unless an unbalanced outside force acts ...
... whatever frame of reference is chosen, for there is no motionless frame from which to judge all motion. Whenever one thing exerts a force on another, an equal amount of force is exerted back on it. Any object maintains a constant speed and direction of motion unless an unbalanced outside force acts ...
Integrated Science - Pocono Mountain School District
... change the size of a force needed, the direction of a force, or the distance over which a force acts. Work output (done by machine) is always less than work input (done on the machine) The mechanical advantage of a machine is the number of times the machine increases the input force The effici ...
... change the size of a force needed, the direction of a force, or the distance over which a force acts. Work output (done by machine) is always less than work input (done on the machine) The mechanical advantage of a machine is the number of times the machine increases the input force The effici ...
CAS English 1
... Key 2: An object will continue to move at a constant speed, in a straight line, without a net force acting on it. Key 3: If a net force acts on an object, it will cause the object to speed up, slow down, or change direction. Key 4: Forces are interactions between objects that always occur in actionr ...
... Key 2: An object will continue to move at a constant speed, in a straight line, without a net force acting on it. Key 3: If a net force acts on an object, it will cause the object to speed up, slow down, or change direction. Key 4: Forces are interactions between objects that always occur in actionr ...
Recall: Gravitational Potential Energy
... Cart B has greater mass than cart A (mB > mA). The final speed of cart A is greater than that of cart B (vA > vB). After the force has stopped acting on the carts, the kinetic energy of cart B is A. less than the kinetic energy of cart A (KB < KA). B ...
... Cart B has greater mass than cart A (mB > mA). The final speed of cart A is greater than that of cart B (vA > vB). After the force has stopped acting on the carts, the kinetic energy of cart B is A. less than the kinetic energy of cart A (KB < KA). B ...
External work
... • If the resultant force acting on a body is a conservative force then the body’s total mechanical energy will be conserved. • Resultant force will be conservative if all external forces are conservative. • A force is conservative if it does no work around a closed path (motion cycle). ...
... • If the resultant force acting on a body is a conservative force then the body’s total mechanical energy will be conserved. • Resultant force will be conservative if all external forces are conservative. • A force is conservative if it does no work around a closed path (motion cycle). ...
Force and Motion New and Improved
... The tendency of an object to keep moving or remain at rest is called ________________. ...
... The tendency of an object to keep moving or remain at rest is called ________________. ...
Rotational Kinematics (Part I from chapter 10)
... angular speed of 2 000 rad/s. The engine's rotation slows with an angular acceleration of magnitude 80.0 rad/s2. (a) Determine the angular speed after 10.0 s. (b) How long does it take the rotor to come to rest? ...
... angular speed of 2 000 rad/s. The engine's rotation slows with an angular acceleration of magnitude 80.0 rad/s2. (a) Determine the angular speed after 10.0 s. (b) How long does it take the rotor to come to rest? ...
Chapter 6 Impulse and Momentum Continued
... Conceptual Example Is the Total Momentum Conserved? Imagine two balls colliding on a billiard table that is friction-free. Use the momentum conservation principle in answering the following questions. (a) Is the total momentum of the two-ball system the same before and after the collision? (b) Answe ...
... Conceptual Example Is the Total Momentum Conserved? Imagine two balls colliding on a billiard table that is friction-free. Use the momentum conservation principle in answering the following questions. (a) Is the total momentum of the two-ball system the same before and after the collision? (b) Answe ...
Turntables PPT - Physics of Theatre Home
... td tnet+tf1+tf2=Ia+tf1+tf2 So, to determine the drive torque, we need to find the moment of inertia, the angular acceleration, and the frictional torques. ...
... td tnet+tf1+tf2=Ia+tf1+tf2 So, to determine the drive torque, we need to find the moment of inertia, the angular acceleration, and the frictional torques. ...
$doc.title
... the mass can stay without moving. • Whichever way the mass moves, the force is in the direction of pushing it back to its equilibrium position. • When it gets back to its equilibrium, it’s still moving so it overshoots. ...
... the mass can stay without moving. • Whichever way the mass moves, the force is in the direction of pushing it back to its equilibrium position. • When it gets back to its equilibrium, it’s still moving so it overshoots. ...
Pulleys - Mrs. Thomas Room 218
... 4. Is the mechanical advantage and the ideal mechanical advantage always the same? If not, why do you think that is? 5. Do you notice a relationship between the ideal mechanical advantage and the number of pulleys in each of the parts of the lab? If so, what is it? 6. Is there a relationship between ...
... 4. Is the mechanical advantage and the ideal mechanical advantage always the same? If not, why do you think that is? 5. Do you notice a relationship between the ideal mechanical advantage and the number of pulleys in each of the parts of the lab? If so, what is it? 6. Is there a relationship between ...