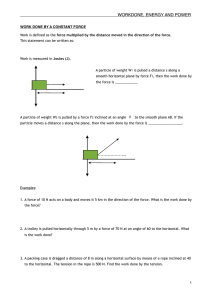
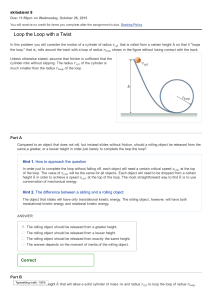
- Review the relationship between force and acceleration
... 2) If there’s a curve, there’s an acceleration. 3) Curved “valley” is forward (positive) acceleration, a curved “hill” is backward (negative) acceleration. ...
... 2) If there’s a curve, there’s an acceleration. 3) Curved “valley” is forward (positive) acceleration, a curved “hill” is backward (negative) acceleration. ...
Vectoring it up – The basic of Vectors and Physics
... add our combined acceleration of an object to its velocity. Note that zero acceleration does not mean we are not moving, it only means we are not accelerating; changing our velocity. A spaceship could for example be traveling super fast and still have zero acceleration. Forces and inertia Force is a ...
... add our combined acceleration of an object to its velocity. Note that zero acceleration does not mean we are not moving, it only means we are not accelerating; changing our velocity. A spaceship could for example be traveling super fast and still have zero acceleration. Forces and inertia Force is a ...
ch12
... • With the inclusion of the inertial vector, the system of forces acting on the particle is equivalent to zero. The particle is in dynamic equilibrium. • Methods developed for particles in static equilibrium may be applied, e.g., coplanar forces may be represented with a closed vector polygon. • Ine ...
... • With the inclusion of the inertial vector, the system of forces acting on the particle is equivalent to zero. The particle is in dynamic equilibrium. • Methods developed for particles in static equilibrium may be applied, e.g., coplanar forces may be represented with a closed vector polygon. • Ine ...
Week 9 Chapter 10 Section 1-5
... Point P will rotate about the origin in a circle of radius r Every particle on the disc undergoes circular motion about the origin, O Polar coordinates are convenient to use to represent the position of P (or any other point) P is located at (r, ) where r is the distance from the origin to P and ...
... Point P will rotate about the origin in a circle of radius r Every particle on the disc undergoes circular motion about the origin, O Polar coordinates are convenient to use to represent the position of P (or any other point) P is located at (r, ) where r is the distance from the origin to P and ...
Rotational Dynamics PowerPoint
... • An object that is rotating has rotational kinetic energy. If it is translating as well, the translational kinetic energy must be added to the rotational to find the total kinetic energy. • Angular momentum is • If the net torque on an object is zero, its angular momentum does not change. ...
... • An object that is rotating has rotational kinetic energy. If it is translating as well, the translational kinetic energy must be added to the rotational to find the total kinetic energy. • Angular momentum is • If the net torque on an object is zero, its angular momentum does not change. ...
Ch. 6 Newton`s Second law of Motion Force and Acceleration
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...