Chapter 6
... The rate of change of velocity is the acceleration. Remember that a = Dv/Dt. The acceleration is related to the force by Newton’s 2nd Law (F = ma), so the acceleration of the boulder is less than that of the pebble (for the same applied force) because the boulder is much more massive. ...
... The rate of change of velocity is the acceleration. Remember that a = Dv/Dt. The acceleration is related to the force by Newton’s 2nd Law (F = ma), so the acceleration of the boulder is less than that of the pebble (for the same applied force) because the boulder is much more massive. ...
Chapter 5
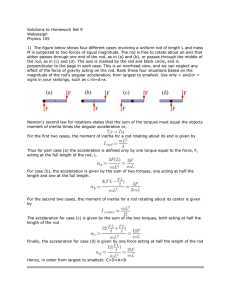
... (a) By Newton’s third law, the force exerted by the block on the surface has that same magnitude but opposite direction: 2.0 N. (b) The direction is down. 15. (a) – (c) In all three cases the scale is not accelerating, which means that the two cords exert forces of equal magnitude on it. The scale r ...
... (a) By Newton’s third law, the force exerted by the block on the surface has that same magnitude but opposite direction: 2.0 N. (b) The direction is down. 15. (a) – (c) In all three cases the scale is not accelerating, which means that the two cords exert forces of equal magnitude on it. The scale r ...
Windsor High School Birdsell Conceptual Physics A Windsor High
... momentum changes with mass distribution D1. Explain why the moon orbits the earth D2. Calculate the force between objects D3. Identify the changes in a gravitational field D4. Explain what is meant by weightless D5. Explain the cause of tides D6. Identify apogee and perigee and explain why the speed ...
... momentum changes with mass distribution D1. Explain why the moon orbits the earth D2. Calculate the force between objects D3. Identify the changes in a gravitational field D4. Explain what is meant by weightless D5. Explain the cause of tides D6. Identify apogee and perigee and explain why the speed ...
Motion - leitl
... Q: Explain why the driver is less likely to suffer a head injury in a collision with the air bag than if his head collided with the car dashboard, or other hard surface. A: The change in momentum suffered by the driver’s head is a FIXED quantity no matter how his head is brought to rest. • Therefore ...
... Q: Explain why the driver is less likely to suffer a head injury in a collision with the air bag than if his head collided with the car dashboard, or other hard surface. A: The change in momentum suffered by the driver’s head is a FIXED quantity no matter how his head is brought to rest. • Therefore ...
Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem for Rotational Motion
... moment of inertia, force with torque, kinetic energy with rotational kinetic energy, and momentum with angular momentum. The relationships between the rotational terms are identical to the relationships between the linear motion terms. Furthermore, we can often convert linear motion expressions to r ...
... moment of inertia, force with torque, kinetic energy with rotational kinetic energy, and momentum with angular momentum. The relationships between the rotational terms are identical to the relationships between the linear motion terms. Furthermore, we can often convert linear motion expressions to r ...
Acceleration
... position D. This is the bottom of the longest descent, so the coaster has had the longest time to accelerate. (Refer to The Other Great Race) ...
... position D. This is the bottom of the longest descent, so the coaster has had the longest time to accelerate. (Refer to The Other Great Race) ...
Coriolis Force
... frame of reference from which we observe the atmosphere. The laws of Newtonian physics are formulated in the absolute, or inertial, frame of reference, but we observe the atmosphere and oceans within a noninertial frame of reference rotating with the earth. The Coriolis force is defined and added to ...
... frame of reference from which we observe the atmosphere. The laws of Newtonian physics are formulated in the absolute, or inertial, frame of reference, but we observe the atmosphere and oceans within a noninertial frame of reference rotating with the earth. The Coriolis force is defined and added to ...
Curriculum Map - Weld RE
... A3. Determine the resultant vector A4, Determine the components of vectors. A5. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving horizontally A6. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving as projectiles. B1. Explain the difference between mass and weight. B2. Explain the law of iner ...
... A3. Determine the resultant vector A4, Determine the components of vectors. A5. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving horizontally A6. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving as projectiles. B1. Explain the difference between mass and weight. B2. Explain the law of iner ...
Honors Review for Midterm
... a. Calculate the drag force on the sky diver when she reaches her terminal velocity. b. Each cord connecting the sky diver and her parachute is rated to hold up to 105 N of tension. How many cords must the parachute have in order to ensure safe operation when the sky diver opens the parachute after ...
... a. Calculate the drag force on the sky diver when she reaches her terminal velocity. b. Each cord connecting the sky diver and her parachute is rated to hold up to 105 N of tension. How many cords must the parachute have in order to ensure safe operation when the sky diver opens the parachute after ...