Introduction to Biomechanics
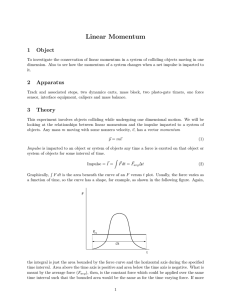
... Lever systems are most easily analyzed under the conditions of equilibrium Force equilibrium: Fi x Li (in-torque) = Fo x Lo (out-torque) ...
... Lever systems are most easily analyzed under the conditions of equilibrium Force equilibrium: Fi x Li (in-torque) = Fo x Lo (out-torque) ...
Appendix B Chapter 2 Extra Practice Problems
... the end of 0.5 s? When would the ball again be this distance from the ground? Appendix B Extra Practice Problems ...
... the end of 0.5 s? When would the ball again be this distance from the ground? Appendix B Extra Practice Problems ...
BilaksPhysiks
... 3. What type of path will the proton follow if only the motion in the x-y plane is considered? A: Straight line (Linear) B: Parabolic C: Circular This is due to the horizontal component of the initial velocity. ...
... 3. What type of path will the proton follow if only the motion in the x-y plane is considered? A: Straight line (Linear) B: Parabolic C: Circular This is due to the horizontal component of the initial velocity. ...
Chapter 9 - Churchill High School
... Yes, the object moves in a straight, inertial path until the spring force (F = -kx) is great enough to keep the object at a constant radius. ...
... Yes, the object moves in a straight, inertial path until the spring force (F = -kx) is great enough to keep the object at a constant radius. ...
Chapter 22
... 24. From the electric field vector at a point, one can determine which of the following? I The direction of the electrostatic force on a test charge of known sign at that point II. The magnitude of the electrostatic force exerted per unit charge on a test charge at that point III. The electrostatic ...
... 24. From the electric field vector at a point, one can determine which of the following? I The direction of the electrostatic force on a test charge of known sign at that point II. The magnitude of the electrostatic force exerted per unit charge on a test charge at that point III. The electrostatic ...