Ch 18 – Electric Forces and Electric Fields
... Charge is quantized. Charge on a proton or electron is the smallest amount of free charge (e). Any charge greater than e will be of some integer multiple of e. Robert Millikan first demonstrated this with his famous oil drop experiment. Charges exert forces on other charges over a distance. Like ...
... Charge is quantized. Charge on a proton or electron is the smallest amount of free charge (e). Any charge greater than e will be of some integer multiple of e. Robert Millikan first demonstrated this with his famous oil drop experiment. Charges exert forces on other charges over a distance. Like ...
Momentum
... • The blue car catches up with the green car and bumps into it. • During the collision, the speed of each car changes. ...
... • The blue car catches up with the green car and bumps into it. • During the collision, the speed of each car changes. ...
Rotational Inertia and Newton`s Second Law
... • In linear motion, net force and mass determine the acceleration of an object. • For rotational motion, torque determines the rotational acceleration. • The rotational counterpart to mass is rotational inertia or moment of inertia. – Just as mass represents the resistance to a change in linear moti ...
... • In linear motion, net force and mass determine the acceleration of an object. • For rotational motion, torque determines the rotational acceleration. • The rotational counterpart to mass is rotational inertia or moment of inertia. – Just as mass represents the resistance to a change in linear moti ...
Chapter 9 Problems - University of Colorado Colorado Springs
... is this? Many people imagine that the ...
... is this? Many people imagine that the ...
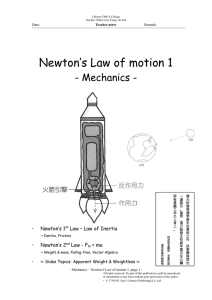
Newton`s Law of motion 1
... Gravitational mass is measured by such method, e.g. spring balance. Measuring the mass (inertia mass) Mass can be defined as the ‘ amount of matter’ in an object. But considering Newton’s 2nd Law of motion, m = FN / a, mass has a new meaning – “Inertia”. Inertia is the resistance of an object to a c ...
... Gravitational mass is measured by such method, e.g. spring balance. Measuring the mass (inertia mass) Mass can be defined as the ‘ amount of matter’ in an object. But considering Newton’s 2nd Law of motion, m = FN / a, mass has a new meaning – “Inertia”. Inertia is the resistance of an object to a c ...
Monday, Nov. 10, 2003
... Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let’s consider a two particle system where the two exert forces on each other. ...
... Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let’s consider a two particle system where the two exert forces on each other. ...
Lecture 7
... Kinematics + Vectors = Vector Kinematics Relative motion Projectile motion Newton’s Laws ...
... Kinematics + Vectors = Vector Kinematics Relative motion Projectile motion Newton’s Laws ...
Stacey Carpenter
... a difference how long you apply the force? Descartes (Need to check this.) took the equation from Newton's 2nd Law, F = ma, and looked at what would happen if the force was applied for a period of time. Ft = ?. Applying the force for a longer time will result in the same acceleration, but a greate ...
... a difference how long you apply the force? Descartes (Need to check this.) took the equation from Newton's 2nd Law, F = ma, and looked at what would happen if the force was applied for a period of time. Ft = ?. Applying the force for a longer time will result in the same acceleration, but a greate ...
Lesson 12 questions – Centripetal Force - science
... Newton’s law of gravitation applied to the situation in the diagram may be expressed as F = GM2/4R2 State what each of the symbols listed below represent F ……force of attraction between Masses/stars…………………………… G ……gravitational constant………………………………………… M ……mass of a star…………………………………………………… R ……radi ...
... Newton’s law of gravitation applied to the situation in the diagram may be expressed as F = GM2/4R2 State what each of the symbols listed below represent F ……force of attraction between Masses/stars…………………………… G ……gravitational constant………………………………………… M ……mass of a star…………………………………………………… R ……radi ...
Part III: Movement Analysis – Learning Outcomes
... The angular form of Newton’s first law - A rotating body will continue to turn about its axis of rotation with constant angular momentum unless an external force is exerted upon it. The angular form of Newton’s second law - The angular acceleration of a body is proportional to the torque causing it ...
... The angular form of Newton’s first law - A rotating body will continue to turn about its axis of rotation with constant angular momentum unless an external force is exerted upon it. The angular form of Newton’s second law - The angular acceleration of a body is proportional to the torque causing it ...
Roller Coaster Project Write Up
... the velocity of the marble. The sum of the GPE and the KE are only going to remain the same if there are no losses of energy throughout the ride. Losses of energy may be due to friction or other sources. Newton’s first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in ...
... the velocity of the marble. The sum of the GPE and the KE are only going to remain the same if there are no losses of energy throughout the ride. Losses of energy may be due to friction or other sources. Newton’s first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in ...