Performance Benchmark P
... Second Law describes what happens when there is a force. And lastly, his Third Law describes what happens when objects interacting. Newton’s Third Law states that for every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. This law is also known as the Law of Action-Reaction Pair. A force ...
... Second Law describes what happens when there is a force. And lastly, his Third Law describes what happens when objects interacting. Newton’s Third Law states that for every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. This law is also known as the Law of Action-Reaction Pair. A force ...
Dynamic Simulation of Non-penetrating Flexible Bodies
... as free motion. The model, which draws on the flexible-body model proposed by Witkin and Welch[9] and on the analytical contact force model for rigid bodies presented by Baraff[1,2], centers on the idea that flexible body simulation can be greatly simplified through the introduction of a suitable ge ...
... as free motion. The model, which draws on the flexible-body model proposed by Witkin and Welch[9] and on the analytical contact force model for rigid bodies presented by Baraff[1,2], centers on the idea that flexible body simulation can be greatly simplified through the introduction of a suitable ge ...
printer-friendly version
... Second Law describes what happens when there is a force. And lastly, his Third Law describes what happens when objects interacting. Newton’s Third Law states that for every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. This law is also known as the Law of Action-Reaction Pair. A force ...
... Second Law describes what happens when there is a force. And lastly, his Third Law describes what happens when objects interacting. Newton’s Third Law states that for every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. This law is also known as the Law of Action-Reaction Pair. A force ...
Document
... Shown to the right are two systems undergoing SHM. The vertical position represents displacement and the horizontal axis represents time. How are the two systems different? A) They have different periods B) They have different amplitudes C) They have different phase constants D) Only two of the abo ...
... Shown to the right are two systems undergoing SHM. The vertical position represents displacement and the horizontal axis represents time. How are the two systems different? A) They have different periods B) They have different amplitudes C) They have different phase constants D) Only two of the abo ...
Report 3082
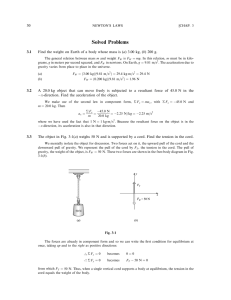
... averages for those sections. While this misrepresents the true values somewhat it gives a solid approximation of the effects of the wind and air densities in these sections. We also assumed that the only possible changes in the direction of the wind would be as Felix landed and that the speeds of th ...
... averages for those sections. While this misrepresents the true values somewhat it gives a solid approximation of the effects of the wind and air densities in these sections. We also assumed that the only possible changes in the direction of the wind would be as Felix landed and that the speeds of th ...
Momentum and Its Conservation
... accord with Newton’s 3rd Law. While the forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, the accelerations of the objects are not necessarily equal in magnitude. According to Newton's second law of motion, Bigger mass has smaller acceleration, smaller mass has bigger acceleration ...
... accord with Newton’s 3rd Law. While the forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, the accelerations of the objects are not necessarily equal in magnitude. According to Newton's second law of motion, Bigger mass has smaller acceleration, smaller mass has bigger acceleration ...
Mass on a plane with friction
... How fast will mass 2 be falling at the end of 3.0 seconds if released from rest? a = - 1.1 m/s2 (negative cuz mass 2 is falling) vi = 0 m/s t = 3.0 s vf = ? vf = vi + at vf = 0 m/s + (- 1.1 m/s2 )(3.0 s) vf = - 3.3 m/s ...
... How fast will mass 2 be falling at the end of 3.0 seconds if released from rest? a = - 1.1 m/s2 (negative cuz mass 2 is falling) vi = 0 m/s t = 3.0 s vf = ? vf = vi + at vf = 0 m/s + (- 1.1 m/s2 )(3.0 s) vf = - 3.3 m/s ...
6. Newton`s Laws of Motion.nb
... 6. Newton's Laws of Motion.nb rises upward) given by ay =Fy /M or since Fy = N + T - W ay = (N + T - W)/M 2. N + T - W < 0 in which case the acceleration is negative which is impossible since this means the mass goes downward through the table top. 3. N + T - W = 0 in which case the acceleration is ...
... 6. Newton's Laws of Motion.nb rises upward) given by ay =Fy /M or since Fy = N + T - W ay = (N + T - W)/M 2. N + T - W < 0 in which case the acceleration is negative which is impossible since this means the mass goes downward through the table top. 3. N + T - W = 0 in which case the acceleration is ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... Newton’s laws of force and motion 1. An object continues in a state of rest or in a state of motion at a constant speed along a straight line, unless compelled to change that state by a net force. (One object) 2. When a net external force acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration that results is ...
... Newton’s laws of force and motion 1. An object continues in a state of rest or in a state of motion at a constant speed along a straight line, unless compelled to change that state by a net force. (One object) 2. When a net external force acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration that results is ...
CE 530 Molecular Simulation
... • same algorithm, with same positions and forces, moves system backward in time ...
... • same algorithm, with same positions and forces, moves system backward in time ...
Physics Beyond 2000
... Angular displacement • After one complete cycle, angular displacement θ= 2π ...
... Angular displacement • After one complete cycle, angular displacement θ= 2π ...
conceptual physics ch.4
... Ans. Action - reaction refers to forces that are applied to different objects. Forces can only cancel each other out if they are applied to the same object. Extra: If the forces that act on a bullet and the recoiling gun from which it is fired are equal in magnitude, why do the bullet and gun have v ...
... Ans. Action - reaction refers to forces that are applied to different objects. Forces can only cancel each other out if they are applied to the same object. Extra: If the forces that act on a bullet and the recoiling gun from which it is fired are equal in magnitude, why do the bullet and gun have v ...
Old Exam - KFUPM Faculty List
... T041: Q7 A 1.0 kg particle is moving with a velocity of 16 m/s along the positive x direction while a 3.0 kg particle is moving with a velocity of 4.0 m/s along the positive y direction. Find the magnitude of their center of mass velocity. (Ans 5.0 m/s ) Q8 A 10 kg bomb initially at rest explodes, b ...
... T041: Q7 A 1.0 kg particle is moving with a velocity of 16 m/s along the positive x direction while a 3.0 kg particle is moving with a velocity of 4.0 m/s along the positive y direction. Find the magnitude of their center of mass velocity. (Ans 5.0 m/s ) Q8 A 10 kg bomb initially at rest explodes, b ...
LCP 5 Part II The Flight of Discovery
... Horwood, who is the CBS News Space Consultant at NASA. The NASA spread sheet provides detailed and authentic information about the prediction of the ascent of flight STS 119, and will be the 36th flight of Discovery, the 125th Shuttle flight to date. After several postponements, the Discovery was su ...
... Horwood, who is the CBS News Space Consultant at NASA. The NASA spread sheet provides detailed and authentic information about the prediction of the ascent of flight STS 119, and will be the 36th flight of Discovery, the 125th Shuttle flight to date. After several postponements, the Discovery was su ...