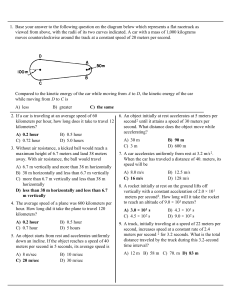
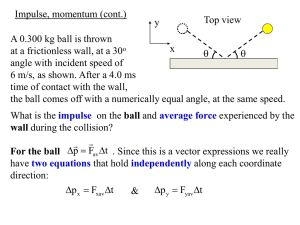
BALANCE PRINCIPLES
... where v is the spatial velocity of the motion. Show that this includes the transport theorem as a special case by choosing
... where v is the spatial velocity of the motion. Show that this includes the transport theorem as a special case by choosing
Chap8
... If the velocity changes over a time interval, the average velocity is not equal to the instantaneous velocity at any given instant. Similarly, the angular velocity calculated in this way is actually the average angular velocity over a time interval, t. Instantaneous angular velocity is equal to the ...
... If the velocity changes over a time interval, the average velocity is not equal to the instantaneous velocity at any given instant. Similarly, the angular velocity calculated in this way is actually the average angular velocity over a time interval, t. Instantaneous angular velocity is equal to the ...
posted
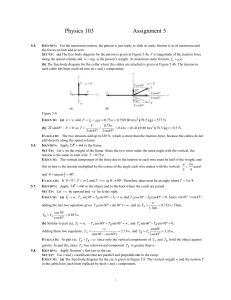
... distance using a constant acceleration equation. The friction force is f k k mg , just as in part (a). SET UP: The free-body diagram is sketched in Figure 5.27b. ...
... distance using a constant acceleration equation. The friction force is f k k mg , just as in part (a). SET UP: The free-body diagram is sketched in Figure 5.27b. ...
Force and Motion Force Classifying Forces
... Newton’s Laws of Motion 1) An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity (that is, in a straight line with constant speed) unless it experiences a net external force 2) The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force act ...
... Newton’s Laws of Motion 1) An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity (that is, in a straight line with constant speed) unless it experiences a net external force 2) The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force act ...
AP free response for last week
... that the electric potential is zero at x = infinity, with the origin 0 of the x-axis at the center of the ring. a. What is the electric potential at a point P on the x-axis? b. Where along the x-axis is the electric potential the greatest? Justify your answer. c. What is the magnitude and direction ...
... that the electric potential is zero at x = infinity, with the origin 0 of the x-axis at the center of the ring. a. What is the electric potential at a point P on the x-axis? b. Where along the x-axis is the electric potential the greatest? Justify your answer. c. What is the magnitude and direction ...
MOMENTUM!
... Ball B deflects much less than ball A when the same force is applied because ball B had a greater initial momentum. ...
... Ball B deflects much less than ball A when the same force is applied because ball B had a greater initial momentum. ...
AP Physics Review - stoweschools.com
... Weight = Force due to Gravity = product of mass and acceleration due to gravity Universal Gravitational Force is directly proportional to the universal gravitational constant, the mass of one object, the mass of another object and inversely proportional to the distance between the center of the obje ...
... Weight = Force due to Gravity = product of mass and acceleration due to gravity Universal Gravitational Force is directly proportional to the universal gravitational constant, the mass of one object, the mass of another object and inversely proportional to the distance between the center of the obje ...
... 42. When Earth and the Moon are separated by a distance of 3.84 × 108 meters, the magnitude of the gravitational force of attraction between them is 2.0 × 1020 newtons. What would be the magnitude of this gravitational force of attraction if Earth and the Moon were separated by a distance of 1.92 × ...
Ch11 - Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum
... taking the cross product of the particle's position vector and the force vector, in either unit-vector notation or magnitude-angle notation. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... taking the cross product of the particle's position vector and the force vector, in either unit-vector notation or magnitude-angle notation. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
phys34210_13 - University of Surrey
... – Co-author of >200 papers in nuclear physics; supervised 25 PhD students so far + 100 Masters. – Led RISING and PreSPEC projects (major nuclear physics research project at GSI, Germany). – Married (to a nurse), 4 kids. – Understands gridiron, baseball, (ice) hockey etc., regular visitor to US (and ...
... – Co-author of >200 papers in nuclear physics; supervised 25 PhD students so far + 100 Masters. – Led RISING and PreSPEC projects (major nuclear physics research project at GSI, Germany). – Married (to a nurse), 4 kids. – Understands gridiron, baseball, (ice) hockey etc., regular visitor to US (and ...
Angular Momentum
... Conceptual Question 4c Two children are playing with a roll of paper towels. One child holds the roll between the index fingers of her hands so that it is free to rotate, and the second child pulls at constant speed on the free end of the paper towels. As the child pulls the paper towels, the radiu ...
... Conceptual Question 4c Two children are playing with a roll of paper towels. One child holds the roll between the index fingers of her hands so that it is free to rotate, and the second child pulls at constant speed on the free end of the paper towels. As the child pulls the paper towels, the radiu ...
Chapter 7
... The principle of conservation of momentum states when no external forces act on a system consisting of two objects that collide with each other, the total momentum of the system remains constant in time • Specifically, the total momentum before the collision will equal the total momentum after the c ...
... The principle of conservation of momentum states when no external forces act on a system consisting of two objects that collide with each other, the total momentum of the system remains constant in time • Specifically, the total momentum before the collision will equal the total momentum after the c ...
here
... bow (particle 1) and the arrow (particle 2) There are no external forces in the x-direction, so it is isolated in terms of momentum in the xdirection Total momentum before releasing the arrow is 0 The total momentum after releasing the arrow is ...
... bow (particle 1) and the arrow (particle 2) There are no external forces in the x-direction, so it is isolated in terms of momentum in the xdirection Total momentum before releasing the arrow is 0 The total momentum after releasing the arrow is ...
Part B: Force, Acceleration and Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... g. A contact force results from the physical contact between two objects. h. A field force results from the action of two objects which are positioned some distance away. i. Spring and tension forces are examples of field forces. j. A force is a vector quantity; there is always a direction associate ...
... g. A contact force results from the physical contact between two objects. h. A field force results from the action of two objects which are positioned some distance away. i. Spring and tension forces are examples of field forces. j. A force is a vector quantity; there is always a direction associate ...