AOSS 321, Fall 2006 Earth Systems Dynamics 10/9/2006
... • Horizontal component does not need to be considered when we consider a coordinate system tangent to the Earth’s surface, because the Earth has bulged to compensate for this force. • Hence, centrifugal force does not appear EXPLICITLY in the equations. ...
... • Horizontal component does not need to be considered when we consider a coordinate system tangent to the Earth’s surface, because the Earth has bulged to compensate for this force. • Hence, centrifugal force does not appear EXPLICITLY in the equations. ...
Devil physics The baddest class on campus IB Physics
... the observed free-fall acceleration of the object (in meters per second squared) is numerically equal to the magnitude of the gravitational field (in newtons/kilogram) at that location. ...
... the observed free-fall acceleration of the object (in meters per second squared) is numerically equal to the magnitude of the gravitational field (in newtons/kilogram) at that location. ...
Interpreting Graphs
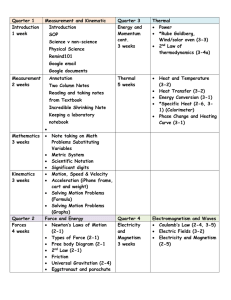
... Define acceleration in terms of position, velocity, and time. Graph accelerated motion on position; velocity, and acceleration graphs. Solving motion problems algebraically To be able to solve for an unknown in algebraic equations, using a systematic problem solving technique. Solving motion p ...
... Define acceleration in terms of position, velocity, and time. Graph accelerated motion on position; velocity, and acceleration graphs. Solving motion problems algebraically To be able to solve for an unknown in algebraic equations, using a systematic problem solving technique. Solving motion p ...
Physics of Motion Lecturer: Mauro Ferreira
... 2nd Newton’s law tells us that If the magnitude of F is proportional to the mass of the object, the acceleration due to the force F will be the same, whatever the object. This is what occurs in the For example, the mass M case of the gravitational of an elephant is many force. The weight is given t ...
... 2nd Newton’s law tells us that If the magnitude of F is proportional to the mass of the object, the acceleration due to the force F will be the same, whatever the object. This is what occurs in the For example, the mass M case of the gravitational of an elephant is many force. The weight is given t ...
Ch33
... How does torque affect angular momentum, in general? • consider a wheel (a hoop, say), that is rotating with M, R d L a large angular velocity (and hence a large angular O momentum • the wheel is supported at one point only at the end of its axis a distance d from wheel’s CM • put an origin at the ...
... How does torque affect angular momentum, in general? • consider a wheel (a hoop, say), that is rotating with M, R d L a large angular velocity (and hence a large angular O momentum • the wheel is supported at one point only at the end of its axis a distance d from wheel’s CM • put an origin at the ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... Example: Rotating Rod A uniform rod of length L=0.5 m and mass m=1 kg is free to rotate ...
... Example: Rotating Rod A uniform rod of length L=0.5 m and mass m=1 kg is free to rotate ...
GRADE 12A: Physics 4
... Choose one point on the circumference of the circle and use trigonometry to show students that the displacement in the x direction is x = r cos ( t ). Draw a velocity vector at the same point and show that its x component is v = r sin ( t ). Draw a vector representing the centripetal acceleratio ...
... Choose one point on the circumference of the circle and use trigonometry to show students that the displacement in the x direction is x = r cos ( t ). Draw a velocity vector at the same point and show that its x component is v = r sin ( t ). Draw a vector representing the centripetal acceleratio ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
Chapter 5 Mutual actions in machinery elements
... • Friction Definition : Friction is the resistance to motion occurring when a body slides on another; • Friction Direction : This resistance action is opposite to the relative motion; • Classification : static friction and dynamic friction(Kinetic friction); • The static friction force: opposing a m ...
... • Friction Definition : Friction is the resistance to motion occurring when a body slides on another; • Friction Direction : This resistance action is opposite to the relative motion; • Classification : static friction and dynamic friction(Kinetic friction); • The static friction force: opposing a m ...
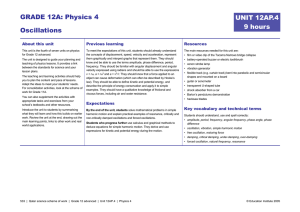
oscillations
... motion and orbital motion of planets in the solar system. In these cases, the motion is repeated after a certain interval of time, that is, it is periodic. In your childhood you must have enjoyed rocking in a cradle or swinging on a swing. Both these motions are repetitive in nature but different fr ...
... motion and orbital motion of planets in the solar system. In these cases, the motion is repeated after a certain interval of time, that is, it is periodic. In your childhood you must have enjoyed rocking in a cradle or swinging on a swing. Both these motions are repetitive in nature but different fr ...