Export To Word
... acceleration. Create and interpret graphs of 1-dimensional motion, such as position versus time, distance versus time, speed versus time, velocity versus time, and acceleration versus time where acceleration is constant. Florida Standards Connections: MAFS.912.N-VM.1.3 (+) Solve problems involving v ...
... acceleration. Create and interpret graphs of 1-dimensional motion, such as position versus time, distance versus time, speed versus time, velocity versus time, and acceleration versus time where acceleration is constant. Florida Standards Connections: MAFS.912.N-VM.1.3 (+) Solve problems involving v ...
ch6 momentum
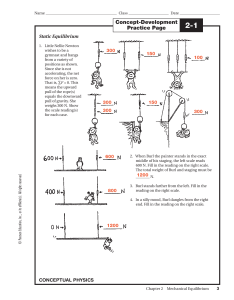
... The time rate of change of momentum of an object is equal to the ____________ acting on the object Net Force ...
... The time rate of change of momentum of an object is equal to the ____________ acting on the object Net Force ...
Objective Assignment - PRADEEP KSHETRAPAL PHYSICS
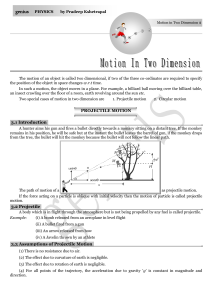
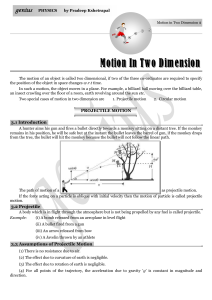
... (1) The motion of a projectile is a two-dimensional motion. So, it can be discussed in two parts. Horizontal motion and vertical motion. These two motions take place independent of each other. This is called the principle of physical independence of motions. (2) The velocity of the particle can be r ...
... (1) The motion of a projectile is a two-dimensional motion. So, it can be discussed in two parts. Horizontal motion and vertical motion. These two motions take place independent of each other. This is called the principle of physical independence of motions. (2) The velocity of the particle can be r ...
5.7 Some Applications of Newton`s Laws
... motion with a constant velocity (that is, with a constant speed in a straight line). In simpler terms, we can say that when no force acts on an object, the acceleration of the object is zero. If nothing acts to change the object’s motion, then its velocity does not change. From the first law, we con ...
... motion with a constant velocity (that is, with a constant speed in a straight line). In simpler terms, we can say that when no force acts on an object, the acceleration of the object is zero. If nothing acts to change the object’s motion, then its velocity does not change. From the first law, we con ...
kg m/s - kcpe-kcse
... tiles used for playground When a child falls to the floor its flooring. Explain how these can reduce injury to children. momentum changes from a high value to zero. ...
... tiles used for playground When a child falls to the floor its flooring. Explain how these can reduce injury to children. momentum changes from a high value to zero. ...
Torque Analyses of a Sliding Ladder
... The problem of a ladder that slides without friction while touching a floor and wall is often used to illustrate Lagrange’s method for deducing the equation of motion of a mechanical system. Suppose the ladder has mass m, length 2l, and makes angle θ to the vertical. Deduce the equation of motion via ...
... The problem of a ladder that slides without friction while touching a floor and wall is often used to illustrate Lagrange’s method for deducing the equation of motion of a mechanical system. Suppose the ladder has mass m, length 2l, and makes angle θ to the vertical. Deduce the equation of motion via ...
Lecture Notes 12: Lienard-Wiechert Retarded Potentials for Moving Point Charge, Retarded Electric and Magnetic Fields Associated with Moving Point Charge
... {However, it is not due to special / general relativity (yet)!!} Consider a long train moving towards a stationary observer. Due to the finite propagation time of EM signals, the train actually appears (a little) longer than it really is! (If c ≈ 10 m/s rather than 3 × 108 m/s, this motional effect ...
... {However, it is not due to special / general relativity (yet)!!} Consider a long train moving towards a stationary observer. Due to the finite propagation time of EM signals, the train actually appears (a little) longer than it really is! (If c ≈ 10 m/s rather than 3 × 108 m/s, this motional effect ...
P3 Booklet FINAL - Highfields School, Wolverhampton
... Harness worn by occupants of motor vehicles to prevent them from being thrown about in a collision Protect occupants in the event of a crash e.g. crumple zones, air bags, seatbelts Bars in the side of a car to lessen the amount of bodywork distortion inside the car How fast an object travels: speed ...
... Harness worn by occupants of motor vehicles to prevent them from being thrown about in a collision Protect occupants in the event of a crash e.g. crumple zones, air bags, seatbelts Bars in the side of a car to lessen the amount of bodywork distortion inside the car How fast an object travels: speed ...
IGCSE-14-Momentum
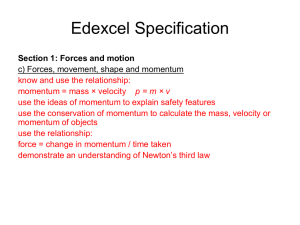
... car: = 1000 kg x +20 m/s = +20000 kg m/s lorry: = 2000 kg x -16 m/s = -32000 kg m/s total initial momentum = -12000 kg m/s Momentum is conserved in the collision so total momentum after collision = -12000 kg m/s total momentum = total mass x velocity -12000 kg m/s = 3000 kg x v -12000 ÷ 3000 = v com ...
... car: = 1000 kg x +20 m/s = +20000 kg m/s lorry: = 2000 kg x -16 m/s = -32000 kg m/s total initial momentum = -12000 kg m/s Momentum is conserved in the collision so total momentum after collision = -12000 kg m/s total momentum = total mass x velocity -12000 kg m/s = 3000 kg x v -12000 ÷ 3000 = v com ...
Introduction to Modern Physics PHYX 2710
... • Vectors: Many measurements in physics require a knowledge of the magnitude and direction of quantity. ...
... • Vectors: Many measurements in physics require a knowledge of the magnitude and direction of quantity. ...