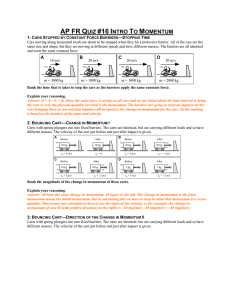
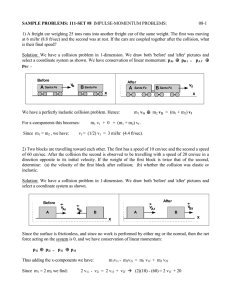
Circular Motion HW-1
... is doubled, or (b) m is doubled? 2. A work W0 is required to stretch a certain spring 2 cm from its equilibrium position. (a) How much work is required to stretch the spring 1 cm from equilibrium? (b) Suppose the spring is already stretched 2 cm from equilibrium. How much additional work is required ...
... is doubled, or (b) m is doubled? 2. A work W0 is required to stretch a certain spring 2 cm from its equilibrium position. (a) How much work is required to stretch the spring 1 cm from equilibrium? (b) Suppose the spring is already stretched 2 cm from equilibrium. How much additional work is required ...
Physics 100 prac exam2
... 11. If two bicyclists move around a circular track of radius 100 m, at the same speed, 10 m/s, but in opposite directions, then A. they have equal size accelerations, 1 m/s2. B. they have opposite accelerations, +1 m/s2 and -1 m/s2. C. one has centripetal acceleration of 1 m/s2 and the other has cen ...
... 11. If two bicyclists move around a circular track of radius 100 m, at the same speed, 10 m/s, but in opposite directions, then A. they have equal size accelerations, 1 m/s2. B. they have opposite accelerations, +1 m/s2 and -1 m/s2. C. one has centripetal acceleration of 1 m/s2 and the other has cen ...
Physicsskiing3
... Physics of Alpine Skiing Skiing is enjoyed by millions of people every year. Skiers enjoy moving fast down steep slopes but seldom stop to think about what is making them move. Skiing is an example of an everyday activity affected by elements of physics. Many aspects of skiing depend fully on physic ...
... Physics of Alpine Skiing Skiing is enjoyed by millions of people every year. Skiers enjoy moving fast down steep slopes but seldom stop to think about what is making them move. Skiing is an example of an everyday activity affected by elements of physics. Many aspects of skiing depend fully on physic ...
Document
... When the ball is displaced from its equilibrium position and released, it moves in simple harmonic motion. Consider the relationship between the angular frequency, the mass, and the spring constant given in the text. Which one of the following statements concerning that relationship is true? a) Incr ...
... When the ball is displaced from its equilibrium position and released, it moves in simple harmonic motion. Consider the relationship between the angular frequency, the mass, and the spring constant given in the text. Which one of the following statements concerning that relationship is true? a) Incr ...
Forces
... “A body acted on by zero net force moves with constant velocity and zero acceleration.” ...
... “A body acted on by zero net force moves with constant velocity and zero acceleration.” ...
3. Higher Our Dynamic Universe Questions [ppt 8MB]
... Two cyclists X and Y choose different routes to travel from point A to point B some distance away. Cyclist X travels 10km due East followed by 14km on a bearing of 210° in 90 minutes. Cyclist Y travels directly from A to B ‘as then crow flies’ and reaches point B at the same time as cyclist X. Calcu ...
... Two cyclists X and Y choose different routes to travel from point A to point B some distance away. Cyclist X travels 10km due East followed by 14km on a bearing of 210° in 90 minutes. Cyclist Y travels directly from A to B ‘as then crow flies’ and reaches point B at the same time as cyclist X. Calcu ...
9.5 Centrifugal Force in a Rotating Reference Frame
... The record rotates around its axis while the bug sitting at its edge revolves around the same axis. ...
... The record rotates around its axis while the bug sitting at its edge revolves around the same axis. ...
Ch 6 - Momentum
... A 1400kg car moving westward with a velocity of 15 m/s collides with a utility pole and is brought to rest in 0.30s. Find the magnitude of the force exerted on the car during the collision. ...
... A 1400kg car moving westward with a velocity of 15 m/s collides with a utility pole and is brought to rest in 0.30s. Find the magnitude of the force exerted on the car during the collision. ...
Motion, Forces, and Newton`s Laws
... C. Velocity 1. The speed and direction of an object’s motion is the velocity of the object. 2. Velocity is often represented by using a(n) arrow. a. The total length of the arrow shows speed. b. The direction of the arrow shows the direction the object moves. 3. When an object’s speed and direction ...
... C. Velocity 1. The speed and direction of an object’s motion is the velocity of the object. 2. Velocity is often represented by using a(n) arrow. a. The total length of the arrow shows speed. b. The direction of the arrow shows the direction the object moves. 3. When an object’s speed and direction ...
Momentum PPT
... If you throw a rock forward from a skateboard, you will move backward in response. ...
... If you throw a rock forward from a skateboard, you will move backward in response. ...
Essential Learning Outcomes (ELOs) Advanced Placement Physics (B & C)
... [B/C] Add or subtract velocity vectors in order to calculate the velocity change or average acceleration of a particle, or the velocity of one particle relative to another. b. ...
... [B/C] Add or subtract velocity vectors in order to calculate the velocity change or average acceleration of a particle, or the velocity of one particle relative to another. b. ...









![3. Higher Our Dynamic Universe Questions [ppt 8MB]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001620458_1-64549958c5de6c7c6c0be1e1ccb97e89-300x300.png)