Orbits - GCSE Science Revision
... Two cars are in a head-on collision. Explain the forces acting on each car that bring them to a stop. ...
... Two cars are in a head-on collision. Explain the forces acting on each car that bring them to a stop. ...
Questions and Problems
... force of friction acts on the disk as it rolls downhill. For both objects the moment of inertia I remains unchanged (the objects don’t change shape) and the angular velocity vz increases, so Lz = Ivz increases. Conservation laws are great when they apply, but remember that they do not apply in all ...
... force of friction acts on the disk as it rolls downhill. For both objects the moment of inertia I remains unchanged (the objects don’t change shape) and the angular velocity vz increases, so Lz = Ivz increases. Conservation laws are great when they apply, but remember that they do not apply in all ...
Met 61: Dynamics
... where is the viscosity coefficient = 1.46 x 10-5 m2 s-1. 4. Apparent (noninertial) forces Newton’s first law of motion states that mass of uniform motion with respect to a coordinate system fixed in space will remain in uniform motion in the absence of any other forces. This is inertial motion, wh ...
... where is the viscosity coefficient = 1.46 x 10-5 m2 s-1. 4. Apparent (noninertial) forces Newton’s first law of motion states that mass of uniform motion with respect to a coordinate system fixed in space will remain in uniform motion in the absence of any other forces. This is inertial motion, wh ...
Dynamics
... 12) Recall and solve problems using the relationship F = ma, appreciating that acceleration and force are always in the same direction. 13) Apply the relationship between resultant force, mass and acceleration to new situations or to solve related problems. 14) Describe the motion of bodies with con ...
... 12) Recall and solve problems using the relationship F = ma, appreciating that acceleration and force are always in the same direction. 13) Apply the relationship between resultant force, mass and acceleration to new situations or to solve related problems. 14) Describe the motion of bodies with con ...
Descriptive Essay: The Night Market
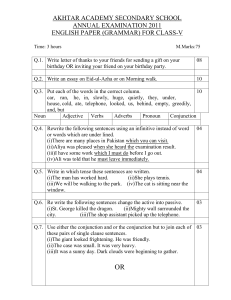
... (i)a word which describes a noun (ii)a word used to show actions (iii)a word used instead of noun An adverb is (i)a word which describes how action are done (ii)a word which is added to the end of the verb (iii)the name of a place or thing A conjunction is a word (i)shown by the sign (ii)a word whic ...
... (i)a word which describes a noun (ii)a word used to show actions (iii)a word used instead of noun An adverb is (i)a word which describes how action are done (ii)a word which is added to the end of the verb (iii)the name of a place or thing A conjunction is a word (i)shown by the sign (ii)a word whic ...
Physics, Mr - TeacherWeb
... 1. A ball is twirled in a circle at the end of a 0.75 m circle. It takes 1.05 s for the ball to complete a single trip around the circle. What is the radius of the motion? _________ Circumference? _____________ Linear velocity: _______________ rpm: ___________________ 2. In circular motion, how does ...
... 1. A ball is twirled in a circle at the end of a 0.75 m circle. It takes 1.05 s for the ball to complete a single trip around the circle. What is the radius of the motion? _________ Circumference? _____________ Linear velocity: _______________ rpm: ___________________ 2. In circular motion, how does ...
Devil physics The baddest class on campus IB Physics
... described through the mathematics of simple harmonic motion. ...
... described through the mathematics of simple harmonic motion. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... a. A force is a push or pull exerted upon an object which results from the interaction of that object with its environment. b. Bubba approaches Billie and gives him a swift shove. Timid little Billie keeps his hands in his pocket during this interaction. Subsequently, while Bubba places a force upon ...
... a. A force is a push or pull exerted upon an object which results from the interaction of that object with its environment. b. Bubba approaches Billie and gives him a swift shove. Timid little Billie keeps his hands in his pocket during this interaction. Subsequently, while Bubba places a force upon ...
SECOND MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS
... Calculate the magnitude of F such that the block moves with a constant acceleration down the plane of 1.25 m/s 2. Use the next page with this sam e problem number for that calculation. A rock is dropped from rest on the moon. Calculate its speed after it has fallen 175 m. On a small planet a rock, w ...
... Calculate the magnitude of F such that the block moves with a constant acceleration down the plane of 1.25 m/s 2. Use the next page with this sam e problem number for that calculation. A rock is dropped from rest on the moon. Calculate its speed after it has fallen 175 m. On a small planet a rock, w ...
Motion and Forces Powerpoint
... • Motion data can be plotted as points on a graph. The line connecting the points shows changes in the motion of the object. • The line on a distance-time graph allows you to calculates an object’s speed at any moment in time. A speed-time graph helps you understand both how fast an object moves and ...
... • Motion data can be plotted as points on a graph. The line connecting the points shows changes in the motion of the object. • The line on a distance-time graph allows you to calculates an object’s speed at any moment in time. A speed-time graph helps you understand both how fast an object moves and ...