Animal_Physiology_Prezi_Assignmen
... 7) Pay very close attention to the section of the Prezi titled: From Air to Blood and Back. It is extremely important that you understand how O2 and CO2 are transported in the blood. A) Oxygen Transport in the Blood: a. Remember, erythrocytes or red blood cells carry LOTS of hemoglobin and hemoglobi ...
... 7) Pay very close attention to the section of the Prezi titled: From Air to Blood and Back. It is extremely important that you understand how O2 and CO2 are transported in the blood. A) Oxygen Transport in the Blood: a. Remember, erythrocytes or red blood cells carry LOTS of hemoglobin and hemoglobi ...
Abiotic- a non living thing
... bird sees, the bird forever sees as its mother. Habituation- becoming so used to something that you cease to be bothered by it or notice it. Ex. not noticing your ceiling fan anymore or a train that passes by your house Classical conditioning- this is making unrelated things become associated. Pavlo ...
... bird sees, the bird forever sees as its mother. Habituation- becoming so used to something that you cease to be bothered by it or notice it. Ex. not noticing your ceiling fan anymore or a train that passes by your house Classical conditioning- this is making unrelated things become associated. Pavlo ...
GOOD BUDDIES - cypresswoodsbiology
... Community Interactions • Community interactions, such as competition, predation, and various forms of symbiosis, can powerfully affect an ecosystem. ...
... Community Interactions • Community interactions, such as competition, predation, and various forms of symbiosis, can powerfully affect an ecosystem. ...
Modern Classification
... – At that point “modern,” science was beginning to realize that system was too simplistic – Too often names for species varied from location to location and did not accurately describe the organism. ...
... – At that point “modern,” science was beginning to realize that system was too simplistic – Too often names for species varied from location to location and did not accurately describe the organism. ...
Vocabulary List: NatureBridge at Santa Monica Mountains and
... Abiotic – Nonliving, as in abiotic factor, which is a nonliving physical and chemical attribute of a system, for example light, temperature, wind patterns, rocks, soil, pH, pressure, etc. in an environment. Autotroph – any organism capable of self-nourishment by using inorganic materials as a source ...
... Abiotic – Nonliving, as in abiotic factor, which is a nonliving physical and chemical attribute of a system, for example light, temperature, wind patterns, rocks, soil, pH, pressure, etc. in an environment. Autotroph – any organism capable of self-nourishment by using inorganic materials as a source ...
Fish - wenjinyezoo
... The most anterior parts of a fish's brain are the olfactory bulbs. These are connected to the two lobes of the cerebrum by stalks. In fish the cerebrum is primarily involved with the sense of smell. It also seems to control behaviors such as taking care of the young and exploring the environment. Th ...
... The most anterior parts of a fish's brain are the olfactory bulbs. These are connected to the two lobes of the cerebrum by stalks. In fish the cerebrum is primarily involved with the sense of smell. It also seems to control behaviors such as taking care of the young and exploring the environment. Th ...
OUTDOOR SCIENCE SCHOOL VOC (#1 – Test)
... (a) fruit forms when pollen fertilizes the egg; from the fertilized egg a seed forms and the ovary around the seed swells and ripens (b) “2” types of fruit: “fleshy” (e.g. apple); “dry” (e.g. nuts) (c) the purpose of fruit is for the protection and dispersal of the seeds 54. (5 Pg 34) CARRYING CAPAC ...
... (a) fruit forms when pollen fertilizes the egg; from the fertilized egg a seed forms and the ovary around the seed swells and ripens (b) “2” types of fruit: “fleshy” (e.g. apple); “dry” (e.g. nuts) (c) the purpose of fruit is for the protection and dispersal of the seeds 54. (5 Pg 34) CARRYING CAPAC ...
ch04_sec1
... ecosystems, while most of the energy of an ecosystem comes from the sun. • If one part of the ecosystem is destroyed or changes, the entire system will be affected. ...
... ecosystems, while most of the energy of an ecosystem comes from the sun. • If one part of the ecosystem is destroyed or changes, the entire system will be affected. ...
The Animal Kingdom
... 97% of animals are invertebrates Many different types of invertebrates: Sponges, Cnidarians, Worms, Echinoderms, Mollusks, Arthropods. ...
... 97% of animals are invertebrates Many different types of invertebrates: Sponges, Cnidarians, Worms, Echinoderms, Mollusks, Arthropods. ...
Nervous system: Detects information from the environment
... Protects the body's internal living tissues and organs against: invasion by infectious organisms dehydration abrupt changes in temperature Disposes of waste materials Contains receptors for touch, pressure, pain, heat, and cold. Stores water and fat. Provides shape and support Allows you to move Pro ...
... Protects the body's internal living tissues and organs against: invasion by infectious organisms dehydration abrupt changes in temperature Disposes of waste materials Contains receptors for touch, pressure, pain, heat, and cold. Stores water and fat. Provides shape and support Allows you to move Pro ...
1 - Holy Family School
... that protect the body organs and give shape and support A body system made of muscles that contract and relax to move body parts ...
... that protect the body organs and give shape and support A body system made of muscles that contract and relax to move body parts ...
Life Science Second Nine Weeks Exam Study Guide Chapters 7
... ____ 31. In order, what are the three levels of classification in addition to kingdom, family, genus, and species? a. phylum, order, class c. phylum, class, order b. class, order, phylum d. class, order, genera ____ 32. What can you find by working through the statements in a dichotomous key? a. the ...
... ____ 31. In order, what are the three levels of classification in addition to kingdom, family, genus, and species? a. phylum, order, class c. phylum, class, order b. class, order, phylum d. class, order, genera ____ 32. What can you find by working through the statements in a dichotomous key? a. the ...
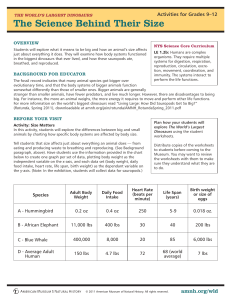
The World`s Largest Dinosaurs: Activities for Grades 9-12
... natural selection favoring large size. An exception is the hummingbird, the smallest bird and living dinosaur.) • Are the individual cells in the body of a big animal the same size as those in a small animal? (Answer: Yes, it’s just that big animals have many more cells. The amount of energy require ...
... natural selection favoring large size. An exception is the hummingbird, the smallest bird and living dinosaur.) • Are the individual cells in the body of a big animal the same size as those in a small animal? (Answer: Yes, it’s just that big animals have many more cells. The amount of energy require ...
Basal Metabolic Rate
... in the size and structure of surfaces involved with nutrient uptake, waste removal, and exchange of respiratory gases, and by combinations of any of these changes. Thus, rather than proposing an explanation based on a physical theory, this empirical “evolutionary” explanation implies that the simpli ...
... in the size and structure of surfaces involved with nutrient uptake, waste removal, and exchange of respiratory gases, and by combinations of any of these changes. Thus, rather than proposing an explanation based on a physical theory, this empirical “evolutionary” explanation implies that the simpli ...
interactions in the ecosystem
... Ex: Wings on a bee, a bird and a bat. The insect wing, bird wing and mammal wing all serve the same purpose but are very different on each organism. Sharks (fish) and dolphins (mammals) look similar, both have fins, but their bodies are very different in structure. ...
... Ex: Wings on a bee, a bird and a bat. The insect wing, bird wing and mammal wing all serve the same purpose but are very different on each organism. Sharks (fish) and dolphins (mammals) look similar, both have fins, but their bodies are very different in structure. ...
Life Science Reference Charts
... function similarly in all organisms. need energy, which animal and plant cells get from cellular respiration. make waste that moves across the cell and out the cell membrane. divide to cause growth and development of the organism. ALL organisms need energy, which animals get by eating and ...
... function similarly in all organisms. need energy, which animal and plant cells get from cellular respiration. make waste that moves across the cell and out the cell membrane. divide to cause growth and development of the organism. ALL organisms need energy, which animals get by eating and ...
Ecology notes - Sterlingmontessoriscience
... Ecology specifically means: The study of interactions between organisms and the nonliving components of their environment. ...
... Ecology specifically means: The study of interactions between organisms and the nonliving components of their environment. ...
SMART Chapter 2.5.notebook
... Ecologists use three different types of ecological pyramids to illustrate ecosystems: ...
... Ecologists use three different types of ecological pyramids to illustrate ecosystems: ...
Arthropod Notes - Lake Stevens High School / Overview
... Skin glands digest inner part of exoskeleton. Other glands make a new skeleton Animal sheds old exoskeleton. While the new exoskeleton is soft, the animal fills with air or fluid to allow room for growth before skeleton hardens. ...
... Skin glands digest inner part of exoskeleton. Other glands make a new skeleton Animal sheds old exoskeleton. While the new exoskeleton is soft, the animal fills with air or fluid to allow room for growth before skeleton hardens. ...
What Is an Animal?
... • A parasite is a type of symbiont that lives within or on another organism, the host. • The parasite feeds on the host, harming it. ...
... • A parasite is a type of symbiont that lives within or on another organism, the host. • The parasite feeds on the host, harming it. ...
Name Answers MOD _____ Living Environment Benchmark Review
... 13. Which system in an animal is most closely related to the vascular system in a plant? circulatory 14. Mitosis allows organisms (plants and animals) to complete what 2 life processes? A. reproduction B. growth and development (repair tissues) 15. There are many parts of a microscope. Which part is ...
... 13. Which system in an animal is most closely related to the vascular system in a plant? circulatory 14. Mitosis allows organisms (plants and animals) to complete what 2 life processes? A. reproduction B. growth and development (repair tissues) 15. There are many parts of a microscope. Which part is ...
Symbiotic Relationships
... • Every living thing is made up of one or more cells • Living things sense and respond to change • Living things have DNA • Living things reproduce • Living things use energy • Living things grow and develop ...
... • Every living thing is made up of one or more cells • Living things sense and respond to change • Living things have DNA • Living things reproduce • Living things use energy • Living things grow and develop ...