life webs practice test with answers
... D) Tapeworms in your stomach are an example of _______________ because they steal nutrients from your body. E) Fish that swim behind a shark and eat its leftovers is an example of _________________. F) __________________ occurs when two species are trying to use the same resource such as fish. 3) Fo ...
... D) Tapeworms in your stomach are an example of _______________ because they steal nutrients from your body. E) Fish that swim behind a shark and eat its leftovers is an example of _________________. F) __________________ occurs when two species are trying to use the same resource such as fish. 3) Fo ...
Diversity if Life Jeopardy Questions
... 5 The diversity of life increases as these two factors increase. HUMIDITY AND TEMPERATURE. 1 Plants are not found in deep ocean areas because of a lack of this. LIGHT 2 85% of all plants on Earth are found here. OCEAN 3 More than 20% of all known mammalian species are this animal. BAT 3 Homeostasis ...
... 5 The diversity of life increases as these two factors increase. HUMIDITY AND TEMPERATURE. 1 Plants are not found in deep ocean areas because of a lack of this. LIGHT 2 85% of all plants on Earth are found here. OCEAN 3 More than 20% of all known mammalian species are this animal. BAT 3 Homeostasis ...
Organism Interactions Limit Population Size Organism Interactions
... (ADD) -- Death rate (or mortality rate)— number of deaths in a period of time (SUBTRACTS) ...
... (ADD) -- Death rate (or mortality rate)— number of deaths in a period of time (SUBTRACTS) ...
Circulatory systems in animals
... An open circulatory system consists of a dorsal tubular heart(s) that, when it contracts, forces the fluid out of openended blood vessels This fluid flows through the spaces in the body and bathes the tissues and organs before returning through holes (ostia) to the heart. The fluid moves at low pres ...
... An open circulatory system consists of a dorsal tubular heart(s) that, when it contracts, forces the fluid out of openended blood vessels This fluid flows through the spaces in the body and bathes the tissues and organs before returning through holes (ostia) to the heart. The fluid moves at low pres ...
Biological Themes Biology: the science of living organisms and the
... Ecology: the study of the relationship between organisms and their environments Interdependence Science and Society Knowledge from biological science can be applied to specific problems in society to improve human life. How biological knowledge should be used involves decisions b ...
... Ecology: the study of the relationship between organisms and their environments Interdependence Science and Society Knowledge from biological science can be applied to specific problems in society to improve human life. How biological knowledge should be used involves decisions b ...
The human body - Channel 4 Learning
... Lesson 19 Unit of study Unit 2 Science for society The human body Resources Human body showing circulatory and respiratory system Aim of lesson To know how the circulatory and respiratory system works in the human body. Activity ...
... Lesson 19 Unit of study Unit 2 Science for society The human body Resources Human body showing circulatory and respiratory system Aim of lesson To know how the circulatory and respiratory system works in the human body. Activity ...
Final Review #1
... 47.What are the four types of swimming locomotion? Describe? Carangiform-front half body rigid, back half moves Ostraciiform-only caudal fin moves Appendicular-appendages move angulliform- most of body used 48.What are the three types of instability? Describe. Roll- move side to side Pitch-up and do ...
... 47.What are the four types of swimming locomotion? Describe? Carangiform-front half body rigid, back half moves Ostraciiform-only caudal fin moves Appendicular-appendages move angulliform- most of body used 48.What are the three types of instability? Describe. Roll- move side to side Pitch-up and do ...
Worksheet 5
... 3. Describe, with examples, how biotic and abiotic factors may affect the distribution of organisms. 4. List the four abiotic factors that are the most important components of climate. 5. Distinguish between macroclimate and microclimate patterns. Provide an example of a microclimate. Chapter 53 Com ...
... 3. Describe, with examples, how biotic and abiotic factors may affect the distribution of organisms. 4. List the four abiotic factors that are the most important components of climate. 5. Distinguish between macroclimate and microclimate patterns. Provide an example of a microclimate. Chapter 53 Com ...
View PDF
... Examples: Short bursts of speed for the cheetah, Tentacles of jellyfish have poison that paralyzes prey, and Big eyes of owls help them see their ...
... Examples: Short bursts of speed for the cheetah, Tentacles of jellyfish have poison that paralyzes prey, and Big eyes of owls help them see their ...
EOC PRACTICE QUESTIONS #5
... Bio.2.1.4 Explain why ecosystems can be relatively stable over hundreds or thousands of years, even though populations may fluctuate (emphasizing availability of food, availability of shelter, number of predators and disease). ...
... Bio.2.1.4 Explain why ecosystems can be relatively stable over hundreds or thousands of years, even though populations may fluctuate (emphasizing availability of food, availability of shelter, number of predators and disease). ...
Science Ch3 Study Guide
... Short Answer 1. How does your pulse rate differ when you are resting and when you are exercising? Explain what causes this difference. 2. Would a marathon runner be wiser to eat steak or spaghetti before a long race? Explain your choice. 3. A giraffe eats tree leaves. A lion eats other animals. What ...
... Short Answer 1. How does your pulse rate differ when you are resting and when you are exercising? Explain what causes this difference. 2. Would a marathon runner be wiser to eat steak or spaghetti before a long race? Explain your choice. 3. A giraffe eats tree leaves. A lion eats other animals. What ...
parasitism
... growth of the ecosystems elements, it is called a limiting factor . • One of the features of an ecosystem is that its growth is limited under normal conditions by competition for resources within the system and by external factors such as environmental changes ...
... growth of the ecosystems elements, it is called a limiting factor . • One of the features of an ecosystem is that its growth is limited under normal conditions by competition for resources within the system and by external factors such as environmental changes ...
Ecology – study of relationships between organisms and between
... Biome – the type of climax ecosystem that develops in large climatic areas; can be terrestrial or aquatic Terrestrial biomes – determined by *latitude– at equator, temp and rainfall are constant; varies toward the poles *altitude – increasing altitude affects vegetation *water, mountains, deserts Aq ...
... Biome – the type of climax ecosystem that develops in large climatic areas; can be terrestrial or aquatic Terrestrial biomes – determined by *latitude– at equator, temp and rainfall are constant; varies toward the poles *altitude – increasing altitude affects vegetation *water, mountains, deserts Aq ...
Introduction and Ecology Answers to Study Guide
... Control group – does not contain the variable being tested Treatment group – contains the variable being tested Constant/controlled variables – these are things that should be the same in an experiment that contains a control and treatment group. They should not be a ‘hidden’ factor that could have ...
... Control group – does not contain the variable being tested Treatment group – contains the variable being tested Constant/controlled variables – these are things that should be the same in an experiment that contains a control and treatment group. They should not be a ‘hidden’ factor that could have ...
Ecology Ch. 3-4
... All the physical, chemical, and biological factors that a species needs to survive, stay healthy, and reproduce It is a species way of life, or the role the species plays in its environment Includes the range of conditions that the species can tolerate How it obtains food, competes with othe ...
... All the physical, chemical, and biological factors that a species needs to survive, stay healthy, and reproduce It is a species way of life, or the role the species plays in its environment Includes the range of conditions that the species can tolerate How it obtains food, competes with othe ...
Overview of Anatomy and Physiology
... • Function always reflects structure • What a structure can do depends on its specific form • Examples: • Bones support and protect because they are hard • Blood flows one way through heart because of valves Levels of Structural Organization • Chemical – atoms combined to form molecules • Cellular – ...
... • Function always reflects structure • What a structure can do depends on its specific form • Examples: • Bones support and protect because they are hard • Blood flows one way through heart because of valves Levels of Structural Organization • Chemical – atoms combined to form molecules • Cellular – ...
2. Shaping Ecosystems and Populations
... – all aspects of the area in which an organism lives (includes both biotic and abiotic). – Habitats may change or disappear due to natural causes or interference by man. ...
... – all aspects of the area in which an organism lives (includes both biotic and abiotic). – Habitats may change or disappear due to natural causes or interference by man. ...
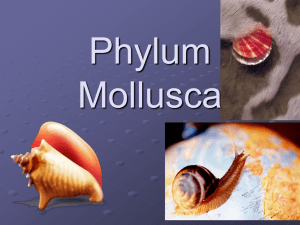
Phylum Mollusca
... The conch feeds on fish and annelid worms that they first paralyze with poison contained in their hollow radula teeth. The poison is also toxic to humans, causing paralysis and sometimes death. ...
... The conch feeds on fish and annelid worms that they first paralyze with poison contained in their hollow radula teeth. The poison is also toxic to humans, causing paralysis and sometimes death. ...
CHAPTER 17
... Positive growth occurs when anabolism exceeds catabolism – there is an increase in the dry mass of the organism – and occurs during the development of an organism from fertilisation to maturation. Negative growth occurs when catabolism exceeds anabolism – there is a decrease in dry mass of the organ ...
... Positive growth occurs when anabolism exceeds catabolism – there is an increase in the dry mass of the organism – and occurs during the development of an organism from fertilisation to maturation. Negative growth occurs when catabolism exceeds anabolism – there is a decrease in dry mass of the organ ...
The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues
... 2. Organ – performs a specific function in your body. 2. Organ system – a set of organs or structures in the body that have a common function. 2. Organ Systems 3. Circulatory System – moves blood and oxygen through the body. 3. Endocrine System – makes hormones the body needs. 3. Urinary System – co ...
... 2. Organ – performs a specific function in your body. 2. Organ system – a set of organs or structures in the body that have a common function. 2. Organ Systems 3. Circulatory System – moves blood and oxygen through the body. 3. Endocrine System – makes hormones the body needs. 3. Urinary System – co ...
The Ecosystem
... from one trophic level to the next. Notice that consumers have different names, depending on what they eat: Herbivores: plant eaters Carnivores: meat eaters Omnivores: eat plants and animals ...
... from one trophic level to the next. Notice that consumers have different names, depending on what they eat: Herbivores: plant eaters Carnivores: meat eaters Omnivores: eat plants and animals ...