Q: What is the function of the skeleton A: the internal skeleton of
... d. use of UV to detect the marker and therefore indicate the position of the gene or the presence of a specific allele in the DNA sample ...
... d. use of UV to detect the marker and therefore indicate the position of the gene or the presence of a specific allele in the DNA sample ...
File
... • Nitrogen fixation is the natural process, either biological or abiotic, by which nitrogen (N2) in the atmosphere is converted into ammonia. This process is essential for life because fixed nitrogen is required to biosynthesize the basic building blocks of life, e.g. DNA and proteins. ...
... • Nitrogen fixation is the natural process, either biological or abiotic, by which nitrogen (N2) in the atmosphere is converted into ammonia. This process is essential for life because fixed nitrogen is required to biosynthesize the basic building blocks of life, e.g. DNA and proteins. ...
End of Course Exam 6th Grade Review Answer Key
... Scientific laws must be simple, true, universal, and absolute. Statements of fact that are universally true. Examples: Motion, Conservation of Energy, Planetary Motion, Universal Gravitation 4. How can scientists use models? To study things in greater detail. They can create physical or mathematical ...
... Scientific laws must be simple, true, universal, and absolute. Statements of fact that are universally true. Examples: Motion, Conservation of Energy, Planetary Motion, Universal Gravitation 4. How can scientists use models? To study things in greater detail. They can create physical or mathematical ...
do not - The Grange School Blogs
... • Why was this? Extension: Read page 23, 24 and 25 answer all the questions ...
... • Why was this? Extension: Read page 23, 24 and 25 answer all the questions ...
Unit B Glossary
... Nutrient -Chemicals that an organism takes in from its environment to use as a source of energy or in promoting growth. Organ -A collection of tissues which performs a particular function or set of functions Pulse -Rhythmic stretching of arteries caused by blood being forced through the arteries by ...
... Nutrient -Chemicals that an organism takes in from its environment to use as a source of energy or in promoting growth. Organ -A collection of tissues which performs a particular function or set of functions Pulse -Rhythmic stretching of arteries caused by blood being forced through the arteries by ...
3). What are four main factors that affect the distribution of organisms?
... is the study of how the distributions and abundances of populations (and species) are determined by the interactions of individual organisms with their physical and biological environment. ...
... is the study of how the distributions and abundances of populations (and species) are determined by the interactions of individual organisms with their physical and biological environment. ...
Animal Unit - Jifted Land
... Earthworms tunnel for a living. They are scavengers that eat decayed plant and animan remains in the soil. Section 4 Review A tapeworm obtains its food by eating the digested material in the intestines. A roundworm eats its food it gets digested and comes out its end opening. But a planarian injects ...
... Earthworms tunnel for a living. They are scavengers that eat decayed plant and animan remains in the soil. Section 4 Review A tapeworm obtains its food by eating the digested material in the intestines. A roundworm eats its food it gets digested and comes out its end opening. But a planarian injects ...
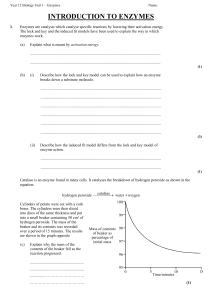
introduction to enzymes
... The lock and key and the induced fit models have been used to explain the way in which enzymes work. (a) ...
... The lock and key and the induced fit models have been used to explain the way in which enzymes work. (a) ...
document
... • At some stage of development, all vertebrates share the four features: 1. Notochord-long supportive rod that runs through the body, most only have it while embryos 2. Dorsal hollow nerve cord-nerves branch from this cord and connects to internal organs, muscles and sense organs 3. Pharyngeal gill ...
... • At some stage of development, all vertebrates share the four features: 1. Notochord-long supportive rod that runs through the body, most only have it while embryos 2. Dorsal hollow nerve cord-nerves branch from this cord and connects to internal organs, muscles and sense organs 3. Pharyngeal gill ...
Chordates powerpoint 2012
... • At some stage of development, all vertebrates share the four features: 1. Notochord-long supportive rod that runs through the body, most only have it while embryos 2. Dorsal hollow nerve cord-nerves branch from this cord and connects to internal organs, muscles and sense organs 3. Pharyngeal gill ...
... • At some stage of development, all vertebrates share the four features: 1. Notochord-long supportive rod that runs through the body, most only have it while embryos 2. Dorsal hollow nerve cord-nerves branch from this cord and connects to internal organs, muscles and sense organs 3. Pharyngeal gill ...
Chapter I
... disruptions – change in the chemical composition due to changes in external or internal environment. Regulation of homeostasis occurs through feedback systems Feedback Systems – information about a homeostatic response that is sent back to the integrating center. - the feedback system constantly mo ...
... disruptions – change in the chemical composition due to changes in external or internal environment. Regulation of homeostasis occurs through feedback systems Feedback Systems – information about a homeostatic response that is sent back to the integrating center. - the feedback system constantly mo ...
Unit 5
... control a population's growth. Extreme climate may result in resource depletion making the population struggle to survive. 10. Explain how density-dependent and density-independent factors may work together to control a population's growth. Depending on the seasons, independent factors such as weath ...
... control a population's growth. Extreme climate may result in resource depletion making the population struggle to survive. 10. Explain how density-dependent and density-independent factors may work together to control a population's growth. Depending on the seasons, independent factors such as weath ...
Chapter 17 Test Study Guide ( )
... When 2 species compete only 1 will win (succeed) the other will have to adapt, move, or die. Secondary Compounds- strong chemicals made by plants to deter animals that eat them (a lot of the spices we eat are secondary compounds, example- mustard) Adaptation: any change that helps an organism survi ...
... When 2 species compete only 1 will win (succeed) the other will have to adapt, move, or die. Secondary Compounds- strong chemicals made by plants to deter animals that eat them (a lot of the spices we eat are secondary compounds, example- mustard) Adaptation: any change that helps an organism survi ...
Classifying Living Organisms Unit 10.4.16
... Fungi – multicellular organisms that have a nucleus and absorb the organism that it is growing on (mushrooms, yeast, and molds) ...
... Fungi – multicellular organisms that have a nucleus and absorb the organism that it is growing on (mushrooms, yeast, and molds) ...
Kingdom Animalia
... – Open C.S. - blood is pumped through a series of sinuses or cavities and comes in direct contact with tissues – Closed C.S. - blood is always contained within vessels ...
... – Open C.S. - blood is pumped through a series of sinuses or cavities and comes in direct contact with tissues – Closed C.S. - blood is always contained within vessels ...
Activity 1 Adaptations
... example, allow the organisms to use the oxygen found in water. On land, oxygen is plentiful. However, the organisms that live there must protect themselves from the dangers of drying up.These dangers increase greatly because air temperatures change daily and seasonally. Air does not provide the same ...
... example, allow the organisms to use the oxygen found in water. On land, oxygen is plentiful. However, the organisms that live there must protect themselves from the dangers of drying up.These dangers increase greatly because air temperatures change daily and seasonally. Air does not provide the same ...
Jan 31 – Symbiotic Relationships
... – Is an organism benefiting? – Is an organism being harmed? – Can you connect this type of relationship to something you have already learned? ...
... – Is an organism benefiting? – Is an organism being harmed? – Can you connect this type of relationship to something you have already learned? ...
Ecosystems- Goal 1
... Most ecosystems conserve the resources naturally. An example would be the exchange of carbon dioxide (given off from animals) and oxygen (given off by plants). Another example is the waste of some species becomes the food of another. When there are limited resources, the conservation process is urge ...
... Most ecosystems conserve the resources naturally. An example would be the exchange of carbon dioxide (given off from animals) and oxygen (given off by plants). Another example is the waste of some species becomes the food of another. When there are limited resources, the conservation process is urge ...
Hyperlink Text
... • You can suffocate an earthworm by touching it with dry hands or by wiping off their mucous layer • However – they cannot survive submerged in puddles of water either • It is a delicate balance ...
... • You can suffocate an earthworm by touching it with dry hands or by wiping off their mucous layer • However – they cannot survive submerged in puddles of water either • It is a delicate balance ...
Chapter-13- Organisms and Population. 1. Important Terms Habitat
... Natality or Birth Rate: It is the average number of new individuals added per unit population due to births, hatchings and germinations. Mortality or Death Rate: It is the average number of natural deaths per unit population per unit time. Immigration: It is the permanent inward coming of individua ...
... Natality or Birth Rate: It is the average number of new individuals added per unit population due to births, hatchings and germinations. Mortality or Death Rate: It is the average number of natural deaths per unit population per unit time. Immigration: It is the permanent inward coming of individua ...
1 EARTH SCIENCE is the earth`s rock layer is the earth`s water layer
... The _______ is the main source of energy for plants, animals, & _________________ An _________________ is where living & _____________ things interact Plants obtain energy from the sun & use it for the process of _________________ to make its food ...
... The _______ is the main source of energy for plants, animals, & _________________ An _________________ is where living & _____________ things interact Plants obtain energy from the sun & use it for the process of _________________ to make its food ...
7th of 7 Review Packets
... 3-D2- Cells communicate with each other through direct contact with other cells or from a distance via chemical signaling. 3-E2- Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce ...
... 3-D2- Cells communicate with each other through direct contact with other cells or from a distance via chemical signaling. 3-E2- Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce ...
AP Biology Review Packet 7: Integration of Information
... 3-D2- Cells communicate with each other through direct contact with other cells or from a distance via chemical signaling. 3-E2- Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce ...
... 3-D2- Cells communicate with each other through direct contact with other cells or from a distance via chemical signaling. 3-E2- Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce ...