* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
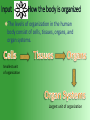
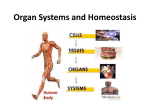
Big Idea Science Standard 7.5.a: Students know that plants and animals have levels of organization for structure and function, including cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and the whole organisms. Cells: the smallest units of organization in the body. Connective Tissue: provides support for your body and connects all of its parts. Muscle Tissue: allows your body to move (can contract and shorten) Nervous Tissue: directs and controls movement( carries electrical messages back and forth between the brain and other parts) Epithelial tissue: the tissue that covers your body inside and out. Homeostasis: the body’s tendency to keep an internal balance. Pathogens: disease causing bacteria and viruses. Stress: your body’s reaction to potentially threatening, challenging, or disturbing events. The levels of organization in the human body consist of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. Smallest unit of organization Largest unit of organization the second largest unit of organization in your body (4 basic types of tissue) 1. Muscle tissue- contract and shorten 2. Nervous tissue – carries electrical charges to brain and other parts 3. Connective tissue – provides support 4. Epithelial tissue – Cover your body inside and out. (e.g. the skin provides protection)(e.g. lining of the digestive system allows you to digest and absorb nutrients from food. The human body has 11 organ systems The Integumentary System Made up of you skin, hair, and nails. Cells and tissue work together to provide a barrier from disease causing bacteria and viruses. Skin also helps regulate body temperature. Also helps the excretory system remove waste (sweating) Works with the nervous system to give you info about your environment. The human body has 11 organ systems All systems of the body work together to maintain homeostasis HOMEOSTASIS IS THE PROCESS BY WHICH AN ORGANISM’S INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT IS KEPT STABLE IN SPITE OF CHANGES IN THE EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT Across Discipline: Language Arts (RC 2.2 (take notes on the 11 body systems. e.g what organs are involved, how does the system help maintain homeostasis.) Patterns: Draw and label one of the 11 body systems.(511-515) Question: Write a question and answer it. Summary: Write a summary of what you have learned. The Skeletal System Made up of your bones and connective tissues. Supports the body and gives structure. Protects your body’s organs Connective Tissues attaches bones and form joints that allow movement The Muscular System work to move your body by pulling your skeleton Voluntary Muscles – work when you want them to Involuntary Muscles – work by themselves Your muscles and bones are also know as the Musculoskeletal system. The Circulatory System Carries food and oxygen to all the cells of your body. Powered by the pumping of your heart. Arteries – take blood away from the heart Veins – carry blood toward the heart Capillaries – smallest blood vessels connect arteries and veins. The Respiratory System lungs are the main organs in the respiratory system Takes in oxygen and disposes carbon dioxide Delivers oxygen to the blood via circulatory system The Digestive System helps breakdown food into small molecules the body uses The Excretory System Removes waste from you blood stream Kidneys are the major organ in this system Each kidney contains 1 million nephrons that filter waste. The Immune System Protects your body from disease-causing bacteria and viruses called PATHOGENS. Specialized white blood cells target and destroy these PATHOGENS. The Nervous System takes the information from your environment and from within our body. Processes information and demands the body to respond Includes the brain and spinal cord Nerve cells reach form spinal cord to all parts of the body The Endocrine System helps regulate the activities of your organs and organ systems.( releasing hormones) Consists of Thyroid gland, Hypothalamus, Parathyroid glands, Thymus gland, Pancreas, Adrenal glands. All systems of the body work together to maintain homeostasis HOMEOSTASIS IS THE PROCESS BY WHICH AN ORGANISM’S INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT IS KEPT STABLE IN SPITE OF CHANGES IN THE EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT