final exam review packet
... 36. Salt dissolves in water; salt is (circle one): soluble / insoluble. 37. Lead Phosphate does not dissolve in water; lead phosphate is (circle one): soluble / insoluble. 38. How do you know if something will dissolve? Fill in the blanks. “________________ dissolves _________________,” which means ...
... 36. Salt dissolves in water; salt is (circle one): soluble / insoluble. 37. Lead Phosphate does not dissolve in water; lead phosphate is (circle one): soluble / insoluble. 38. How do you know if something will dissolve? Fill in the blanks. “________________ dissolves _________________,” which means ...
Pre-AP Chemistry
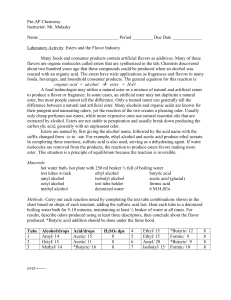
... flavors are organic molecules called esters that are synthesized in the lab. Chemists discovered about two hundred years ago that these compounds could be produced when an alcohol was reacted with an organic acid. The esters have wide applications as fragrances and flavors in many foods, beverages, ...
... flavors are organic molecules called esters that are synthesized in the lab. Chemists discovered about two hundred years ago that these compounds could be produced when an alcohol was reacted with an organic acid. The esters have wide applications as fragrances and flavors in many foods, beverages, ...
Technology: TA3 Engineering: EB3
... Nomenclature: The systematic approach to naming organic compounds was formalized by IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry). There are a number of rules for each type of organic compound only simple hydrocarbon chains and alcohols will be instructed below. When naming straight chai ...
... Nomenclature: The systematic approach to naming organic compounds was formalized by IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry). There are a number of rules for each type of organic compound only simple hydrocarbon chains and alcohols will be instructed below. When naming straight chai ...
Chapter 10
... X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses ...
... X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses ...
Name - rwebbchem
... 1. Would a precipitate form from a reaction of aluminum chloride and sodium hydroxide? If yes, write and balance the equation that illustrates the reaction. ...
... 1. Would a precipitate form from a reaction of aluminum chloride and sodium hydroxide? If yes, write and balance the equation that illustrates the reaction. ...
Matter Key
... Coefficient vs. Subscript – Coefficient: number of whole molecules place before chemical formula 3X Subscript : number of atoms of the element BEFORE it X2 Homogeneous Mixture vs. Heterogeneous Mixture – Homogeneous is spread evenly throughout, it is a mixture composed of more than one substance uni ...
... Coefficient vs. Subscript – Coefficient: number of whole molecules place before chemical formula 3X Subscript : number of atoms of the element BEFORE it X2 Homogeneous Mixture vs. Heterogeneous Mixture – Homogeneous is spread evenly throughout, it is a mixture composed of more than one substance uni ...
GCE Chemistry Teachers` Guide (A2) Word Document
... Aldehydes and ketones Carboxylic acid and derivatives ...
... Aldehydes and ketones Carboxylic acid and derivatives ...
Untitled
... FUNCTIONAL GROUPS- Affect a molecule’s function by participating in chemical reactions in characteristic ways. These groups are polar, because their oxygen or nitrogen atoms exert a strong pull on shared electrons. This polarity tends to make the compounds containing these groups HYDROPHILIC (waterl ...
... FUNCTIONAL GROUPS- Affect a molecule’s function by participating in chemical reactions in characteristic ways. These groups are polar, because their oxygen or nitrogen atoms exert a strong pull on shared electrons. This polarity tends to make the compounds containing these groups HYDROPHILIC (waterl ...
Chapter 1 Chemistry: the study of the composition of matter and the
... Be able to solve for the missing value in a density problem Temperature conversion: kelvin-Celsius and reverse Chapter 5 ...
... Be able to solve for the missing value in a density problem Temperature conversion: kelvin-Celsius and reverse Chapter 5 ...
Final Exam Practice-2017
... 92. What is the element that is reduced in the following reaction? Br2 (g) + 2HI (aq) 2HBr (aq) + I2 (l) a) Br b) H c) I 93. Which of the following is the correct balanced half reaction for I2O5 I2 in a basic solution? a) 10H+ + I2O5 + 5e- I2 + 5H2O c) 5H2O + I2O5 + 5e- I2 + 10 OHb) 10H+ + I ...
... 92. What is the element that is reduced in the following reaction? Br2 (g) + 2HI (aq) 2HBr (aq) + I2 (l) a) Br b) H c) I 93. Which of the following is the correct balanced half reaction for I2O5 I2 in a basic solution? a) 10H+ + I2O5 + 5e- I2 + 5H2O c) 5H2O + I2O5 + 5e- I2 + 10 OHb) 10H+ + I ...
Drug Design
... synthesis with amino acids. • The starting material or pharmacore is covalently bonded to small polystyrene resin beads. • The beads are reacted with various groups in successive steps. • The beads are separated from the reaction mixture and then undergo preliminary screening for drug activity. • Th ...
... synthesis with amino acids. • The starting material or pharmacore is covalently bonded to small polystyrene resin beads. • The beads are reacted with various groups in successive steps. • The beads are separated from the reaction mixture and then undergo preliminary screening for drug activity. • Th ...
Intro to Organic Reactions
... dissolves in organic solvents. • PS foam is mostly air, and when it dissolves it collapses to a much smaller volume. ...
... dissolves in organic solvents. • PS foam is mostly air, and when it dissolves it collapses to a much smaller volume. ...
Organic Chemistry Chapter 25 - Ms. Ose's Chemistry Website
... when there are four or more carbon atoms Geometric isomers: compounds that have the same molecular formula and the same groups bonded but different spatial arrangements; results from the carbon carbon double bond’s resistance to twisting ...
... when there are four or more carbon atoms Geometric isomers: compounds that have the same molecular formula and the same groups bonded but different spatial arrangements; results from the carbon carbon double bond’s resistance to twisting ...
Course Structure - Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science
... F. A. Cotton, Chemical Applications of GroupTheory, John Wiley. J. M. Hollas, Symmetry in Molecules, Chapman I. Hargittai and M. Hargittai, Symmetry Through the Eyes of a Chemist, Plenum ...
... F. A. Cotton, Chemical Applications of GroupTheory, John Wiley. J. M. Hollas, Symmetry in Molecules, Chapman I. Hargittai and M. Hargittai, Symmetry Through the Eyes of a Chemist, Plenum ...
Tellurium
... • The major difference between these two isomers noted in the article was the length of the Te---Cl bonds. • The explanation for this arises when the ability of the molecule to form a dimer or a chains examined. • It was found that the R,R isomer can form a chain with intermolecular interactions bet ...
... • The major difference between these two isomers noted in the article was the length of the Te---Cl bonds. • The explanation for this arises when the ability of the molecule to form a dimer or a chains examined. • It was found that the R,R isomer can form a chain with intermolecular interactions bet ...
Chemstry 355
... The overall average will be calculated by two methods and the higher result will be used in determining the course grade. Method 1. The quiz average, each hour exam score, and the final exam score will be added together and the total will be divided by 5. Thus, each exam counts 20%, the quizzes coun ...
... The overall average will be calculated by two methods and the higher result will be used in determining the course grade. Method 1. The quiz average, each hour exam score, and the final exam score will be added together and the total will be divided by 5. Thus, each exam counts 20%, the quizzes coun ...