CHM 105 - Test 2 Review
... 8. Rank the boiling points of carboxylic acids, hydrocarbons, alcohols, ethers, aldehydes and ketones. Draw a specific example for each class of compound listed. 9. Draw the following molecules: potassium formate, ethylpropyl amine, N-methylbenzamide. Where possible, rename using the IUPAC system. 1 ...
... 8. Rank the boiling points of carboxylic acids, hydrocarbons, alcohols, ethers, aldehydes and ketones. Draw a specific example for each class of compound listed. 9. Draw the following molecules: potassium formate, ethylpropyl amine, N-methylbenzamide. Where possible, rename using the IUPAC system. 1 ...
Terminology 1
... (The chemical identity of an atom can be determined solely by it’s atomic number) When the atom is neutral, i.e. not electrically charged, the atomic number equals the number of electrons in its shells ...
... (The chemical identity of an atom can be determined solely by it’s atomic number) When the atom is neutral, i.e. not electrically charged, the atomic number equals the number of electrons in its shells ...
Carbon Compounds. Organic Molecules.
... Compounds that contain other elements besides C and H are regarded as derivatives of hydrocarbons. The groups of C and H that appear in hydrocarbon derivatives are named from the hydrocarbons. Examples: methyl group (CH3), ethyl group (C2H5). ...
... Compounds that contain other elements besides C and H are regarded as derivatives of hydrocarbons. The groups of C and H that appear in hydrocarbon derivatives are named from the hydrocarbons. Examples: methyl group (CH3), ethyl group (C2H5). ...
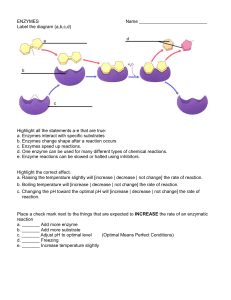
ENZYMES
... a. _______ Add more enzyme b. _______ Add more substrate c. _______ Adjust pH to optimal level (Optimal Means Perfect Conditions) d. _______ Freezing e. _______ Increase temperature slightly ...
... a. _______ Add more enzyme b. _______ Add more substrate c. _______ Adjust pH to optimal level (Optimal Means Perfect Conditions) d. _______ Freezing e. _______ Increase temperature slightly ...
Guided Reading Worksheet #1 – Chapter 3 USE THE BOOK FOR
... 9. The differences in the amino acids is in the “R”groups. The R groups give the different proteins different ___________________. The different _____________allow proteins to carry out many different activities in ______________things. 10. Amino acids are bonded together with bonds called _________ ...
... 9. The differences in the amino acids is in the “R”groups. The R groups give the different proteins different ___________________. The different _____________allow proteins to carry out many different activities in ______________things. 10. Amino acids are bonded together with bonds called _________ ...
organic chemistry - Mr. Walsh`s AP Chemistry
... in environmental and societal issues, should not be isolated from the principles being studied but should be taught throughout the course to illustrate and illuminate the principles. The following areas should be covered: 3. Introduction to organic chemistry: hydrocarbons and functional groups (stru ...
... in environmental and societal issues, should not be isolated from the principles being studied but should be taught throughout the course to illustrate and illuminate the principles. The following areas should be covered: 3. Introduction to organic chemistry: hydrocarbons and functional groups (stru ...
Chapter 14 – Chemical Reactions
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
Lecture 4 - Winthrop Chemistry, Physics, and Geology
... • Hydrocarbons are compounds consisting of only carbon and hydrogen • Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Contain a benzene ring • Aliphatic Hydrocarbons: No benzene ring; usually a chain • Some molecules have both (remember ...
... • Hydrocarbons are compounds consisting of only carbon and hydrogen • Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Contain a benzene ring • Aliphatic Hydrocarbons: No benzene ring; usually a chain • Some molecules have both (remember ...
Part a
... hydrogen of one molecule and an electronegative atom of another molecule ◦ Common between dipoles such as water ◦ Also act as intramolecular bonds, holding a large molecule in a three-dimensional shape ...
... hydrogen of one molecule and an electronegative atom of another molecule ◦ Common between dipoles such as water ◦ Also act as intramolecular bonds, holding a large molecule in a three-dimensional shape ...
All you need to know about Additional Science
... • Chlorine's Ar of 35.5 is an average of the masses of the different isotopes of chlorine. This is calculated by working out the relative abundance of each isotope. For example, in any sample of Chlorine 25% will be 37 Cl and 75% 35 Cl. The relative atomic mass is therefore calculated using the ...
... • Chlorine's Ar of 35.5 is an average of the masses of the different isotopes of chlorine. This is calculated by working out the relative abundance of each isotope. For example, in any sample of Chlorine 25% will be 37 Cl and 75% 35 Cl. The relative atomic mass is therefore calculated using the ...
The collision theory of reactions
... than the concentration of O atoms. How significant is reaction 6? do assignment 7, p.69 Chlorine atoms are particularly effective at removing ozone. A single atom can remove about 1 million ozone molecules. Add equations 6 and 7 together to produce the equation for the overall reaction caused by c ...
... than the concentration of O atoms. How significant is reaction 6? do assignment 7, p.69 Chlorine atoms are particularly effective at removing ozone. A single atom can remove about 1 million ozone molecules. Add equations 6 and 7 together to produce the equation for the overall reaction caused by c ...
CH 115 Exam 2 - UAB General Chemistry Supplemental Instruction
... Assume the chemical equations on this exam are NOT balanced unless stated otherwise. 1. Balance the equation and give the stoichiometric coefficient for HCl ...
... Assume the chemical equations on this exam are NOT balanced unless stated otherwise. 1. Balance the equation and give the stoichiometric coefficient for HCl ...
Chemical Reactions Chemical Arithmetic
... Oxidation-Reduction Reactions • Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reaction- A chemical reaction in which the oxidation numbers of elements change because of a loss or gain of electrons • Oxidation Number- A number that indicates the charge that an atom in a molecule or polyatomic ion would have if all bon ...
... Oxidation-Reduction Reactions • Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reaction- A chemical reaction in which the oxidation numbers of elements change because of a loss or gain of electrons • Oxidation Number- A number that indicates the charge that an atom in a molecule or polyatomic ion would have if all bon ...
Ch 4 Carbon & Molec Divrsty
... carbon compounds • Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon • Organic compounds range from simple molecules to colossal ones • Most organic compounds contain hydrogen atoms as well as carbon atoms • Vitalism said that organic compounds are only in organisms; disproved when chemi ...
... carbon compounds • Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon • Organic compounds range from simple molecules to colossal ones • Most organic compounds contain hydrogen atoms as well as carbon atoms • Vitalism said that organic compounds are only in organisms; disproved when chemi ...
Science Notes on Physical and Chemical Properties
... 2. Reactions with acid – how well something reacts with an acid. Main reaction with and acid results in bubbling. When an acid reacts with another substance, usually hydrogen gas (which is highly explosive) is released 3. Other Reactions – include heat being released, bubbling, strong odor, smoke, f ...
... 2. Reactions with acid – how well something reacts with an acid. Main reaction with and acid results in bubbling. When an acid reacts with another substance, usually hydrogen gas (which is highly explosive) is released 3. Other Reactions – include heat being released, bubbling, strong odor, smoke, f ...
Order date : 24-07-2010
... Application of Experimental criteria to mechanistic studies, Thermodynamic and kinetic data, Curtius- Hammet principles, Kinetic versus thermodynamic control. Acidity constant, Hammet acidity function. Reactive intermediates and their characterization. Isotope effect (labeling experiments), stereoch ...
... Application of Experimental criteria to mechanistic studies, Thermodynamic and kinetic data, Curtius- Hammet principles, Kinetic versus thermodynamic control. Acidity constant, Hammet acidity function. Reactive intermediates and their characterization. Isotope effect (labeling experiments), stereoch ...
Biogas Student Presentation
... What types of organic waste Cow, sheep and and crops from Sewage could be turned in biogas? chicken manure farming Leftover meat and blood from abattoirs ...
... What types of organic waste Cow, sheep and and crops from Sewage could be turned in biogas? chicken manure farming Leftover meat and blood from abattoirs ...
constitutional isomers
... such a system. Each name contains exactly enough information for us to draw exactly one organic compound. e.g. 6-chloro-2,3,3-trimethylhexan-2-ol substituents ...
... such a system. Each name contains exactly enough information for us to draw exactly one organic compound. e.g. 6-chloro-2,3,3-trimethylhexan-2-ol substituents ...