Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found • No orbital can contain more than two el ...
... • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found • No orbital can contain more than two el ...
chapt02_lecture from text
... • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found • No orbital can contain more than two el ...
... • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found • No orbital can contain more than two el ...
Chemical Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry
... When a hydrocarbon is fully combusted, the mass of water and carbon dioxide collected can be used directly to determine the amount of carbon and hydrogen in the original compound. ...
... When a hydrocarbon is fully combusted, the mass of water and carbon dioxide collected can be used directly to determine the amount of carbon and hydrogen in the original compound. ...
Document
... The boron-hydrogen bond adds across double bonds. Borane, BH3, adds to double bonds without catalytic activation: ...
... The boron-hydrogen bond adds across double bonds. Borane, BH3, adds to double bonds without catalytic activation: ...
CHEMISTRY
... Many are in aqueous solutions Less E required The more active element replaces the less active one Most active metals (group 1) react w/water and produce metal hydroxides ...
... Many are in aqueous solutions Less E required The more active element replaces the less active one Most active metals (group 1) react w/water and produce metal hydroxides ...
Benzene and Aromatics
... carcinogen, its use as an additive in gasoline is now limited, but it is an important industrial solvent and precursor in the production of drugs, plastics, synthetic rubber, and dyes. Benzene is a natural constituent of crude oil, and may be synthesized from other compounds present in petroleum. Be ...
... carcinogen, its use as an additive in gasoline is now limited, but it is an important industrial solvent and precursor in the production of drugs, plastics, synthetic rubber, and dyes. Benzene is a natural constituent of crude oil, and may be synthesized from other compounds present in petroleum. Be ...
template
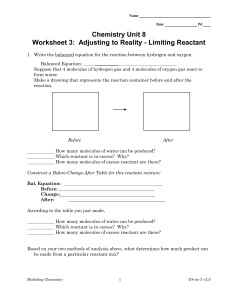
... Construct a Before-Change-After Table for this reactant mixture: Bal. Equation: Before: __________________________________________ Change:__________________________________________ After: ___________________________________________ According to the table you just made, How many molecules of ammonia ...
... Construct a Before-Change-After Table for this reactant mixture: Bal. Equation: Before: __________________________________________ Change:__________________________________________ After: ___________________________________________ According to the table you just made, How many molecules of ammonia ...
Nugget
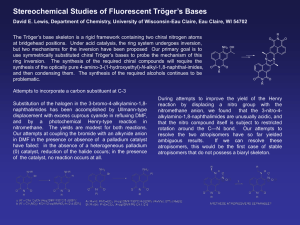
... David E. Lewis, Department of Chemistry, University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire, Eau Claire, WI 54702 The Tröger’s base skeleton is a rigid framework containing two chiral nitrogen atoms at bridgehead positions. Under acid catalysis, the ring system undergoes inversion, but two mechanisms for the invers ...
... David E. Lewis, Department of Chemistry, University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire, Eau Claire, WI 54702 The Tröger’s base skeleton is a rigid framework containing two chiral nitrogen atoms at bridgehead positions. Under acid catalysis, the ring system undergoes inversion, but two mechanisms for the invers ...
File - Mr. J`s Chemistry 4U
... C- A type of chemical reaction in which one element replaces a similar element in a compound. D- A type of chemical reaction in which the ions of two compounds exchange places in an aqueous solution to form two new compounds. E- A type of chemical reaction in which a substance combines with oxygen r ...
... C- A type of chemical reaction in which one element replaces a similar element in a compound. D- A type of chemical reaction in which the ions of two compounds exchange places in an aqueous solution to form two new compounds. E- A type of chemical reaction in which a substance combines with oxygen r ...
Worked Example 21.1
... Analysis Look at each ring carefully. Ring 2 does not include an O. It cannot be a sugar. Rings 1,3, and 4 all contain O as a ring number. Imagine the rings as underivatized sugars, that is with —OH groups instead of —NH2 groups; count the number of carbon atoms in each sugar and draw the sugar form ...
... Analysis Look at each ring carefully. Ring 2 does not include an O. It cannot be a sugar. Rings 1,3, and 4 all contain O as a ring number. Imagine the rings as underivatized sugars, that is with —OH groups instead of —NH2 groups; count the number of carbon atoms in each sugar and draw the sugar form ...
Answers to Final Exam Review
... 32. Given the pairs of atoms below, predict whether the bond formed between the atoms is either ionic or covalent, and if ionic, write the formula for the predicted compound. a. Na and Fionic c. K and Brionic e. H and Ncovalent b. C and Ocovalent d. Ca and Fionic f. Mg and Oionic 33. Which statement ...
... 32. Given the pairs of atoms below, predict whether the bond formed between the atoms is either ionic or covalent, and if ionic, write the formula for the predicted compound. a. Na and Fionic c. K and Brionic e. H and Ncovalent b. C and Ocovalent d. Ca and Fionic f. Mg and Oionic 33. Which statement ...
Quantities, Units, Symbols and Nomenclature used in
... size of an object can be described in terms of its ‘length in metres’, rather than its ‘number of metres’. Graph Axes and Table Headings Labelled as quantity / unit, eg c / mol L–1. Only values will then be written on the axes or in a table. ...
... size of an object can be described in terms of its ‘length in metres’, rather than its ‘number of metres’. Graph Axes and Table Headings Labelled as quantity / unit, eg c / mol L–1. Only values will then be written on the axes or in a table. ...
Chem_def - GEOCITIES.ws
... itself to the carbon atom already carrying the large number of hydrogen atom ...
... itself to the carbon atom already carrying the large number of hydrogen atom ...
Unit 2.2 Test Review Key
... Are they, H2O2 and 2OH, the same substance? __No___ Explain your answer: No they are not the same substance even though they have the same amount and type of atoms. H2O2 is one molecule of Hydrogen Peroxide that has all of its atoms bonded together. Whereas, 2OH is two molecules of OH bonded togethe ...
... Are they, H2O2 and 2OH, the same substance? __No___ Explain your answer: No they are not the same substance even though they have the same amount and type of atoms. H2O2 is one molecule of Hydrogen Peroxide that has all of its atoms bonded together. Whereas, 2OH is two molecules of OH bonded togethe ...
4 Organic and Biochemical Compounds
... atom. A carbon atom forms a double bond if it shares two of its electrons with another atom. A carbon atom forms a triple bond if it shares three of its electrons. A carbon atom cannot form more than four total bonds at one time. ...
... atom. A carbon atom forms a double bond if it shares two of its electrons with another atom. A carbon atom forms a triple bond if it shares three of its electrons. A carbon atom cannot form more than four total bonds at one time. ...
Ch3notes
... • organic molecules consisting of only hydrogen and carbon • The molecules’ chain of carbon atoms is called the carbon skeleton • Ex: methane, ethane, propane Isomer – compounds with the same molecular formula but different structure ...
... • organic molecules consisting of only hydrogen and carbon • The molecules’ chain of carbon atoms is called the carbon skeleton • Ex: methane, ethane, propane Isomer – compounds with the same molecular formula but different structure ...
Grant MacEwan College - Faculty Web Pages
... Course Description:(3 credits) This course studies the molecular structure and reactivity of organic compounds based on their functional groups and is intended for students who have obtained at least three credits in Introductory University Chemistry. The course provides an introduction to nomenclat ...
... Course Description:(3 credits) This course studies the molecular structure and reactivity of organic compounds based on their functional groups and is intended for students who have obtained at least three credits in Introductory University Chemistry. The course provides an introduction to nomenclat ...
CP Chemistry Final Review – Chap. 10-19
... 4. Explain a calorimeter and how it is used. 5. Describe how energy is involved in these phase changes: fusion, freezing, vaporization, and condensation. Chapter 18 - Equilibrium ...
... 4. Explain a calorimeter and how it is used. 5. Describe how energy is involved in these phase changes: fusion, freezing, vaporization, and condensation. Chapter 18 - Equilibrium ...