File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... coefficients mean? How can you tell which elements are present. Know the Law of Conservation of Mass and how it is applied to chemical reactions Know what makes a compound organic or not Know the difference between physical and chemical properties and changes Exothermic and endothermic react ...
... coefficients mean? How can you tell which elements are present. Know the Law of Conservation of Mass and how it is applied to chemical reactions Know what makes a compound organic or not Know the difference between physical and chemical properties and changes Exothermic and endothermic react ...
Course: Advanced Placement (AP) Chemistry
... 2. Atomic masses; determination by chemical and physical means 3. Atomic number and mass number; isotopes 4. Electron energy levels: atomic spectra, quantum numbers, atomic orbitals 5. Periodic relationships including, for example, atomic radii, ionization energies, electron affinities, oxidation st ...
... 2. Atomic masses; determination by chemical and physical means 3. Atomic number and mass number; isotopes 4. Electron energy levels: atomic spectra, quantum numbers, atomic orbitals 5. Periodic relationships including, for example, atomic radii, ionization energies, electron affinities, oxidation st ...
158KB - NZQA
... The added MnO2 acts as a catalyst and is added in small amounts because it is not used up in the reaction, so can be reused over and over again in the chemical reaction. ...
... The added MnO2 acts as a catalyst and is added in small amounts because it is not used up in the reaction, so can be reused over and over again in the chemical reaction. ...
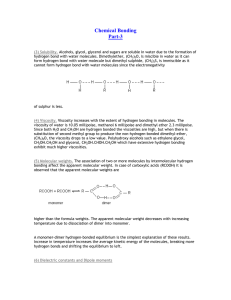
Chemical Bonding
... hydrogen bond, and 2,6-dihydroxy benzoic acid is much more stronger (pKa = 2.30) than osalicylic acid. Similarly, o-salicylic acid (pKa = 2.98) is much stronger due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding than its meta (pKa = 4.08) and para (pKa = 4.58) isomers. ...
... hydrogen bond, and 2,6-dihydroxy benzoic acid is much more stronger (pKa = 2.30) than osalicylic acid. Similarly, o-salicylic acid (pKa = 2.98) is much stronger due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding than its meta (pKa = 4.08) and para (pKa = 4.58) isomers. ...
Weiguang Zhang 1,* Yun Zhong 1, Minyu Tan 2,*, Ning Tang 2 and
... Investigation of the role that zinc thiolate complexes play in biological chemistry has stimulated numerous studies on zinc coordination compounds with sulfur ligation [1-4]. In particular, zinc complexes with NS2 ligand cores are of increasing interest as structural and spectroscopic models for met ...
... Investigation of the role that zinc thiolate complexes play in biological chemistry has stimulated numerous studies on zinc coordination compounds with sulfur ligation [1-4]. In particular, zinc complexes with NS2 ligand cores are of increasing interest as structural and spectroscopic models for met ...
Electron Arrangement
... forces holding the molecules together. Van der Waals’ forces increase with increasing size. Polar Covalent Bonding This occurs when 2 non-metal atoms form a covalent bond but the electrons are not shared equally. They sit closer to one atom than the other. The one closest to the electrons then has a ...
... forces holding the molecules together. Van der Waals’ forces increase with increasing size. Polar Covalent Bonding This occurs when 2 non-metal atoms form a covalent bond but the electrons are not shared equally. They sit closer to one atom than the other. The one closest to the electrons then has a ...
Slide 1
... •ability of two or more substances to combine and form a new substance •Oxygen and iron create rust ...
... •ability of two or more substances to combine and form a new substance •Oxygen and iron create rust ...
Document
... electron pairs from Lewis bases Transition-metal compounds, such as TiCl4, FeCl3, ZnCl2, and SnCl4, are Lewis acids Organic compounds that undergo addition reactions with Lewis bases (discussed later) are called electrophiles and therefore Lewis Acids The combination of a Lewis acid and a Lewis base ...
... electron pairs from Lewis bases Transition-metal compounds, such as TiCl4, FeCl3, ZnCl2, and SnCl4, are Lewis acids Organic compounds that undergo addition reactions with Lewis bases (discussed later) are called electrophiles and therefore Lewis Acids The combination of a Lewis acid and a Lewis base ...
Rethinking Quant The Importance of Analytical Thinking
... To determine whether there is a relationship between two variables you must ensure that all other variables remain fixed. A calorimeter will absorb some of the heat released during the reaction. You will need to establish if the amount of heat absorbed by your calorimeter is significant and, if so, ...
... To determine whether there is a relationship between two variables you must ensure that all other variables remain fixed. A calorimeter will absorb some of the heat released during the reaction. You will need to establish if the amount of heat absorbed by your calorimeter is significant and, if so, ...
The Chemistry of Life: Organic Compounds
... Functional groups change the properties of organic molecules The existence of isomers is not the only source of variety among organic molecules. The addition of various combinations of atoms generates a vast array of molecules with different properties. Because covalent bonds between hydrogen and ca ...
... Functional groups change the properties of organic molecules The existence of isomers is not the only source of variety among organic molecules. The addition of various combinations of atoms generates a vast array of molecules with different properties. Because covalent bonds between hydrogen and ca ...
Electron
... • The fixed amount of energy that a system described by quantum mechanics, such as a molecule, atom, electron, or nucleus, can have. ...
... • The fixed amount of energy that a system described by quantum mechanics, such as a molecule, atom, electron, or nucleus, can have. ...
Instrumental Methods of Analysis
... environment ,whose temperature is changing in a predetermined manner, generally at linear rate. ...
... environment ,whose temperature is changing in a predetermined manner, generally at linear rate. ...
Chemistry - Tumkur University
... of stating II law of thermodynamics with respect to its spontaneity, spontaneous and nonspontaneous processes. Concept of entropy and its significance-illustrations for order, disorder, physical, chemical process and probability. Heat engine: Carnot’s cycle and derivation of the expression for its e ...
... of stating II law of thermodynamics with respect to its spontaneity, spontaneous and nonspontaneous processes. Concept of entropy and its significance-illustrations for order, disorder, physical, chemical process and probability. Heat engine: Carnot’s cycle and derivation of the expression for its e ...
PS.Ch6.Test.95 - cloudfront.net
... Calculate the mass of hydrogen formed when 25 g of aluminum reacts with excess hydrochloric acid. 2Al + 6HCl 2 AlCl3 + 3 H2 a) 0.41 g c) 1.2 g b) 0.92 g d) 2.8 g How many grams of nitric acid, HNO3, can be prepared from the reaction of 92.0 g of NO2 with 36.0 g H2O? a) b) ...
... Calculate the mass of hydrogen formed when 25 g of aluminum reacts with excess hydrochloric acid. 2Al + 6HCl 2 AlCl3 + 3 H2 a) 0.41 g c) 1.2 g b) 0.92 g d) 2.8 g How many grams of nitric acid, HNO3, can be prepared from the reaction of 92.0 g of NO2 with 36.0 g H2O? a) b) ...
Chemical Reactions
... Covalent Compounds • Covalent compounds are two nonmetals • Use prefixes to represent a number (tells how many atoms) • Study table on page 393 ...
... Covalent Compounds • Covalent compounds are two nonmetals • Use prefixes to represent a number (tells how many atoms) • Study table on page 393 ...
Document
... the reactants and appear on the left side of the arrow, 44) In a chemical reaction, the name(s) of the material(s) that you end with are called the products and appear on the right side of the arrow. 45) In a chemical reaction, the mass of reactants should be _______________ mass of the products. a) ...
... the reactants and appear on the left side of the arrow, 44) In a chemical reaction, the name(s) of the material(s) that you end with are called the products and appear on the right side of the arrow. 45) In a chemical reaction, the mass of reactants should be _______________ mass of the products. a) ...
C h e m g u i d e ... ALCOHOLS: AN INTRODUCTION
... c) The boiling point of the ethanol is greater because it has two additional forces between the molecules, particularly the hydrogen bonds which are quite strong. Both of these molecules have identical numbers of electrons and a similar length so that the dispersion forces are going to be similar in ...
... c) The boiling point of the ethanol is greater because it has two additional forces between the molecules, particularly the hydrogen bonds which are quite strong. Both of these molecules have identical numbers of electrons and a similar length so that the dispersion forces are going to be similar in ...