Course : Chem 312F
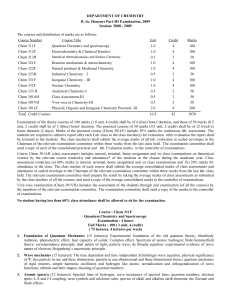
... Organic Reactions (12 lectures) : (a) Mechanisms: Brief idea of the following: Carbocations, carbanions, free radicals, electrophiles and nucleophiles. Important organic reactions with their mechanisms and synthetic applications: Reformatsky, Reimer-Tiemann & ArndtEistert. Carbanion Condensation: Al ...
... Organic Reactions (12 lectures) : (a) Mechanisms: Brief idea of the following: Carbocations, carbanions, free radicals, electrophiles and nucleophiles. Important organic reactions with their mechanisms and synthetic applications: Reformatsky, Reimer-Tiemann & ArndtEistert. Carbanion Condensation: Al ...
Lesson 4 halogenoalkanes
... Reaction is carried out under reflux. Reaction is useful as it extends the carbon chain. ...
... Reaction is carried out under reflux. Reaction is useful as it extends the carbon chain. ...
Chapter 3 - Biochemistry
... 3. amino acids (monomers) Example-Tryptophan a. 20 different kinds 1) all have central carbon bonded to hydrogen 2) R group (radical) - part that differs in each 4. dehyd. syn. joins 2 amino acids to form dipeptide a. OH from acid(COOH) and H from NH2 forms H2O b. C-N bond formed (peptide bond) c. m ...
... 3. amino acids (monomers) Example-Tryptophan a. 20 different kinds 1) all have central carbon bonded to hydrogen 2) R group (radical) - part that differs in each 4. dehyd. syn. joins 2 amino acids to form dipeptide a. OH from acid(COOH) and H from NH2 forms H2O b. C-N bond formed (peptide bond) c. m ...
Document
... •In graphite, only three of the four electrons in the outer shell of each carbon atom (2.4) are involved in covalent bonds. •Graphite is soft and slippery – layers can easily slide over each other because the weak forces of attraction are easily broken. This is why graphite is used as a lubricant. • ...
... •In graphite, only three of the four electrons in the outer shell of each carbon atom (2.4) are involved in covalent bonds. •Graphite is soft and slippery – layers can easily slide over each other because the weak forces of attraction are easily broken. This is why graphite is used as a lubricant. • ...
Objectives - Dixie State University
... energy diagrams differ, whether their enthalpy is positive or negative, and what causes a reaction to be endothermic or exothermic. 9. Explain the relationship between G, H, and S. II. Kinetics of Reactions 1. Explain what kinetics tells us about a reaction, and why it is important. 2. Explain why t ...
... energy diagrams differ, whether their enthalpy is positive or negative, and what causes a reaction to be endothermic or exothermic. 9. Explain the relationship between G, H, and S. II. Kinetics of Reactions 1. Explain what kinetics tells us about a reaction, and why it is important. 2. Explain why t ...
Chem 30BL_Lecture 2_.. - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... • Regiocontrol is observed due to pre-existing double bonds 33% H 2SO4 ...
... • Regiocontrol is observed due to pre-existing double bonds 33% H 2SO4 ...
136KB - NZQA
... Two products are formed in this reaction because propene is an asymmetric alkene. When another asymmetric molecule such as hydrogen chloride, HCl, is added to it, there are two possible products. One product is produced in greater quantities (the major product) than the other (minor product). The ru ...
... Two products are formed in this reaction because propene is an asymmetric alkene. When another asymmetric molecule such as hydrogen chloride, HCl, is added to it, there are two possible products. One product is produced in greater quantities (the major product) than the other (minor product). The ru ...
How are Molecules Depicted? - Belle Vernon Area School District
... E level of an atom and determines the chemical properties Lewis Structure = a structure in which e- are represented by dots: dot pairs or dashes b/t 2 atomic symbols represents pairs in covalent bonds ...
... E level of an atom and determines the chemical properties Lewis Structure = a structure in which e- are represented by dots: dot pairs or dashes b/t 2 atomic symbols represents pairs in covalent bonds ...
Lecture #3 – Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... a. AMINO GROUP: (Your “basic” relative) -NH2 a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms and the carbon skeleton. Organic compounds in this group are called amines. b. Because glycine has an amine group and a carboxylic acid, compounds with both are called something very important – amino acids – t ...
... a. AMINO GROUP: (Your “basic” relative) -NH2 a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms and the carbon skeleton. Organic compounds in this group are called amines. b. Because glycine has an amine group and a carboxylic acid, compounds with both are called something very important – amino acids – t ...
Introduction_to_organic
... naturalprocesses or by human intervention in the laboratory. This was the most common definition of "organic" until Wohler's 1828 synthesis of urea (an organic compound) from ammonium cyanate (a salt, and therefore? Organic/inorganic). But we no longer use this definition, for the simple reason that ...
... naturalprocesses or by human intervention in the laboratory. This was the most common definition of "organic" until Wohler's 1828 synthesis of urea (an organic compound) from ammonium cyanate (a salt, and therefore? Organic/inorganic). But we no longer use this definition, for the simple reason that ...
Describing Chemical Reactions
... Helpful Tips for Balancing Equations Balance one element at a time Update ALL atoms counts after adding a coefficient If an element appears more than once per side, balance it last ...
... Helpful Tips for Balancing Equations Balance one element at a time Update ALL atoms counts after adding a coefficient If an element appears more than once per side, balance it last ...
Chem 30BL * Lecture 2 - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... • Regiocontrol is observed due to pre-existing double bonds 33% H2SO4 ...
... • Regiocontrol is observed due to pre-existing double bonds 33% H2SO4 ...
Organic Families: Summary Chart
... The more C atoms present, the harder it is to break the bonds. The more C atoms, the higher the boiling point. Alkenes and alkynes are more reactive than alkanes due to their double/triple bonds (unsaturated). Presence of OH group makes alcohol more polar than hydrocarbons. Therefore, boiling point ...
... The more C atoms present, the harder it is to break the bonds. The more C atoms, the higher the boiling point. Alkenes and alkynes are more reactive than alkanes due to their double/triple bonds (unsaturated). Presence of OH group makes alcohol more polar than hydrocarbons. Therefore, boiling point ...
Chemistry - talcher autonomous college
... application, Solvation energy. (ii) Covalent bond: Lewis structure, Valence Bond theory (Heitler-London approach). Energetics of hybridization, equivalent and non-equivalent hybrid orbitals. Bent’s rule, Resonance and resonance energy, Molecular orbital theory. Molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic ...
... application, Solvation energy. (ii) Covalent bond: Lewis structure, Valence Bond theory (Heitler-London approach). Energetics of hybridization, equivalent and non-equivalent hybrid orbitals. Bent’s rule, Resonance and resonance energy, Molecular orbital theory. Molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic ...























