11. Reactions of Alkyl Halides
... • The overall rate of a reaction is controlled by the rate of the slowest step • The rate depends on the concentration of the species and the rate constant of the step • The highest energy transition state point on the diagram is that for the rate determining step (which is not always the highest ba ...
... • The overall rate of a reaction is controlled by the rate of the slowest step • The rate depends on the concentration of the species and the rate constant of the step • The highest energy transition state point on the diagram is that for the rate determining step (which is not always the highest ba ...
Question 1. Phosgene was used during the World War - IQ
... Consider half-cell A and B, draw an electrochemical cell with spontaneous reaction (write the global equation) and calculate the cell potential. Furthermore, you need to indicate: the flow of electrons, cathode and anode. (b) Metallic copper (Cu0) can be dissolved by HNO3(conc) and it is observed th ...
... Consider half-cell A and B, draw an electrochemical cell with spontaneous reaction (write the global equation) and calculate the cell potential. Furthermore, you need to indicate: the flow of electrons, cathode and anode. (b) Metallic copper (Cu0) can be dissolved by HNO3(conc) and it is observed th ...
Name / Functional Group
... heat it to boiling by turning on the hot plate to “10”. 2. Place one spatula-tip of solid salicylic acid into the test tube (about ¼ tsp). 3. Add 20 drop of methanol (methyl alcohol). Be careful, the alcohol is volatile and tends to pour out rather than drip. 4. Add two drops of concentrated sulfuri ...
... heat it to boiling by turning on the hot plate to “10”. 2. Place one spatula-tip of solid salicylic acid into the test tube (about ¼ tsp). 3. Add 20 drop of methanol (methyl alcohol). Be careful, the alcohol is volatile and tends to pour out rather than drip. 4. Add two drops of concentrated sulfuri ...
Introduction (HL)
... The two enantiomers rotate the plane of the polarized light by the same amount but in opposite directions. The rotations cancel each other out and the mixture appears to be optically inactive. ...
... The two enantiomers rotate the plane of the polarized light by the same amount but in opposite directions. The rotations cancel each other out and the mixture appears to be optically inactive. ...
Chemistry 101 2007
... 1.1 The Atomic and molecular Perspectives of Chemistry. Chemistry is the study of the properties and behavior of matter. A property is a characteristic that allows us to recognize a particular type of matter. All the matter in the world is comprised of about 116 elements. ...
... 1.1 The Atomic and molecular Perspectives of Chemistry. Chemistry is the study of the properties and behavior of matter. A property is a characteristic that allows us to recognize a particular type of matter. All the matter in the world is comprised of about 116 elements. ...
Esters A class of organic compounds that react with water to
... attached to the oxygen atom. Number according to the closest to the -CO- group regardless of where the alkyl substituents are . Determine the alkane that links the carbon atoms together. If there is a separation of a continuous link of carbon atoms due to the oxygen atom, individually name the t ...
... attached to the oxygen atom. Number according to the closest to the -CO- group regardless of where the alkyl substituents are . Determine the alkane that links the carbon atoms together. If there is a separation of a continuous link of carbon atoms due to the oxygen atom, individually name the t ...
Chapter 14 - An Introduction to Chemistry
... • Electronegativity, a measure of the electron attracting ability of atoms in chemical bonds is used to predict. – whether a chemical bond is nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. – which atom in a polar covalent bond is partial negative and which is partial positive. – which atom in an i ...
... • Electronegativity, a measure of the electron attracting ability of atoms in chemical bonds is used to predict. – whether a chemical bond is nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. – which atom in a polar covalent bond is partial negative and which is partial positive. – which atom in an i ...
Sample Questions
... 3. The average mass of a carbon atom is 12.011. Assuming you were able to pick up only one carbon unit, the chances that you would randomly get one with a mass of 12.011 is 4. Iron is biologically important in the transport of oxygen by red blood cells from the lungs to the various organs of the bod ...
... 3. The average mass of a carbon atom is 12.011. Assuming you were able to pick up only one carbon unit, the chances that you would randomly get one with a mass of 12.011 is 4. Iron is biologically important in the transport of oxygen by red blood cells from the lungs to the various organs of the bod ...
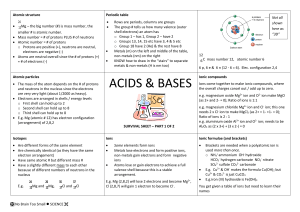
acids and bases - No Brain Too Small
... Ions come together to make ionic compounds, where the overall charges cancel out / add up to zero. e.g. magnesium oxide Mg2+ ion and O2- ion make MgO (as 2+ and 2- = 0); Ratio of ions is 1:1 ...
... Ions come together to make ionic compounds, where the overall charges cancel out / add up to zero. e.g. magnesium oxide Mg2+ ion and O2- ion make MgO (as 2+ and 2- = 0); Ratio of ions is 1:1 ...
1. What is a Chemical Reaction?
... • A chemical reaction is the process by which atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances(s) with new chemical and physical properties. • A chemical reaction is another name for a chemical change. • When substances chemically react, observations can be made that provi ...
... • A chemical reaction is the process by which atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances(s) with new chemical and physical properties. • A chemical reaction is another name for a chemical change. • When substances chemically react, observations can be made that provi ...
Organic Chemistry
... • As atomic size increases down the group, bonds between identical atoms become longer and weaker. – A C–C bond is much stronger than a Si–Si bond. ...
... • As atomic size increases down the group, bonds between identical atoms become longer and weaker. – A C–C bond is much stronger than a Si–Si bond. ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... Reactions of Aromatic Compounds • Unlike in alkenes and alkynes, electrons do not sit between two atoms. • Electrons are delocalized; this stabilizes aromatic compounds. Organic and Biological Chemistry ...
... Reactions of Aromatic Compounds • Unlike in alkenes and alkynes, electrons do not sit between two atoms. • Electrons are delocalized; this stabilizes aromatic compounds. Organic and Biological Chemistry ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... Reactions of Aromatic Compounds • Unlike in alkenes and alkynes, electrons do not sit between two atoms. • Electrons are delocalized; this stabilizes aromatic compounds. Organic and Biological Chemistry ...
... Reactions of Aromatic Compounds • Unlike in alkenes and alkynes, electrons do not sit between two atoms. • Electrons are delocalized; this stabilizes aromatic compounds. Organic and Biological Chemistry ...
Chem 30 Diploma Review
... • Compound with the same molecular formula but different structures – They will have different chemical and physical properties – based on their different structures ...
... • Compound with the same molecular formula but different structures – They will have different chemical and physical properties – based on their different structures ...
Chapter 12 - "Chemical Formulas and Equations"
... – An oxidation reduction reaction is one in which electrons are transferred between atoms. – Oxidation is the loss of electrons – Reduction is the gain of electrons – Oxidizing agents are substances which take electrons away from other atoms. • An oxidizing agent is reduced when it oxidizes another ...
... – An oxidation reduction reaction is one in which electrons are transferred between atoms. – Oxidation is the loss of electrons – Reduction is the gain of electrons – Oxidizing agents are substances which take electrons away from other atoms. • An oxidizing agent is reduced when it oxidizes another ...
Chapter 8 Test Review
... •Single replacement reaction •Double replacement reaction •Synthesis reaction ...
... •Single replacement reaction •Double replacement reaction •Synthesis reaction ...
CHEMISTRY
... (4) I-isopropyl ethylene 26. Usually ionic compounds are soluble in polar solvents and covalent compounds is non-polar solvents. However covalent compounds dissolve in polar solvents like water due to: ...
... (4) I-isopropyl ethylene 26. Usually ionic compounds are soluble in polar solvents and covalent compounds is non-polar solvents. However covalent compounds dissolve in polar solvents like water due to: ...
GRADE 12A: Chemistry 5
... central atom. A group of electrons might be a lone pair of electrons, a single, double or triple covalent bond. Ask students to model various atoms in molecules (e.g. the carbon in methane could be represented by twisting two bilobar balloons together). The lobes automatically arrange themselves int ...
... central atom. A group of electrons might be a lone pair of electrons, a single, double or triple covalent bond. Ask students to model various atoms in molecules (e.g. the carbon in methane could be represented by twisting two bilobar balloons together). The lobes automatically arrange themselves int ...