CHM 101 - Academic Computer Center
... Cold packs, whose temperatures are lowered when ammonium nitrate dissolves in water, are carried by athletic trainers when transporting ice is not possible. Which of the following is true of this reaction? A. H < 0, process is exothermic B. H > 0, process is exothermic C. H < 0, process is endoth ...
... Cold packs, whose temperatures are lowered when ammonium nitrate dissolves in water, are carried by athletic trainers when transporting ice is not possible. Which of the following is true of this reaction? A. H < 0, process is exothermic B. H > 0, process is exothermic C. H < 0, process is endoth ...
Aim: How can we describe Hydrocarbons?
... • Have low melting points (due to weak intermolecular forces that hold them together) – The great number of carbons leads to a higher melting point. ...
... • Have low melting points (due to weak intermolecular forces that hold them together) – The great number of carbons leads to a higher melting point. ...
Exam 3 Review - CHEMpossible
... 2. Which statement is true regarding bond order, bond length, and bond energy? a. As the bond order increases, the bond length increases. b. As the bond order increases, the bond length decreases. c. As the bond order increases, the bond energy decreases. d. As the bond energy increases, the bond le ...
... 2. Which statement is true regarding bond order, bond length, and bond energy? a. As the bond order increases, the bond length increases. b. As the bond order increases, the bond length decreases. c. As the bond order increases, the bond energy decreases. d. As the bond energy increases, the bond le ...
atoms
... The number of protons in an atom defines what element it is. For example carbon atoms have six protons, hydrogen atoms have one, and oxygen atoms have eight. The number of protons in an atom is referred to as the atomic number of that element. ...
... The number of protons in an atom defines what element it is. For example carbon atoms have six protons, hydrogen atoms have one, and oxygen atoms have eight. The number of protons in an atom is referred to as the atomic number of that element. ...
2. Essential Chemistry
... Chemical Reactions o Cells constantly rearrange molecules by breaking existing chemical bonds and forming new ones o Such changes in the chemical composition of matter are called chemical reactions o Chemical reactions enable atoms to give up or acquire electrons in order to complete their outer she ...
... Chemical Reactions o Cells constantly rearrange molecules by breaking existing chemical bonds and forming new ones o Such changes in the chemical composition of matter are called chemical reactions o Chemical reactions enable atoms to give up or acquire electrons in order to complete their outer she ...
www.theallpapers.com
... Dot-and-cross structures for the molecules mentioned (outer shells only). Emphasise that bonds are stable entities, so give out heat when they form. This stability is due to attraction of the bonding electrons to two nuclei rather than just one. The use of two dots (or two crosses) in a dative bond ...
... Dot-and-cross structures for the molecules mentioned (outer shells only). Emphasise that bonds are stable entities, so give out heat when they form. This stability is due to attraction of the bonding electrons to two nuclei rather than just one. The use of two dots (or two crosses) in a dative bond ...
MSWord
... Wen-Xiong Zhang, Masayoshi Nishiura and Zhaomin Hou* Organometallic Chemistry Laboratory, RIKEN, Hirosawa 2-1, Wako, Saitama 351-0198, Japan [email protected] ...
... Wen-Xiong Zhang, Masayoshi Nishiura and Zhaomin Hou* Organometallic Chemistry Laboratory, RIKEN, Hirosawa 2-1, Wako, Saitama 351-0198, Japan [email protected] ...
Organic Molecules Lab
... Introduction: Organic molecules are the chemicals that sustain biological processes in all living things. These compounds are always made up of more than one type of element and must be synthesized by living organisms. What makes an organic molecule different from an inorganic molecule is that organ ...
... Introduction: Organic molecules are the chemicals that sustain biological processes in all living things. These compounds are always made up of more than one type of element and must be synthesized by living organisms. What makes an organic molecule different from an inorganic molecule is that organ ...
Final Exam Review
... Identify valid α-amino acids and peptides that could be found in nature. Know the following reaction mechanisms: SN1/SN2/E1/E2 reactions: SN2/E2 transition states and SN1/E1 intermediates Electrophilic aromatic substitution – draw out resonance structures for the cationic intermediate Acetal formati ...
... Identify valid α-amino acids and peptides that could be found in nature. Know the following reaction mechanisms: SN1/SN2/E1/E2 reactions: SN2/E2 transition states and SN1/E1 intermediates Electrophilic aromatic substitution – draw out resonance structures for the cationic intermediate Acetal formati ...
how reactions occur
... • Reactions between oppositely-charged ions in solution occur almost instantaneously. This is because the ions are strongly attracted to each other because of their opposite electrical charges. ...
... • Reactions between oppositely-charged ions in solution occur almost instantaneously. This is because the ions are strongly attracted to each other because of their opposite electrical charges. ...
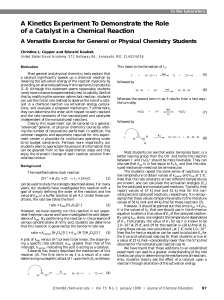
JCE0198 p0087 A Kinetics Experiment To Demonstrate the Role of
... a catalyst significantly speeds up a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy of the reaction (typically by providing an alternate pathway from reactants to products) (1–3). Although this statement seems reasonable, students rarely have a chance to experimentally test its validity. We fin ...
... a catalyst significantly speeds up a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy of the reaction (typically by providing an alternate pathway from reactants to products) (1–3). Although this statement seems reasonable, students rarely have a chance to experimentally test its validity. We fin ...
atoms-chemical
... unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that one atom strips an electron completely from the other becoming ions and form an ionic bond. • sodium with one valence electron • chlorine with 7 valence electrons ...
... unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that one atom strips an electron completely from the other becoming ions and form an ionic bond. • sodium with one valence electron • chlorine with 7 valence electrons ...
Classes of organic acids and bases
... acids. Acetic acids (2 carbons) has a pKa of 4.8. Anion has 3 unhybridized p orbitals w/ total of 4 e-. They form a 3-atom π molecular orbital system; ½ π connects C to each O. ...
... acids. Acetic acids (2 carbons) has a pKa of 4.8. Anion has 3 unhybridized p orbitals w/ total of 4 e-. They form a 3-atom π molecular orbital system; ½ π connects C to each O. ...
FHN - Chemical and Physical Changes
... change, but the substances in the material stay the same. Change in state Solid melting to a liquid Liquid evaporating to a gas Gas condensing to a liquid Liquid freezing into a solid Usually occur with a change in temperature Can also be when a substance dissolves in a liquid, but doe ...
... change, but the substances in the material stay the same. Change in state Solid melting to a liquid Liquid evaporating to a gas Gas condensing to a liquid Liquid freezing into a solid Usually occur with a change in temperature Can also be when a substance dissolves in a liquid, but doe ...
Lipids
... A molecule of fat (triglyceride) is produced by the combination of three fatty acid molecules with one glycerol molecule. A condensation reaction takes place between a hydroxyl group of the glycerol and the carboxyl group of a fatty acid. The bond is called an ester linkage. ...
... A molecule of fat (triglyceride) is produced by the combination of three fatty acid molecules with one glycerol molecule. A condensation reaction takes place between a hydroxyl group of the glycerol and the carboxyl group of a fatty acid. The bond is called an ester linkage. ...
Exam 2 Fall 2005 Chemsitry 1211
... Ca(OH)2 solution, what is the molarity of the Ca(OH)2 solution? a.) b.) c.) d.) e.) ...
... Ca(OH)2 solution, what is the molarity of the Ca(OH)2 solution? a.) b.) c.) d.) e.) ...
Chapter 1: Matter, Measurement and Problem Solving
... elements found as multi-atom molecules in nature) 2) combine together to make compounds ...
... elements found as multi-atom molecules in nature) 2) combine together to make compounds ...
chemical reaction - Peoria Public Schools
... chemical reaction that uses symbols to show the relationship between the reactants and products ...
... chemical reaction that uses symbols to show the relationship between the reactants and products ...
Chemistry A - Montgomery County Public Schools
... identify traditional nomenclature (-ic and -ous suffixes). (H) name straight chain organic compounds (alkanes through decane). write symbols to represent elements, including diatomic elements, given a periodic table. Reactions transpose word equations into symbolic chemical equations and vic ...
... identify traditional nomenclature (-ic and -ous suffixes). (H) name straight chain organic compounds (alkanes through decane). write symbols to represent elements, including diatomic elements, given a periodic table. Reactions transpose word equations into symbolic chemical equations and vic ...
Structure of Molecules and Compounds | Principles of Biology from
... refer to the carbons that have attached chain branches or multiple bonds. © 2012 Nature Education All rights reserved. Figure Detail Carbon's unique bonding properties allow complex structures to form around the carbon atom. Isomers are compounds with the same number of atoms of the same elements co ...
... refer to the carbons that have attached chain branches or multiple bonds. © 2012 Nature Education All rights reserved. Figure Detail Carbon's unique bonding properties allow complex structures to form around the carbon atom. Isomers are compounds with the same number of atoms of the same elements co ...