Chem Course Desc2. New
... your life more comfortable. Chemistry is needed to understand many processes in a variety of industries: pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, petroleum, plastics, food technology, etc. Chemistry is also the basis of all life on Earth, from bacteria to human beings and everything in between. In our most basic ...
... your life more comfortable. Chemistry is needed to understand many processes in a variety of industries: pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, petroleum, plastics, food technology, etc. Chemistry is also the basis of all life on Earth, from bacteria to human beings and everything in between. In our most basic ...
CHEMISTRY 133 LECTURE / STUDY GUIDE FOR R.H. LANGLEY
... Write balanced chemical equations for each of the following reactions. a. Water reacts with phosphorus trichloride to produce hydrogen chloride and H3PO3. b. Water reacts with diboron trisulfide to produce H3BO3 (boric acid) and hydrogen sulfide. c. Zinc metal (Zn) reacts with hydrochloric acid to p ...
... Write balanced chemical equations for each of the following reactions. a. Water reacts with phosphorus trichloride to produce hydrogen chloride and H3PO3. b. Water reacts with diboron trisulfide to produce H3BO3 (boric acid) and hydrogen sulfide. c. Zinc metal (Zn) reacts with hydrochloric acid to p ...
STUDY MATERIAL 2016-17 CHEMISTRY CLASS XII
... 12. Packing efficiency =volume occupied by spheres (Particles)/volume of unit cell x 100 13. For simple cubic unit cell the packing efficiency=1x4/3 x πr3/8 x r3 x 100 =52.4 % 14. The packing efficiency in fcc =4 x 4/3 x πr3/16 x 2 1/2 r3 x 100 =74 % 15. The packing efficiency in bcc =2 x 4/3 x πr3/ ...
... 12. Packing efficiency =volume occupied by spheres (Particles)/volume of unit cell x 100 13. For simple cubic unit cell the packing efficiency=1x4/3 x πr3/8 x r3 x 100 =52.4 % 14. The packing efficiency in fcc =4 x 4/3 x πr3/16 x 2 1/2 r3 x 100 =74 % 15. The packing efficiency in bcc =2 x 4/3 x πr3/ ...
Handout
... Can you recognize molecules that have interactions through induced-dipoleinduced-dipole (van der Waals), dipole-dipole and hydrogen bond? Can you compare the b.p. and solubility of molecules based on their structures? ...
... Can you recognize molecules that have interactions through induced-dipoleinduced-dipole (van der Waals), dipole-dipole and hydrogen bond? Can you compare the b.p. and solubility of molecules based on their structures? ...
Version A
... of questions that you have skipped and place that number next to your name ON YOUR ANSWER SHEET and circle it. ...
... of questions that you have skipped and place that number next to your name ON YOUR ANSWER SHEET and circle it. ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... the ions that each contains. We then correlate these charged ionic species with the ones shown in the diagram. Solve: The diagram shows twice as many cations as anions, consistent with the formulation K 2SO4. Aqueous Check: Notice that the total net charge in the diagram is zero, as it must be if it ...
... the ions that each contains. We then correlate these charged ionic species with the ones shown in the diagram. Solve: The diagram shows twice as many cations as anions, consistent with the formulation K 2SO4. Aqueous Check: Notice that the total net charge in the diagram is zero, as it must be if it ...
Mead Chemistry Lap 11: Stoichiometry Chapter 12 12.1 Balanced
... Mead Chemistry Lap 11: Stoichiometry Chapter 12 12.1 Balanced Chemical Equations A. Balanced equations • Used to find how much reactant is needed • Used to predict how much product will be made • You can use amount of one substance to find the amounts of the other substances • Quantity usually in mo ...
... Mead Chemistry Lap 11: Stoichiometry Chapter 12 12.1 Balanced Chemical Equations A. Balanced equations • Used to find how much reactant is needed • Used to predict how much product will be made • You can use amount of one substance to find the amounts of the other substances • Quantity usually in mo ...
6 Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory
... ith a knowledge of the electronic structure of atoms and their orbitals as background, we now proceed to discuss the behaviour of atoms when their ‘atomic orbitals’ interact to form chemical bonds. Free atoms have a random motion and possess energies. Farther the atoms are more will be the energy of ...
... ith a knowledge of the electronic structure of atoms and their orbitals as background, we now proceed to discuss the behaviour of atoms when their ‘atomic orbitals’ interact to form chemical bonds. Free atoms have a random motion and possess energies. Farther the atoms are more will be the energy of ...
Chapter 8 "Ionic versus Covalent Bonding"
... What you learn in this chapter about chemical bonding and molecular structure will help you understand how different substances with the same atoms can have vastly different physical and chemical properties. For example, oxygen gas (O 2) is essential for life, yet ozone (O3) is toxic to cells, altho ...
... What you learn in this chapter about chemical bonding and molecular structure will help you understand how different substances with the same atoms can have vastly different physical and chemical properties. For example, oxygen gas (O 2) is essential for life, yet ozone (O3) is toxic to cells, altho ...
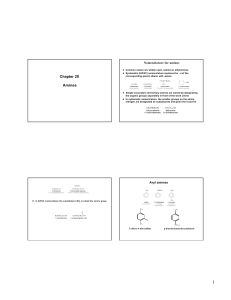
Amines
... are used to indicate that nitrogen has replaced carbon in the corresponding hydrocarbon H The nitrogen is assigned position 1 and the ring is numbered to give the lowest overall set of locants to the heteroatoms ...
... are used to indicate that nitrogen has replaced carbon in the corresponding hydrocarbon H The nitrogen is assigned position 1 and the ring is numbered to give the lowest overall set of locants to the heteroatoms ...
Unit XI Laboratory work № 11 Physical chemistry Questions: Surface
... Molecules of adsorbate are not changed during physical adsorption. In case of chemical adsorption the transit of changes take place. Liquid-gas and liquid-liquid adsorption. The particles of gases or dissolved substances can not be adsorbed by liquids. Adsorption accompanies the dissolution process. ...
... Molecules of adsorbate are not changed during physical adsorption. In case of chemical adsorption the transit of changes take place. Liquid-gas and liquid-liquid adsorption. The particles of gases or dissolved substances can not be adsorbed by liquids. Adsorption accompanies the dissolution process. ...
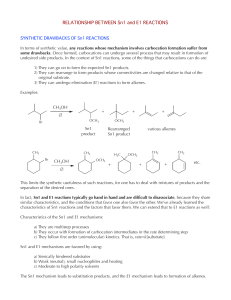
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN Sn1 and E1 REACTIONS
... This limits the synthetic usefulness of such reactions, for one has to deal with mixtures of products and the separation of the desired ones. In fact, Sn1 and E1 reactions typically go hand in hand and are difficult to disassociate, because they share similar characteristics, and the conditions that ...
... This limits the synthetic usefulness of such reactions, for one has to deal with mixtures of products and the separation of the desired ones. In fact, Sn1 and E1 reactions typically go hand in hand and are difficult to disassociate, because they share similar characteristics, and the conditions that ...
CHAPTER 10-11 PRACTICE FOR TEST Answer Section
... ____ 33. The lowest whole-number ratio of the elements in a compound is called the ____. a. empirical formula c. binary formula b. molecular formula d. representative formula ____ 34. What is the empirical formula of a compound that is 40% sulfur and 60% oxygen by weight? a. SO c. SO b. SO d. S O __ ...
... ____ 33. The lowest whole-number ratio of the elements in a compound is called the ____. a. empirical formula c. binary formula b. molecular formula d. representative formula ____ 34. What is the empirical formula of a compound that is 40% sulfur and 60% oxygen by weight? a. SO c. SO b. SO d. S O __ ...
Introduction: A Historical Approach to Catalysis
... same way, produce the same crystal forms: the crystal form does not depend on the nature of the atoms, but only on their number and mode of combination” v synthesized benzene F.C. Jentoft Dept. AC / FHI Berlin ...
... same way, produce the same crystal forms: the crystal form does not depend on the nature of the atoms, but only on their number and mode of combination” v synthesized benzene F.C. Jentoft Dept. AC / FHI Berlin ...
Organic Chemistry II with Dr Roche
... Since ethers are relatively unreactive and are strongly polar (due to the lone pairs on the oxygen), they are commonly used as solvents for organic reactions. (Diethyl ether and THF, the Grignard reaction). Ethers will often form complexes with molecules that have vacant orbitals, enabling ‘unstable ...
... Since ethers are relatively unreactive and are strongly polar (due to the lone pairs on the oxygen), they are commonly used as solvents for organic reactions. (Diethyl ether and THF, the Grignard reaction). Ethers will often form complexes with molecules that have vacant orbitals, enabling ‘unstable ...
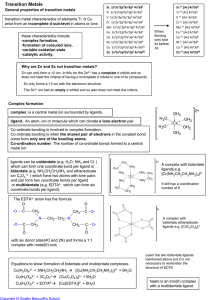
The d-Block Elements
... the overall trends are rather common, however, and in many cases, they are attributable to the stability associated with filled and half-filled subshells. For example, the 4s23d10 electron configuration of zinc results in its strong tendency to form the stable Zn2+ ion, with a 3d10 electron configur ...
... the overall trends are rather common, however, and in many cases, they are attributable to the stability associated with filled and half-filled subshells. For example, the 4s23d10 electron configuration of zinc results in its strong tendency to form the stable Zn2+ ion, with a 3d10 electron configur ...
PC_Chemistry_Macomb_April08
... The integrity of the scientific process depends on scientists and citizens understanding and respecting the “Nature of Science.” Openness to new ideas, skepticism, and honesty are attributes required for good scientific practice. Scientists must use logical reasoning during investigation design, ana ...
... The integrity of the scientific process depends on scientists and citizens understanding and respecting the “Nature of Science.” Openness to new ideas, skepticism, and honesty are attributes required for good scientific practice. Scientists must use logical reasoning during investigation design, ana ...