Chapter 3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions
... 29. The molecular formula of aspirin is C9H8O4. How many aspirin molecules are present in one 500-milligram tablet? A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 29. The molecular formula of aspirin is C9H8O4. How many aspirin molecules are present in one 500-milligram tablet? A. B. C. D. E. ...
Kinetic multi-layer model of aerosol surface and bulk chemistry (KM
... The model is based on the PRA framework of gas–particle interactions (Pöschl et al., 2007), and it includes reversible adsorption, surface reactions and surface-bulk exchange as well as bulk diffusion and reaction. Unlike earlier models, KM-SUB does not require simplifying assumptions about steady- ...
... The model is based on the PRA framework of gas–particle interactions (Pöschl et al., 2007), and it includes reversible adsorption, surface reactions and surface-bulk exchange as well as bulk diffusion and reaction. Unlike earlier models, KM-SUB does not require simplifying assumptions about steady- ...
Ionic Conductivity in the Metal–Organic Framework UiO
... Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are a class of microporous materials consisting of metal ion nodes linked together by multitopic organic ligands. These compounds have been studied extensively in recent years for their record high surface areas and a wide range of related potential applications. Most ...
... Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are a class of microporous materials consisting of metal ion nodes linked together by multitopic organic ligands. These compounds have been studied extensively in recent years for their record high surface areas and a wide range of related potential applications. Most ...
Specification and sample assessment material - Edexcel
... understand that the noble gases (Group 0) are a family of inert gases and explain their lack of reactivity in terms of their electronic configurations. ...
... understand that the noble gases (Group 0) are a family of inert gases and explain their lack of reactivity in terms of their electronic configurations. ...
Palladium and Ruthenium Catalyzed Reactions By Bryan Jaksic
... provide a simple method for the formation of substituted alkynes, a commonly found functionality within important organic molecules. These reactions are generally believed to be catalyzed by a Pd(0)L2 species which are generated in situ from a palladium precatalyst and are often co-catalyzed by CuI ...
... provide a simple method for the formation of substituted alkynes, a commonly found functionality within important organic molecules. These reactions are generally believed to be catalyzed by a Pd(0)L2 species which are generated in situ from a palladium precatalyst and are often co-catalyzed by CuI ...
Lipids - Food Science & Human Nutrition
... Naturally occurring biological substances made primarily of C, H, and O of pronounced hydrophobicity that are soluble in organic solvents but have limited solubility in water ...
... Naturally occurring biological substances made primarily of C, H, and O of pronounced hydrophobicity that are soluble in organic solvents but have limited solubility in water ...
Document
... • To make solutions of lower concentrations from these stock solutions, more solvent is added the amount of solute doesn’t change, just the volume of solution moles solute in solution 1 = moles solute in solution 2 ...
... • To make solutions of lower concentrations from these stock solutions, more solvent is added the amount of solute doesn’t change, just the volume of solution moles solute in solution 1 = moles solute in solution 2 ...
Lectures 4-6
... Collins Oxidation (CrO3 • 2pyridine) TL 1969, 336 - CrO3 (anhydrous) + pyridine (anhydrous) ...
... Collins Oxidation (CrO3 • 2pyridine) TL 1969, 336 - CrO3 (anhydrous) + pyridine (anhydrous) ...
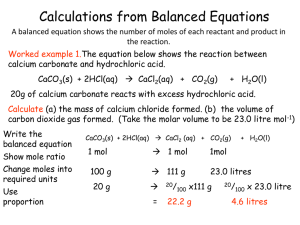
Calculations from Balanced Equations
... You can use the relative numbers of moles of substances, as shown in balanced equations, to calculate the amounts of reactants needed or the amounts of products produced. A limiting reactant is the substance that is fully used up and thereby limits the possible extent of the reaction. Other reactant ...
... You can use the relative numbers of moles of substances, as shown in balanced equations, to calculate the amounts of reactants needed or the amounts of products produced. A limiting reactant is the substance that is fully used up and thereby limits the possible extent of the reaction. Other reactant ...
When wood, paper, and wax are burned, they ap
... compound contains. A knowledge of its chemical formula allows us to calculate the percent composition. Experimental determination of percent composition and the molar mass of a compound enables us to determine its chemical formula. Writing Chemical Equations An effective way to represent the outcome ...
... compound contains. A knowledge of its chemical formula allows us to calculate the percent composition. Experimental determination of percent composition and the molar mass of a compound enables us to determine its chemical formula. Writing Chemical Equations An effective way to represent the outcome ...
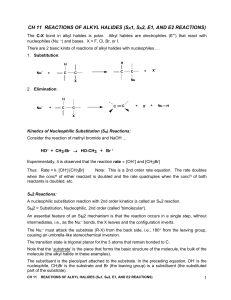
Alkyl Halides02
... A nucleophilic substitution reaction with 2nd order kinetics is called an SN2 reaction. SN2 = Substitution, Nucleophilic, 2nd order (called 'bimolecular'). An essential feature of an SN2 mechanism is that the reaction occurs in a single step, without intermediates, i.e., as the Nu:- bonds, the X lea ...
... A nucleophilic substitution reaction with 2nd order kinetics is called an SN2 reaction. SN2 = Substitution, Nucleophilic, 2nd order (called 'bimolecular'). An essential feature of an SN2 mechanism is that the reaction occurs in a single step, without intermediates, i.e., as the Nu:- bonds, the X lea ...
Organic Chemistry
... Organic nitriles (R-C≡N) are usually considered together with R-C(=O)-Z compounds in organic chemistry textbooks. This is because nitriles (R-C≡N) are readily hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids (R-C(=O)-OH) via intermediate amides (R-C(=O)-NH2) (Figure 15.13). Figure 15.13 ...
... Organic nitriles (R-C≡N) are usually considered together with R-C(=O)-Z compounds in organic chemistry textbooks. This is because nitriles (R-C≡N) are readily hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids (R-C(=O)-OH) via intermediate amides (R-C(=O)-NH2) (Figure 15.13). Figure 15.13 ...
Part 3-ICHO-31-35
... The standard enthalpy of formation of CO2(g) and H2O(l) at 25.00 °C are –393.51 and –285.83 kJ mol-1, respectively. The gas constant, R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1. (Relative atomic masses : H = 1.0; C = 12.0; O = 16.0) A sample of solid Q that weighs 0.6000 g, is combusted in an excess of oxygen in a bomb ...
... The standard enthalpy of formation of CO2(g) and H2O(l) at 25.00 °C are –393.51 and –285.83 kJ mol-1, respectively. The gas constant, R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1. (Relative atomic masses : H = 1.0; C = 12.0; O = 16.0) A sample of solid Q that weighs 0.6000 g, is combusted in an excess of oxygen in a bomb ...
Orgo 1-Test 1 - HCC Learning Web
... Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________ ...
... Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________ ...
amine
... with water has the following form, illustrated for the reaction of methylamine with water to give methylammonium hydroxide. • pKb is defined as the negative logarithm of Kb. ...
... with water has the following form, illustrated for the reaction of methylamine with water to give methylammonium hydroxide. • pKb is defined as the negative logarithm of Kb. ...
CHE 1402 Lab Manual
... Place 0.30 g of CaCO3 in a test tube and carefully insert another smaller test tube in it containing 5mL of 4 M HCl (be sure NOT to mix CaCO3 and HCl before the experiment). Assemble the apparatus illustrated in Figure 2.1 but do not attach the test tube. Be sure that tube B does not extend below th ...
... Place 0.30 g of CaCO3 in a test tube and carefully insert another smaller test tube in it containing 5mL of 4 M HCl (be sure NOT to mix CaCO3 and HCl before the experiment). Assemble the apparatus illustrated in Figure 2.1 but do not attach the test tube. Be sure that tube B does not extend below th ...
PART 3-ICHO 11-15
... of this alloy weighing 1.2860 g, was treated with a solution of concentrated nitric acid. The individual compound of metal A obtained as a precipitate, was separated, thoroughly washed, dried and calcinated. The mass of the precipitate after the calcination to constant mass, was 0.3265 g. An aqueous ...
... of this alloy weighing 1.2860 g, was treated with a solution of concentrated nitric acid. The individual compound of metal A obtained as a precipitate, was separated, thoroughly washed, dried and calcinated. The mass of the precipitate after the calcination to constant mass, was 0.3265 g. An aqueous ...
Alkenes notes
... Secondary carbocations are more stable than primary carbocations. Tertiary carbocations are even more stable than secondary cations. Therefore the product of route 1 (2-bromopropane) is a more likely product than the product of route 2 (1-bromopropane). Thus 2-bromopropane will be the major product ...
... Secondary carbocations are more stable than primary carbocations. Tertiary carbocations are even more stable than secondary cations. Therefore the product of route 1 (2-bromopropane) is a more likely product than the product of route 2 (1-bromopropane). Thus 2-bromopropane will be the major product ...
Modern Chemistry
... the answer as 0.571429. a. Is the setup for calculating density correct? b. How many significant figures should the answer contain? 4. It was shown in the text that in a value such as 4000 g, the precision of the number is uncertain. The zeros may or may not be significant. a. Suppose that the mass ...
... the answer as 0.571429. a. Is the setup for calculating density correct? b. How many significant figures should the answer contain? 4. It was shown in the text that in a value such as 4000 g, the precision of the number is uncertain. The zeros may or may not be significant. a. Suppose that the mass ...
The bite angle makes the catalyst
... work has shown that replacing the propyl group by a methyl group leads indeed to lower linearities (60±80%) [33]. The increasing embracement of the allyl fragment at large bite angles not only dictates the regioselectivity, but it increasingly hampers the reaction. It is therefore not surprising, th ...
... work has shown that replacing the propyl group by a methyl group leads indeed to lower linearities (60±80%) [33]. The increasing embracement of the allyl fragment at large bite angles not only dictates the regioselectivity, but it increasingly hampers the reaction. It is therefore not surprising, th ...
EDEXCEL A LeveL - Hodder Education
... which react. This gives an empirical formula which shows the simplest whole number ratio for the atoms of different elements in a compound. ...
... which react. This gives an empirical formula which shows the simplest whole number ratio for the atoms of different elements in a compound. ...
Carbonyl Chemistry (12 Lectures) Aldehydes and Ketones
... The mechanism involves nucleophilic addition of the amine to the carbonyl to form a carbinolamine. Enamines form only if the carbonyl compound has at least one hydrogen on a carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Formation of the alkene may be recognized as an elimination reaction. ...
... The mechanism involves nucleophilic addition of the amine to the carbonyl to form a carbinolamine. Enamines form only if the carbonyl compound has at least one hydrogen on a carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Formation of the alkene may be recognized as an elimination reaction. ...
Problem Authors - PianetaChimica
... Kinetics: Integrated first order rate equation; analysis of complex reaction mechanisms using the steady state approximation; determination of reaction order and activation energy. Thermodynamics: Relationship between equilibrium constant, electromotive force and standard Gibbs free energy; the vari ...
... Kinetics: Integrated first order rate equation; analysis of complex reaction mechanisms using the steady state approximation; determination of reaction order and activation energy. Thermodynamics: Relationship between equilibrium constant, electromotive force and standard Gibbs free energy; the vari ...