1. (a) (i) 2Ca(NO3)2 → 2CaO + 4NO2 + O2 formulae correct (1
... • Recognizing the existence of hydrogen bonds ( between molecules) (1) • That each molecule can form more than one hydrogen bond because of the two OH (and two S=O groups) / or a description of hydrogen bonds in this case / or a diagram showing the hydrogen bonds (1) ...
... • Recognizing the existence of hydrogen bonds ( between molecules) (1) • That each molecule can form more than one hydrogen bond because of the two OH (and two S=O groups) / or a description of hydrogen bonds in this case / or a diagram showing the hydrogen bonds (1) ...
Unit 3: 1 Equilibrium and the Constant, K
... environmental processes that are reversible, construct an explanation that connects the observations to the reversibility of the underlying chemical reactions or processes. [See SP 6.2; Essential knowledge 6.A.1] Learning objective 6.2 The student can, given a manipulation of a chemical reaction or ...
... environmental processes that are reversible, construct an explanation that connects the observations to the reversibility of the underlying chemical reactions or processes. [See SP 6.2; Essential knowledge 6.A.1] Learning objective 6.2 The student can, given a manipulation of a chemical reaction or ...
Document
... • Alkenes have low melting points and boiling points. • Melting and boiling points increase as the number of carbons increases because of increased surface area. • Alkenes are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in water. • The C—C single bond between an alkyl group and one of the double bond ...
... • Alkenes have low melting points and boiling points. • Melting and boiling points increase as the number of carbons increases because of increased surface area. • Alkenes are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in water. • The C—C single bond between an alkyl group and one of the double bond ...
Laboratory Manual
... lot of fun. But chemistry can also be dangerous, and getting hurt is definitely not fun! For this reason there are safety rules to follow and protective equipment to know its location and how to use it. This manual has “Green Chemistry” in the title. This means that when compared to similar experime ...
... lot of fun. But chemistry can also be dangerous, and getting hurt is definitely not fun! For this reason there are safety rules to follow and protective equipment to know its location and how to use it. This manual has “Green Chemistry” in the title. This means that when compared to similar experime ...
Document
... Now let us apply this background to the study of the organic chemistry of metabolism We study two key metabolic pathways • -oxidation of fatty acids • glycolysis ...
... Now let us apply this background to the study of the organic chemistry of metabolism We study two key metabolic pathways • -oxidation of fatty acids • glycolysis ...
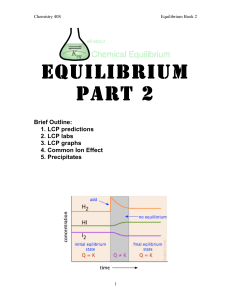
Equilibrium Part 2
... a system at equilibrium. The system attempts to remove added heat by using it up in the forward reaction (endothermic reaction). The equilibrium position shifts towards the right (products). The concentration of NO2 increases and the concentration of N2O4 decreases. We can also think of adding heat ...
... a system at equilibrium. The system attempts to remove added heat by using it up in the forward reaction (endothermic reaction). The equilibrium position shifts towards the right (products). The concentration of NO2 increases and the concentration of N2O4 decreases. We can also think of adding heat ...
aldehyde group - Imperial Valley College Faculty Websites
... This is a section of a phenolic ( i.e. Bakelite) which is an example of a thermosetting polymer. These polymers are used in electrical equipment because of their insulating and fire-resistant properties. ...
... This is a section of a phenolic ( i.e. Bakelite) which is an example of a thermosetting polymer. These polymers are used in electrical equipment because of their insulating and fire-resistant properties. ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
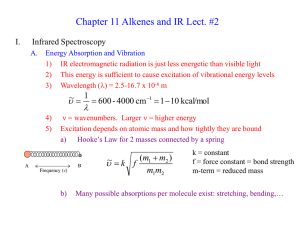
... Energy Absorption and Vibration 1) IR electromagnetic radiation is just less energetic than visible light 2) This energy is sufficient to cause excitation of vibrational energy levels 3) Wavelength (l) = 2.5-16.7 x 10-6 m ...
... Energy Absorption and Vibration 1) IR electromagnetic radiation is just less energetic than visible light 2) This energy is sufficient to cause excitation of vibrational energy levels 3) Wavelength (l) = 2.5-16.7 x 10-6 m ...
class notes 4
... Acid-Base Reactions (Acid-Base Reactions Always Go) Acid: Substance that produces H+ ions in aqueous solution is the Arrhenius definition of acid. Base: Substance that produces OH- in aqueous solution is the Arrhenius definition of base. Actually a hydrogen ion is a bare proton and will associate wi ...
... Acid-Base Reactions (Acid-Base Reactions Always Go) Acid: Substance that produces H+ ions in aqueous solution is the Arrhenius definition of acid. Base: Substance that produces OH- in aqueous solution is the Arrhenius definition of base. Actually a hydrogen ion is a bare proton and will associate wi ...
Chapter 3
... The formula of a compound indicates the number of atoms of each element in a unit of the compound. From a molecular or empirical formula, we can calculate what percent of the total mass is contributed by each element in a compound. A list of the percent by mass of each element in a compound is known ...
... The formula of a compound indicates the number of atoms of each element in a unit of the compound. From a molecular or empirical formula, we can calculate what percent of the total mass is contributed by each element in a compound. A list of the percent by mass of each element in a compound is known ...
Chapter 12
... The study of quantitative relationships between amounts of reactants used and products formed by a chemical reaction is called stoichiometry. Stoichiometry is based on the law of conservation of mass, which was introduced by Antoine Lavoisier in the eighteenth century. The law states that matter is ...
... The study of quantitative relationships between amounts of reactants used and products formed by a chemical reaction is called stoichiometry. Stoichiometry is based on the law of conservation of mass, which was introduced by Antoine Lavoisier in the eighteenth century. The law states that matter is ...
9: Formation of Alkenes and Alkynes. Elimination Reactions
... 2-methylpropene by an E1 reaction. t-Butyl bromide cannot undergo SN2 substitution since CH3 groups prevent backside approach of any nucleophile to its C-Br carbon. However, an E2 mechanism requires only that -:OEt approach a β-H, and there are 9 β-H's on t-butyl bromide that are all easily accessib ...
... 2-methylpropene by an E1 reaction. t-Butyl bromide cannot undergo SN2 substitution since CH3 groups prevent backside approach of any nucleophile to its C-Br carbon. However, an E2 mechanism requires only that -:OEt approach a β-H, and there are 9 β-H's on t-butyl bromide that are all easily accessib ...
Chapter 1: Chemistry: The Study of Change
... 24. Oxidation of a hydrocarbon gave a product composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The product that was purified and sent off for elemental analysis giving the following mass percents: 68.85% C and 4.95% H. Determine the empirical formula of this compound. (Section: 3.6) Ans: C7H6O2 25. Acetyle ...
... 24. Oxidation of a hydrocarbon gave a product composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The product that was purified and sent off for elemental analysis giving the following mass percents: 68.85% C and 4.95% H. Determine the empirical formula of this compound. (Section: 3.6) Ans: C7H6O2 25. Acetyle ...
Water deuteration and ortho-to-para nuclear spin ratio of H2 in
... increases, which assists molecular formation by absorbing interstellar radiation. The column density at a given time t after passing through the shock front is NH = n0 v0 t, where n0 and v0 are preshock H i gas density and velocity of the accretion flow, respectively. NH is converted into AV using t ...
... increases, which assists molecular formation by absorbing interstellar radiation. The column density at a given time t after passing through the shock front is NH = n0 v0 t, where n0 and v0 are preshock H i gas density and velocity of the accretion flow, respectively. NH is converted into AV using t ...
Chemistry 1250 - Sp17 Solutions for Midterm 1
... throughout. These are often referred to as solutions. Gases dissolve in each other to form solutions and gases dissolve in liquids to form solutions. Heterogeneous mixtures have physical and chemical properties that are NOT uniform throughout the sample. Heterogeneous mixtures may contain elements a ...
... throughout. These are often referred to as solutions. Gases dissolve in each other to form solutions and gases dissolve in liquids to form solutions. Heterogeneous mixtures have physical and chemical properties that are NOT uniform throughout the sample. Heterogeneous mixtures may contain elements a ...
J. Phys. Chem. 1993,97, 2618
... proposed that the addition of auxiliary substituents such as a 4'-dialkylamino group on the &phenyl ring of 3HF (see Figure 1) may greatly change the electron density distribution due to its strong electron donating property. Thus, the photophysical and photochemical properties may besignificantly a ...
... proposed that the addition of auxiliary substituents such as a 4'-dialkylamino group on the &phenyl ring of 3HF (see Figure 1) may greatly change the electron density distribution due to its strong electron donating property. Thus, the photophysical and photochemical properties may besignificantly a ...
Chapter 3
... – Long hydrocarbon chain (non-polar, hydrophobic) – Carboxylic acid functional group (polar, hydrophilic) ...
... – Long hydrocarbon chain (non-polar, hydrophobic) – Carboxylic acid functional group (polar, hydrophilic) ...
CHAPTER 19 TRANSITION METALS AND COORDINATION
... Sc3+ has no electrons in d orbitals. Ti3+ and V3+ have d electrons present. The color of transition metal complexes results from electron transfer between split d orbitals. If no d electrons are present, no electron transfer can occur, and the compounds are not colored. ...
... Sc3+ has no electrons in d orbitals. Ti3+ and V3+ have d electrons present. The color of transition metal complexes results from electron transfer between split d orbitals. If no d electrons are present, no electron transfer can occur, and the compounds are not colored. ...