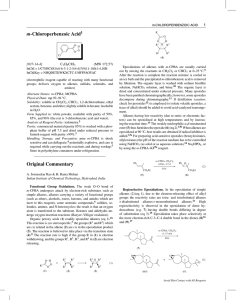
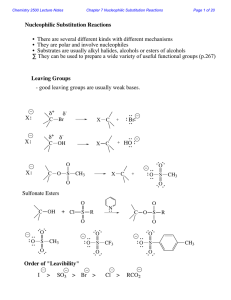
Chloroperbenzoic_aci..
... inert to this reagent), some aromatic compounds,6 sulfides, selenides, amines, and N-heterocycles; the result is that an oxygen atom is transferred to the substrate. Ketones and aldehydes undergo oxygen insertion reactions (Baeyer–Villiger oxidation). Organic peroxy acids (1) readily epoxidize alken ...
... inert to this reagent), some aromatic compounds,6 sulfides, selenides, amines, and N-heterocycles; the result is that an oxygen atom is transferred to the substrate. Ketones and aldehydes undergo oxygen insertion reactions (Baeyer–Villiger oxidation). Organic peroxy acids (1) readily epoxidize alken ...
Catalytic Asymmetric Induction. Highly Enantioselective Addition of
... Benzaldehyde does not react with diethylzinc at 0 "C in toluene. When a 1:1 :1 or 1 :2:2 mixture of benzaldehyde, diethylzinc, and (-)-DAIB in toluene was allowed to stand at 0 "C, the aldehyde was consumed slowly but only benzyl alcohol was obtained. No ethylation product could be detected. If, how ...
... Benzaldehyde does not react with diethylzinc at 0 "C in toluene. When a 1:1 :1 or 1 :2:2 mixture of benzaldehyde, diethylzinc, and (-)-DAIB in toluene was allowed to stand at 0 "C, the aldehyde was consumed slowly but only benzyl alcohol was obtained. No ethylation product could be detected. If, how ...
ALcohols CPP
... • select the longest chain of C atoms containing the O-H group; • remove the e and add ol after the basic name • number the chain starting from the end nearer the O-H group • the number is placed after the an and before the ol ... e.g butan-2-ol • as in alkanes, prefix with alkyl substituents ...
... • select the longest chain of C atoms containing the O-H group; • remove the e and add ol after the basic name • number the chain starting from the end nearer the O-H group • the number is placed after the an and before the ol ... e.g butan-2-ol • as in alkanes, prefix with alkyl substituents ...
Chemistry - Department of Education and Skills
... extremely low proportion of girls taking Physics. Another factor is the growing awareness among girls of the importance of science for future careers. A further important component in the improvement in the take-up of Physics by girls is the impact of the various phases of the Intervention Projects ...
... extremely low proportion of girls taking Physics. Another factor is the growing awareness among girls of the importance of science for future careers. A further important component in the improvement in the take-up of Physics by girls is the impact of the various phases of the Intervention Projects ...
Introduction - St. Olaf College
... interest. Note that proton shifts in addition to 13C shifts are available. ...
... interest. Note that proton shifts in addition to 13C shifts are available. ...
Hybridization of atomic orbitals
... hybrid orbitals to form a C-H bond. Four H atoms form four such bonds, and they are all equivalent. The CH4 molecule is the most cited molecule to have a tetrahedral shape. Other molecules and ions having tetrahedral shapes are SiO44-, SO42-, As are the cases with sp2, hybrid orbitals, one or two of ...
... hybrid orbitals to form a C-H bond. Four H atoms form four such bonds, and they are all equivalent. The CH4 molecule is the most cited molecule to have a tetrahedral shape. Other molecules and ions having tetrahedral shapes are SiO44-, SO42-, As are the cases with sp2, hybrid orbitals, one or two of ...
Chapter 19
... of an element changing to ions or the reverse. Some redox reactions involve changes in molecular substances or polyatomic ions in which atoms are covalently bonded to other atoms. For example, the following equation represents the redox reaction used to manufacture ammonia (NH 3). N 2(g) + 3H 2(g) → ...
... of an element changing to ions or the reverse. Some redox reactions involve changes in molecular substances or polyatomic ions in which atoms are covalently bonded to other atoms. For example, the following equation represents the redox reaction used to manufacture ammonia (NH 3). N 2(g) + 3H 2(g) → ...
Chapter 16 Controlling the yield of reactions
... is 48.8 at 455°C. An equilibrium mixture in a 2.0 L vessel at this temperature contains 0.220 mol of H2 and 0.110 mol of I2. a Calculate the concentration of HI in this mixture. b Another mixture was prepared by placing 4.0 mol of HI in a 2.0 L vessel at 330°C. At equilibrium 0.44 mol of H2 and 0.44 ...
... is 48.8 at 455°C. An equilibrium mixture in a 2.0 L vessel at this temperature contains 0.220 mol of H2 and 0.110 mol of I2. a Calculate the concentration of HI in this mixture. b Another mixture was prepared by placing 4.0 mol of HI in a 2.0 L vessel at 330°C. At equilibrium 0.44 mol of H2 and 0.44 ...
Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... Check The units of the answer are correct. The magnitude of the answer (25.8 g) is less than the initial mass of CO2 (37.8 g). This is reasonable because each carbon in CO2 has two oxygen atoms associated with it, while in C6H12O6 each carbon has only one oxygen atom associated with it and two hydro ...
... Check The units of the answer are correct. The magnitude of the answer (25.8 g) is less than the initial mass of CO2 (37.8 g). This is reasonable because each carbon in CO2 has two oxygen atoms associated with it, while in C6H12O6 each carbon has only one oxygen atom associated with it and two hydro ...
Toward Greener Chemistry Methods for Preparation of
... Recent technological advances and the need for materials with new functionalities and bet‐ ter performance have generated an enormous demand for novel materials. Nanostructures such as carbon nanotubes (CNTs) possess outstanding mechanical, electrical, thermal and chemical properties which make them ...
... Recent technological advances and the need for materials with new functionalities and bet‐ ter performance have generated an enormous demand for novel materials. Nanostructures such as carbon nanotubes (CNTs) possess outstanding mechanical, electrical, thermal and chemical properties which make them ...
Chemical Aspects of Distilling Wines into Brandy
... distill most rapidly in the earliest fractions of simple pot distillation. ...
... distill most rapidly in the earliest fractions of simple pot distillation. ...
EVS - RSC - Developments in Microwave Chemistry
... Initially, microwave chemistry was primarily used to carry out analytical processes such as ashing, digestion, extraction, fat analysis and protein hydrolysis. As microwave chemical synthesis has advanced, its applications have been extended to include the synthesis of fine chemicals, organometallic ...
... Initially, microwave chemistry was primarily used to carry out analytical processes such as ashing, digestion, extraction, fat analysis and protein hydrolysis. As microwave chemical synthesis has advanced, its applications have been extended to include the synthesis of fine chemicals, organometallic ...
Homework1-4-Answers
... 24. Oxidation of a hydrocarbon gave a product composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The product that was purified and sent off for elemental analysis giving the following mass percents: 68.85% C and 4.95% H. Determine the empirical formula of this compound. (Section: 3.6) Ans: C7H6O2 25. Acetyle ...
... 24. Oxidation of a hydrocarbon gave a product composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The product that was purified and sent off for elemental analysis giving the following mass percents: 68.85% C and 4.95% H. Determine the empirical formula of this compound. (Section: 3.6) Ans: C7H6O2 25. Acetyle ...
Organic Chemistry Curriculum Map - Belle Vernon Area School District
... (e.g., number of valence electrons, potential types of bonds, reactivity. Anchor: CHEM.A.2.2 – Describe the behavior of electrons in atoms. Eligible Content CHEM.A.2.2.4 – Relate the existence of quantized energy levels to atomic emission spectra. Standard: 3.2.C.A2 – Explain how atoms combine to ...
... (e.g., number of valence electrons, potential types of bonds, reactivity. Anchor: CHEM.A.2.2 – Describe the behavior of electrons in atoms. Eligible Content CHEM.A.2.2.4 – Relate the existence of quantized energy levels to atomic emission spectra. Standard: 3.2.C.A2 – Explain how atoms combine to ...