1 Course Code– CH1141 Semester – I Credit
... process. Heat capacity of gases at constant volume and constant pressure, derivation of CP – CV = R. Second law of thermodynamics, entropy and free energies, significance of DG, DH and available work – criteria of equilibrium, and spontaneity, on the basis of entropy and free energy. 9 Hrs Module IV ...
... process. Heat capacity of gases at constant volume and constant pressure, derivation of CP – CV = R. Second law of thermodynamics, entropy and free energies, significance of DG, DH and available work – criteria of equilibrium, and spontaneity, on the basis of entropy and free energy. 9 Hrs Module IV ...
Page 1
... Name______________________________________________period______IB chemistry ch. 10 organic chemistry 1. What makes carbon able to form so many different compounds? It bonds to itself to form long chains 2. What is the maximum number of other atoms to which a given carbon atom can be attached? Why? Fo ...
... Name______________________________________________period______IB chemistry ch. 10 organic chemistry 1. What makes carbon able to form so many different compounds? It bonds to itself to form long chains 2. What is the maximum number of other atoms to which a given carbon atom can be attached? Why? Fo ...
Redox Reactions: Transferring Electrons
... Reducing Agent: the one that does the reducing. Oxidizing Agent: the one that does the oxidizing. Be Careful Here! Oxidation States: Electron Bookkeeping How do we know when a redox reaction is occurring? Oxidation Numbers: positive or negative numbers assigned to atoms depending on their electroneg ...
... Reducing Agent: the one that does the reducing. Oxidizing Agent: the one that does the oxidizing. Be Careful Here! Oxidation States: Electron Bookkeeping How do we know when a redox reaction is occurring? Oxidation Numbers: positive or negative numbers assigned to atoms depending on their electroneg ...
Reaction Kinetics. The Bromination of Acetone
... Determination of the B constant: The constant B of equation [10] is determined by measuring the absorbance of at least three solutions of known bromine concentration. At room temperature, prepare one solution by pipetting 10.0 ml of stock 0.02 M Br2 into a clean 125-ml Erlenmeyer flask. Add 10.0 ml ...
... Determination of the B constant: The constant B of equation [10] is determined by measuring the absorbance of at least three solutions of known bromine concentration. At room temperature, prepare one solution by pipetting 10.0 ml of stock 0.02 M Br2 into a clean 125-ml Erlenmeyer flask. Add 10.0 ml ...
3. What is the empirical formula of a compound that is
... 7.When 10.0 g of copper was reacted with 60.0 g of silver nitrate solution. How many grams of silver are produced? How much of each reactant is left over?( Calculate the amount in grams) ...
... 7.When 10.0 g of copper was reacted with 60.0 g of silver nitrate solution. How many grams of silver are produced? How much of each reactant is left over?( Calculate the amount in grams) ...
Chemistry (SPA)
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
Camp 1 - drjosephryan.com Home Page
... The following chemical equation tells us that propane gas and oxygen gas react to form carbon dioxide gas and water vapor C3 H8 ( g) + O2 (g) ...
... The following chemical equation tells us that propane gas and oxygen gas react to form carbon dioxide gas and water vapor C3 H8 ( g) + O2 (g) ...
Chemistry 30 - SharpSchool
... generalized knowledge of their origins and applications 30-C1.3k name and draw structural, condensed structural and line diagrams and formulas, using IUPAC nomenclature guidelines, for saturated and unsaturated aliphatic (including cyclic) and aromatic carbon compounds 30-C1.1sts explain how sci ...
... generalized knowledge of their origins and applications 30-C1.3k name and draw structural, condensed structural and line diagrams and formulas, using IUPAC nomenclature guidelines, for saturated and unsaturated aliphatic (including cyclic) and aromatic carbon compounds 30-C1.1sts explain how sci ...
The carbonyl group
... Physical properties • The carbonyl group is a strong dipole. This causes the B.P of aldehydes and ketones to be higher than similar molecular weight alkanes and others but lower than alcohols which are held together by H-bonds. Aldehyde < Alcohols > Alkane ...
... Physical properties • The carbonyl group is a strong dipole. This causes the B.P of aldehydes and ketones to be higher than similar molecular weight alkanes and others but lower than alcohols which are held together by H-bonds. Aldehyde < Alcohols > Alkane ...
Unit 2: Practice
... 20. Determine the molar mass of mercury(II) sulfide. 21. Ammonium carbonate is commonly found in smelling salts. Determine the molar mass of (NH4)2CO3. 22. Convert 6.27 mol hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, into mass (in grams). 23. Convert a mass of 89.7 g of lithium hydroxide, LiOH, into an amount in moles ...
... 20. Determine the molar mass of mercury(II) sulfide. 21. Ammonium carbonate is commonly found in smelling salts. Determine the molar mass of (NH4)2CO3. 22. Convert 6.27 mol hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, into mass (in grams). 23. Convert a mass of 89.7 g of lithium hydroxide, LiOH, into an amount in moles ...
File
... stereoisomerism, in terms of restricted rotation about a double bond and the requirement for two different groups to be attached to each carbon atom of the C=C group, cis-trans isomerism; a special case of E/Z isomerism in which two of the substituent groups are the same; describe a ‘curly arrow’ as ...
... stereoisomerism, in terms of restricted rotation about a double bond and the requirement for two different groups to be attached to each carbon atom of the C=C group, cis-trans isomerism; a special case of E/Z isomerism in which two of the substituent groups are the same; describe a ‘curly arrow’ as ...
Tech Info - Davis Instruments
... In many undergraduate organic teaching programs, the aldol condensation reaction is the first exposure students have to NMR as an analytical tool. While the technical aspects of executing the aldol reaction are not difficult, the analysis of products is challenging since this is frequently a student ...
... In many undergraduate organic teaching programs, the aldol condensation reaction is the first exposure students have to NMR as an analytical tool. While the technical aspects of executing the aldol reaction are not difficult, the analysis of products is challenging since this is frequently a student ...
IB2 SL CHEMISTRY Name: …………………………… Topic 10
... the bond at 0.1373 nm is a double bond and the bond at 0.1424 nm is a single bond; in CO2(g) both bonds are double bonds and would have a value around 0.137 nm; Ester; Arene/benzene ring; Alcohol; Award 2 for any three correct, award [1] for any two correct. Do not accept alkane as a type of functio ...
... the bond at 0.1373 nm is a double bond and the bond at 0.1424 nm is a single bond; in CO2(g) both bonds are double bonds and would have a value around 0.137 nm; Ester; Arene/benzene ring; Alcohol; Award 2 for any three correct, award [1] for any two correct. Do not accept alkane as a type of functio ...
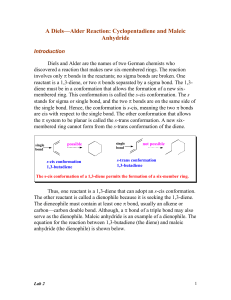
Lab 2 - Academic Computer Center
... reactants governs how easily the reactants produce a Diels-Alder product. When you give someone directions, you tell them where to go. In that case, you are the “director.” A group that “tells another group where to go” is called a directing group. A directing group can either donate or withdraw ele ...
... reactants governs how easily the reactants produce a Diels-Alder product. When you give someone directions, you tell them where to go. In that case, you are the “director.” A group that “tells another group where to go” is called a directing group. A directing group can either donate or withdraw ele ...
chapter
... (b) Double covalent bond formation. In molecular oxygen, two oxygen atoms share two pairs of electrons, forming a double covalent bond. The parallel straight lines in the structural formula represent a double covalent bond. ...
... (b) Double covalent bond formation. In molecular oxygen, two oxygen atoms share two pairs of electrons, forming a double covalent bond. The parallel straight lines in the structural formula represent a double covalent bond. ...
1.7 FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
... Certain combinations of bonds show up repeatedly in organic chemistry and organic chemists give those bonding combinations specific names. It is very useful to know the names of those specific types of bonds. Examples are shown below and you should make flash cards and learn them by heart. There can ...
... Certain combinations of bonds show up repeatedly in organic chemistry and organic chemists give those bonding combinations specific names. It is very useful to know the names of those specific types of bonds. Examples are shown below and you should make flash cards and learn them by heart. There can ...
Today Electrochemistry electrons moving about equilibrium with a
... Easy in ions! "Book keeping" in molecules! for molecules oxidation numbers are a convention ! in which we imagine what the ! charge would be if it broke up into ionic pieces! (we can't really assign electrons to different elements)! ...
... Easy in ions! "Book keeping" in molecules! for molecules oxidation numbers are a convention ! in which we imagine what the ! charge would be if it broke up into ionic pieces! (we can't really assign electrons to different elements)! ...
Chemistry: The Central Science, 12e (Brown et al
... 39) Alkenes have the general formula __________. A) CnH2n. B) CnH2n-2. C) CnH2n+2 D) CnHn. E) C2nHn. 40) In general, __________ are the most reactive hydrocarbons. A) alkenes B) alkynes C) alkanes D) cycloalkanes E) olefins 41) The addition of HBr to 2-butene produces __________. A) 1-bromobutane B) ...
... 39) Alkenes have the general formula __________. A) CnH2n. B) CnH2n-2. C) CnH2n+2 D) CnHn. E) C2nHn. 40) In general, __________ are the most reactive hydrocarbons. A) alkenes B) alkynes C) alkanes D) cycloalkanes E) olefins 41) The addition of HBr to 2-butene produces __________. A) 1-bromobutane B) ...
end of year review
... _____ 3. Which of the following statements explains why the bond in hydrogen chloride (HCl) is polar covalent? A. The atomic mass of chlorine is greater than that of hydrogen. B. The electronegativity of chlorine is greater than that of hydrogen. C. The diameter of a chlorine atom is greater than th ...
... _____ 3. Which of the following statements explains why the bond in hydrogen chloride (HCl) is polar covalent? A. The atomic mass of chlorine is greater than that of hydrogen. B. The electronegativity of chlorine is greater than that of hydrogen. C. The diameter of a chlorine atom is greater than th ...