Honors Chemistry Name Julien Period _____ Date Chapter 17
... 10. The bonding characteristics of carbon allow the formation of many different organic molecules of varied sizes, shapes, and chemical properties and provide the biochemical basis of life. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know large molecules (polymers), such as proteins, nucl ...
... 10. The bonding characteristics of carbon allow the formation of many different organic molecules of varied sizes, shapes, and chemical properties and provide the biochemical basis of life. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know large molecules (polymers), such as proteins, nucl ...
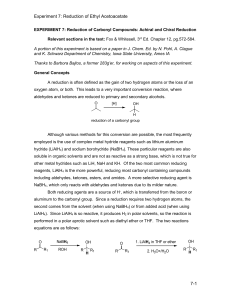
Experiment 7-Reduction
... A reduction is often defined as the gain of two hydrogen atoms or the loss of an oxygen atom, or both. This leads to a very important conversion reaction, where aldehydes and ketones are reduced to primary and secondary alcohols. O ...
... A reduction is often defined as the gain of two hydrogen atoms or the loss of an oxygen atom, or both. This leads to a very important conversion reaction, where aldehydes and ketones are reduced to primary and secondary alcohols. O ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... 76. An open flask contains 0.200 mol of air. Atmospheric pressure is 745 mmHg and room temperature is 68˚F. How many moles are present in the flask when the pressure is 1.10 atm and the temperature is 33˚C? 77. On a warm day, an amusement park balloon is filled with 47.8 g He. The temperature is 33˚ ...
... 76. An open flask contains 0.200 mol of air. Atmospheric pressure is 745 mmHg and room temperature is 68˚F. How many moles are present in the flask when the pressure is 1.10 atm and the temperature is 33˚C? 77. On a warm day, an amusement park balloon is filled with 47.8 g He. The temperature is 33˚ ...
Chem 150 Unit 2 - Hydrocarbons & Functional Groups
... The members of different families can interact differently with the receptors in your nose to produce smells that are characteristic of the families they belong to. ...
... The members of different families can interact differently with the receptors in your nose to produce smells that are characteristic of the families they belong to. ...
Chapter Three PPT
... Acidity of Carboxylic Acids: Resonance • Conjugate Base of a Carboxylic Acid is Resonance Stabilized O ...
... Acidity of Carboxylic Acids: Resonance • Conjugate Base of a Carboxylic Acid is Resonance Stabilized O ...
Question - Bellingham High School
... When the quantities of reactants are available in the exact ratio described by the balanced equation, the chemists say that the reactants are in stoichiometric proportions. When this is the case, all the reactants will take part in the reaction and there will be no reactants left over one the react ...
... When the quantities of reactants are available in the exact ratio described by the balanced equation, the chemists say that the reactants are in stoichiometric proportions. When this is the case, all the reactants will take part in the reaction and there will be no reactants left over one the react ...
ppt Lewis Dot Diagram Rules
... In general when there is a single central atom in the molecule, CH2ClF, SeCl2, O3 (CO2, NH3, PO43-), the central atom is the first atom in the chemical formula. Except when the first atom in the chemical formula is Hydrogen (H) or fluorine (F). In which case the central atom is the second atom in th ...
... In general when there is a single central atom in the molecule, CH2ClF, SeCl2, O3 (CO2, NH3, PO43-), the central atom is the first atom in the chemical formula. Except when the first atom in the chemical formula is Hydrogen (H) or fluorine (F). In which case the central atom is the second atom in th ...
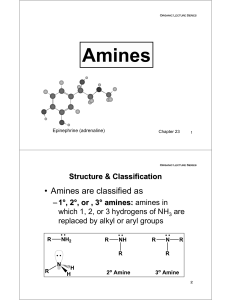
Amines
... 1° RNH2 with HNO2 • Aliphatic diazonium ions are unstable and lose N2 to give a carbocation which may 1. lose a proton to give an alkene 2. react with a nucleophile to give a substitution product 3. rearrange and then react by 1 and/or 2 ...
... 1° RNH2 with HNO2 • Aliphatic diazonium ions are unstable and lose N2 to give a carbocation which may 1. lose a proton to give an alkene 2. react with a nucleophile to give a substitution product 3. rearrange and then react by 1 and/or 2 ...
What is matter?
... cylinder using the metric unit milliliters. Volume of irregular objects can be found by dropping the object into a graduated cylinder containing water and measuring the change in the volume of water. This method is called water displacement. 1 mL = 1 cm3 ...
... cylinder using the metric unit milliliters. Volume of irregular objects can be found by dropping the object into a graduated cylinder containing water and measuring the change in the volume of water. This method is called water displacement. 1 mL = 1 cm3 ...
Sample Exam 1 – 2008 Solutions
... (b) The indicator should change colour in a pH range that includes the equivalence point (pH approx 9). Phenolphthalein is the indicator (Table 11 – Data Booklet) that changes in the range of pH 8.3 - 10.0. At the start of the titration the solution will be acidic (pH < 7) due to the citric acid and ...
... (b) The indicator should change colour in a pH range that includes the equivalence point (pH approx 9). Phenolphthalein is the indicator (Table 11 – Data Booklet) that changes in the range of pH 8.3 - 10.0. At the start of the titration the solution will be acidic (pH < 7) due to the citric acid and ...
Lipids PowerPoint2 - Valhalla High School
... The equation for the hydrolysis of lipids would then be. 1 Lipid + 3 molecules H20 1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids ...
... The equation for the hydrolysis of lipids would then be. 1 Lipid + 3 molecules H20 1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids ...
General Chemistry Questions
... analyzed and is found to contain 1.27 mol CO2, 3.04 mol CO, and 1.50 mol Ar. What is the partial pressure of Ar? a. b. c. d. e. ...
... analyzed and is found to contain 1.27 mol CO2, 3.04 mol CO, and 1.50 mol Ar. What is the partial pressure of Ar? a. b. c. d. e. ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... Ethane, C2H6, has a boiling point of ⫺89°C at standard pressure. Ethanol, C2H5OH, has a much higher boiling point than ethane at standard pressure. At STP, ethane is a gas and ethanol is a liquid. 59 Identify the class of organic compounds to which ethanol belongs. [1] 60 A liquid boils when the vap ...
... Ethane, C2H6, has a boiling point of ⫺89°C at standard pressure. Ethanol, C2H5OH, has a much higher boiling point than ethane at standard pressure. At STP, ethane is a gas and ethanol is a liquid. 59 Identify the class of organic compounds to which ethanol belongs. [1] 60 A liquid boils when the vap ...
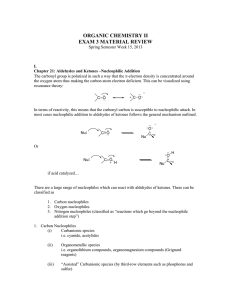
organic chemistry ii
... Aldehydes and ketones which possess -hydrogens can undergo enolization. Most enols are unstable and reactive and instantly equilibrate to the “keto” form. Certain enols, such as -dicarbonyl compounds, among others, are exceptionally stable. Under basic conditions aldehydes and ketones form enolate ...
... Aldehydes and ketones which possess -hydrogens can undergo enolization. Most enols are unstable and reactive and instantly equilibrate to the “keto” form. Certain enols, such as -dicarbonyl compounds, among others, are exceptionally stable. Under basic conditions aldehydes and ketones form enolate ...