CHEMISTRY-1 CHAPTER 8 CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... as a model 3. Balance it Don’t forget about the diatomic elements! (BrINClHOF) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
... as a model 3. Balance it Don’t forget about the diatomic elements! (BrINClHOF) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
File
... – Basically hydrocarbons with a few substitutions • These substituted bonds are more reactive than C-H bonds • Therefore, when molecules with the substituted bonds react, the reaction site is generally at the substituted bonds ...
... – Basically hydrocarbons with a few substitutions • These substituted bonds are more reactive than C-H bonds • Therefore, when molecules with the substituted bonds react, the reaction site is generally at the substituted bonds ...
Question Paper - Revision Science
... (Total for Question 2 = 4 marks) 3 Which of the following mixtures would form the best buffer solution with pH 9 for use in a school laboratory? A Ethanoic acid and sodium ethanoate B Sodium chloride and sodium hydroxide C Hydrocyanic acid and sodium cyanide D Ammonium chloride and ammonia (Total fo ...
... (Total for Question 2 = 4 marks) 3 Which of the following mixtures would form the best buffer solution with pH 9 for use in a school laboratory? A Ethanoic acid and sodium ethanoate B Sodium chloride and sodium hydroxide C Hydrocyanic acid and sodium cyanide D Ammonium chloride and ammonia (Total fo ...
3UE-Exam Review-June2010 - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... 39. The increase in boiling points observed for F2 , Cl2 , Br2 , I2 is best attributed to... a) an increase in Van der Waals’ forces with increasing atomic number. b) a decrease in the electronegativity with increasing atomic number. c) an increase in the X - X bond energy with increasing atomic nu ...
... 39. The increase in boiling points observed for F2 , Cl2 , Br2 , I2 is best attributed to... a) an increase in Van der Waals’ forces with increasing atomic number. b) a decrease in the electronegativity with increasing atomic number. c) an increase in the X - X bond energy with increasing atomic nu ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... An amount of an element or compound in moles can be converted to a mass in grams by multiplying by the appropriate molar mass. • example: ...
... An amount of an element or compound in moles can be converted to a mass in grams by multiplying by the appropriate molar mass. • example: ...
Document
... gas produced •same as (g) - H2↑ •after product, indicates solid produced •same as (s) - PbI2↓ ...
... gas produced •same as (g) - H2↑ •after product, indicates solid produced •same as (s) - PbI2↓ ...
Worksheet
... 3. True or False (Circle One) The seven elements that form diatomic molecules ALWAYS have a subscript of two, even when they are bonded to other atoms. 4. When we use the compound water in this chapter, we will not write H2O. Instead, we will write the formula as __________ and ________ will be the ...
... 3. True or False (Circle One) The seven elements that form diatomic molecules ALWAYS have a subscript of two, even when they are bonded to other atoms. 4. When we use the compound water in this chapter, we will not write H2O. Instead, we will write the formula as __________ and ________ will be the ...
Chapter 1-
... Reaction Mechanisms and Chemical Intermediates Reaction mechanisms are detailed descriptions of changes at the molecular level as reactants become products. Often the reactions involve a sequence of steps with one or more chemical species called intermediates that are formed and consumed. ...
... Reaction Mechanisms and Chemical Intermediates Reaction mechanisms are detailed descriptions of changes at the molecular level as reactants become products. Often the reactions involve a sequence of steps with one or more chemical species called intermediates that are formed and consumed. ...
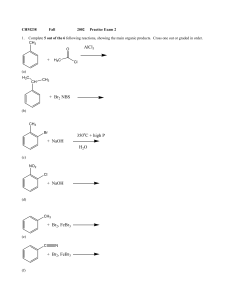
C6_rev - boswellsrcd
... An acid-base titration is the determination of the concentration of an acid or base by exactly neutralizing the acid/base with an acid or base of known concentration. This allows for quantitative analysis of the concentration of an unknown acid or soluble base. It makes use of the neutralisation rea ...
... An acid-base titration is the determination of the concentration of an acid or base by exactly neutralizing the acid/base with an acid or base of known concentration. This allows for quantitative analysis of the concentration of an unknown acid or soluble base. It makes use of the neutralisation rea ...
Intermolecular Forces
... argon is of the same order of magnitude as that of the highly polar isoelectronic species HCl. Debye’ suggested in 1921 that argon atoms, while known to be non-dipolar, may be quadrupolar; however, after the advent of quantum mechanics in 1926, it was clear that the charge distribution of an inert-g ...
... argon is of the same order of magnitude as that of the highly polar isoelectronic species HCl. Debye’ suggested in 1921 that argon atoms, while known to be non-dipolar, may be quadrupolar; however, after the advent of quantum mechanics in 1926, it was clear that the charge distribution of an inert-g ...
15iredpp
... organic molecules have a lot of C-C and C-H bonds within their structure spectra obtained will have peaks in the 1400 cm-1 to 800 cm-1 range this is referred to as the “fingerprint” region the pattern obtained is characteristic of a particular compound the frequency of any absorption is also affecte ...
... organic molecules have a lot of C-C and C-H bonds within their structure spectra obtained will have peaks in the 1400 cm-1 to 800 cm-1 range this is referred to as the “fingerprint” region the pattern obtained is characteristic of a particular compound the frequency of any absorption is also affecte ...
infra red spectroscopy
... organic molecules have a lot of C-C and C-H bonds within their structure spectra obtained will have peaks in the 1400 cm-1 to 800 cm-1 range this is referred to as the “fingerprint” region the pattern obtained is characteristic of a particular compound the frequency of any absorption is also affecte ...
... organic molecules have a lot of C-C and C-H bonds within their structure spectra obtained will have peaks in the 1400 cm-1 to 800 cm-1 range this is referred to as the “fingerprint” region the pattern obtained is characteristic of a particular compound the frequency of any absorption is also affecte ...
EE3 2007 Hannes Jónsson Transition state theory A very important
... A very important topic in chemistry is the study of the dynamics of atoms and in particular the rate of chemical reactions, i.e. the rate of transitions from one arrangement of the atoms to another. The study of the relationship between the rate constant of a reaction and the basic properties of the ...
... A very important topic in chemistry is the study of the dynamics of atoms and in particular the rate of chemical reactions, i.e. the rate of transitions from one arrangement of the atoms to another. The study of the relationship between the rate constant of a reaction and the basic properties of the ...
Lab Stuff - WW-P K
... 4. Compounds can be isomers if they have the same molecular formula, but different structural formulas. 5. Hydrocarbons can be evaluated as possible fuel sources by examining their heats of combustion. 6. Energy values can be inserted into a balanced chemical equation. 7. The specific heat of a subs ...
... 4. Compounds can be isomers if they have the same molecular formula, but different structural formulas. 5. Hydrocarbons can be evaluated as possible fuel sources by examining their heats of combustion. 6. Energy values can be inserted into a balanced chemical equation. 7. The specific heat of a subs ...
Cold encounters: Electrons and molecules
... overlap is zero. But let us say that the molecule borrows some time from the classically inaccessible quantum world, in a manner restricted by the Heisenberg relationship Llli.~12h/27t. In this borrowed time, the system may explore paths in which the molecule is "virtually bent", where virtual impli ...
... overlap is zero. But let us say that the molecule borrows some time from the classically inaccessible quantum world, in a manner restricted by the Heisenberg relationship Llli.~12h/27t. In this borrowed time, the system may explore paths in which the molecule is "virtually bent", where virtual impli ...
Thermochemistry
... H2 + ½ O2 H2O H = -285.8 kJ H is related to the molar amounts of reactants and products present. Thus, if we wanted to mathematically manipulate our chemical reaction, for fun or, as you will see later, as a necessity in Hess’ law reactions, you must manipulate the H value as well. Above is an ...
... H2 + ½ O2 H2O H = -285.8 kJ H is related to the molar amounts of reactants and products present. Thus, if we wanted to mathematically manipulate our chemical reaction, for fun or, as you will see later, as a necessity in Hess’ law reactions, you must manipulate the H value as well. Above is an ...
Fate of Organic Matter over Geologic Time
... that the majority of organically-bound sulfur in sediments is the result of an abiogenic reaction of reduced sulfur species with organic matter during the early stages of diagenesis. Mass balance calculations and sulfur isotopic analysis indicates that biogenic sulfur (e.g. proteins such as cysteine ...
... that the majority of organically-bound sulfur in sediments is the result of an abiogenic reaction of reduced sulfur species with organic matter during the early stages of diagenesis. Mass balance calculations and sulfur isotopic analysis indicates that biogenic sulfur (e.g. proteins such as cysteine ...
Stereoselective synthesis: chiral auxiliaries
... ........................Often override substrate control ........................Can be far milder than chiral auxiliaries Disadvantages - Need a stoichiometric quantity (not atom economic) .............................Frequently expensive .............................Problematic work-ups 123.702 Or ...
... ........................Often override substrate control ........................Can be far milder than chiral auxiliaries Disadvantages - Need a stoichiometric quantity (not atom economic) .............................Frequently expensive .............................Problematic work-ups 123.702 Or ...